|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Chapter 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | Final Exam 01 02 Microeconomics: Test 9 General Test Questions & Answers Which of the following statements about opportunity cost is true? a) Opportunity cost may be larger than monetary cost. b) All of the answers are correct. c) The real or opportunity cost of something is what you must give up to get it. d) Opportunity cost includes both explicit and implicit costs. The implicit cost of financial capital is: a) irrelevant for determining economic profit. b) the expense associated with buying machines. c) the opportunity cost of the capital used by a business such as earning interests from saving that money in a bank. d) the expense associated with leasing machines. Profit computed using explicit costs as the only measure of costs is: a) accounting profit. b) explicit profit. c) economic profit. d) implicit profit. The amount by which an additional unit of an activity increases total cost is: a) marginal cost. b) negative benefit. c) marginal benefit. d) net benefit. Marginal benefit: a) must be increasing if total benefit is increasing. b) is the addition benefit due to undertaking one more unit of an activity. c) normally increases as more of an activity is undertaken. d) is the subsidiary benefit from an activity; for example, the main benefit from weight training is an increase in muscle mass, and the subsidiary or marginal benefit might be a reduction in cholesterol. 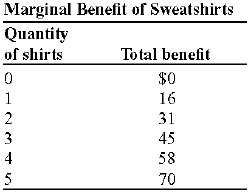
(Table: Marginal Benefit of Sweatshirts) Look at the table Marginal Benefit of Sweatshirts. The marginal benefit of producing the fourth sweatshirt is: a) $58. b) $14. c) $13. d) $12. Whenever marginal benefit is less than marginal cost, the decision maker should do ________ of the activity. a) that exact amount b) none c) Less d) more To determine the quantity of any activity that will maximize total net benefit, economists employ the ________ rule. a) principle of marginal analysis b) total decision c) principle of average analysis d) average decision Economic profits are calculated by: a) summing total revenue, explicit and implicit costs. b) taking the difference between total revenue and the sum of explicit and implicit costs. c) taking the difference between the total revenue and implicit costs only. d) taking the difference between total revenue and explicit costs only. After earning your BA, you have to decide whether to accept the offer of a job that will pay you $45,000 per year or spend an additional two years earning an MBA. If you decide to pursue the graduate degree, your annual expenses for tuition, books, board, and lodging will be $32,000. The annual opportunity cost of earning your MBA is: a) $77,000. b) $45,000. c) $32,000. d) $77,500. For most firms, economic profit is: a) less than accounting profit. b) greater than accounting profit. c) negative. d) equal to accounting profit. Accountants use only ________ costs in their computations of short-run total cost. a) implicit b) variable c) opportunity d) explicit In economics, a marginal benifit refers to: a) a benefit entered as an explanatory item in the margin of a balance sheet or other accounts. b) a benefit that is most appropriately identified in a footnote. c) the benefit associated with an unimportant, or marginal, activity. d) the benefit associated with one more unit of an activity. 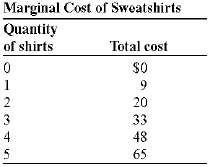
(Table: Marginal Cost of Sweatshirts) Look at the table Marginal Cost of Sweatshirts. The marginal cost of the fourth sweatshirt is: a) $20. b) $24. c) $15. d) $9. The amount by which an additional unit of an activity increases total benefit is: a) marginal benefit. b) net benefit. c) marginal cost. d) utility. 
