|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Chapter 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | Final Exam 01 02 Microeconomics: Test 3 General Test Questions & Answers The law of demand states that other things equal: a) as the price decreases, the demand will increase. b) as the price increases, the quantity demanded will decrease. c) as the price increases, the quantity demanded will increase. d) as the price increases, the demand will decrease. The law of demand implies that: a) sellers will offer more on the market at higher prices. b) consumers will buy more at lower prices. c) sellers will offer less on the market at lower prices. d) consumers are not responsive to price changes. A good is normal if which of the following is true? a) When income increases, the demand decreases. b) When income increases, the demand increases. c) When income increases, the demand remains unchanged. d) Income and the demand are unrelated. Pizza is a normal good. If students' incomes at your college increase, the effect on pizza would be: a) no change in the demand. b) a decrease in the demand. c) a decrease in the quantity demanded. d) an increase in the demand. If the price of a good increases, you would expect the: b) quantity supplied to increase. c) quantity supplied to decrease. d) supply curve to shift to the right. A decrease in supply is caused by: a) an advancement in the technology for producing the good. b) an increase in demand. c) an increase in the price of input that are used in production. d) an increase in the number of producers. (Table: Supply of Lemonade) Look at the table Supply of Lemonade. When the price of lemonade is $1 per cup, the quantity of lemonade supplied by Eli will be: 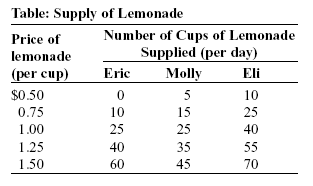
a) 10 cups. b) 40 cups. c) 90 cups. d) 25 cups. Excess supply occurs when: a) the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied. b) the price is below the equilibrium price. c) the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied and when the price is below the equilibrium price. d) the price is above the equilibrium price. (Figure: The DVD Rental Market) Look at the figure The DVD Rental Market. The figure shows the weekend rental market for DVDs in Collegetown. The equilibrium price for DVD rentals is ________ and the equilibrium quantity is ________. 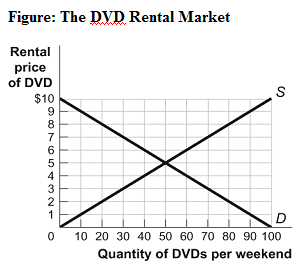
a) $5; 50 b) $6; 40 c) $9; 90 d) $3; 30 The demand curve for a product might shift as the result of a change in: A. consumer tastes. B. consumer incomes. C. the prices of related goods. D. all of these. An inferior good is: A. one whose demand curve will shift rightward as incomes rise. B. one whose price and quantity demanded vary directly. C. one which has not been approved by the Federal Food and Drug Administration. D. not accurately defined by any of the above statements. A negative relationship between the quantity demanded and price is called the law of: a) increasing returns. b) market clearing. c) demand. d) supply. A decrease in the price of a good will result in: a) an increase in demand. b) an increase in supply. c) an increase in the quantity demanded. d) an increase in the quantity supplied. A good is inferior if which of the following is true? a) When income increases, the demand remains unchanged. b) When income increases, the demand decreases. c) When income increases, the demand increases. d) Income and the demand are unrelated. An increase in the demand for gasoline today caused by concerns that gasoline prices will be higher tomorrow is most likely attributable to which of the following? a) consumer expectations b) income c) prices of other goods d) consumer preferences 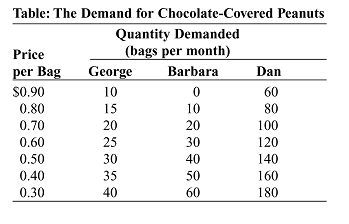
(Table: The Demand for Chocolate-Covered Peanuts.) Look at the table The Demand for Chocolate-Covered Peanuts. If the price of chocolate-covered peanuts is $0.30, the quantity demanded by George is ________ bags per month. a) 35 b) 25 c) 40 d) 30 Which of the following is not a cause of a shift in supply curve? a) consumer tastes b) the technology of production c) the cost of production