(Table: Marginal Cost of Sweatshirts) Look at the table Marginal Cost of Sweatshirts. The marginal cost of the fourth sweatshirt is: a) $20. b) $24. c) $15. d) $9. The amount by which an additional unit of an activity increases total benefit is: a) marginal benefit. b) net benefit. c) marginal cost. d) utility. 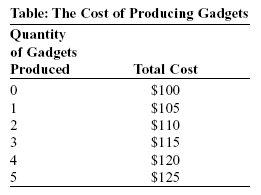
Reference: Ref 9-13 (Table: The Cost of Producing Gadgets) Look at the table The Cost of Producing Gadgets. You own a small manufacturing company that produces gadgets. According to this table, the marginal cost is: a) $10. b) $20. c) $5. d) $15. As George eats pizza during one recent outing, he finds that he enjoys each additional slice less and less. This implies that his marginal benefit is: a) decreasing. b) increasing. c) vertical. d) constant. To maximize total profit from a particular activity, consumers and firms evaluate each activity at the: margin Joan loves sushi. Her first piece of sushi normally gives her a marginal benefit of $5. Each additional piece yields a marginal benefit that declines by $0.25 per piece. If her favorite sushi bar charges $2.75 per piece of sushi, how many pieces should she eat? 10 Expenses associated with factors of production may be _____ costs. implicit, opportunity, or explicit Economic profit is: less than accounting profit if implicit costs exist Anytime the marginal benefit of an activity is greater than zero, more activity should be undertaken. False If at a given quantity _____, the decision maker should do _____ of the activity. MB > MC; more If marginal costs of production are greater than marginal benefits of production: too much of the good is being produced The dormitories of Eastland College are part of its: Capital When a decision maker chooses the option leading to the outcome that he or she most prefers, he or she has made a _____ decision. Rational Part of the _____ associated with the Chicago Cubs baseball team is their batting cages used in practice. Capital To maximize her grade in economics, Stacey should study until: her marginal benefit of studying equals her marginal cost of studying Which of the following is NOT a common mistake that leads to irrational decisions? risk aversion If the marginal cost of any activity is constant at $4, then at the optimal quantity of the activity, the marginal benefit will be $4. True In general, when marginal benefit is greater than marginal cost, the decision maker should do _____ of the activity. More The willingness to sacrifice some economic payoff to avoid a potential loss is: risk aversion Some highways have one lane; others have two, three, or more. If each lane costs $10 million per mile, an economist assumes that the total benefit of a three-lane highway must be _____ million per mile. $30 or more Firms will continue to produce if: the marginal benefits of producing an additional unit are greater than the marginal costs of producing that unit Pauli's Pizza offers one slice for $2, two slices for $3.50, three slices for $4.50, and four slices for $5.00. Sal orders two slices. From this we know that Sal's marginal benefit from the second slice must be at least _____ and the marginal benefit from the third slice must be less than _____. $1.50; $1.00 A person who is risk averse: is willing to pay to avoid economic loss The costs economists use in the concept of economic profit are: accounting costs and implicit costs (i.e., the value of the best opportunity forgone) A sunk cost should be ignored in decisions about future actions. True Sunk costs: affect economic profit Wendy sells ice-making machines. She can sell six per week at a price of $2,000 per machine. If she charges $2,100 per machine, she will sell only five per week. The marginal benefit of selling the sixth ice-making machine is: $1,500 When a person makes a quick decision without taking the time to compare the opportunity cost of all possible options, he or she is using: bounded rationality In central Florida, the demand for real estate has been increasing rapidly for years. Therefore, the _____ cost of capital is _____ in central Florida's orange groves. implicit; increasing Betty runs a cookie shop where she sells cookies for $1 each. She employs five people, each of whom worked a total of 500 hours last year; she paid them $10 per hour. Her costs of equipment and raw materials add up to $75,000. Her business ability is legendary, and other companies have offered to pay Betty $100,000 to come to work for them. She also knows she could sell her cookie shop for $150,000. The bank in town pays an annual interest rate of 3% on all funds deposited with it. (Scenario: Betty's Cookie Shop) Betty's implicit and explicit costs are equal to: $204,500 While eating pizza, you discover that the marginal benefit of eating one more slice is greater than the marginal cost of that slice. You conclude that: you will be better off if you eat one more slice The government should spend whatever amount is necessary to save a life. False Marginal benefit: is the addition to total benefit due to undertaking one more unit of an activity In economic analysis, the principle of marginal analysis refers to: the result that the optimal quantity of an activity is that at which marginal benefit is equal to marginal cost When a person makes a choice that is close to but not exactly the one that leads to the best possible economic outcome, he or she is: operating with bounded rationality Which of the following is a systematic mistake that leads to irrational decisions? Overconfidence If the marginal benefit received from consuming a good is less than the marginal cost of production: society's well-being can be improved if production decreases. Werner installs custom sound systems in cars. If he installs seven systems per day, his total costs are $300. If he installs eight systems per day, his total costs are $400. Werner will install eight sound systems per day only if the eighth customer is willing to pay at least: $100 If the marginal benefit received from consuming a good is equal to the marginal cost of production: society's well-being cannot be improved by changing production After earning your BA, you have to decide whether to take a job that will pay you $45,000 per year or spend an additional two years earning an MBA. If you decide to pursue the graduate degree, your annual expenses for tuition, books, board, and lodging will be $32,000. You have been offered a scholarship for $10,000 per year, but to pay the remaining $22,000 per year, you would have to cash in savings bonds from your grandparents that have been earning $500 in interest per year. The annual opportunity cost of earning your MBA is: $67,500 If the marginal benefit received from consuming a good is greater than the marginal cost of production: society's well-being can be improved if production increases When making decisions, a person should consider only costs that actually involve an explicit money outlay. This is because such costs actually have to be paid, whereas implicit costs are only notional or hypothetical. False |
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |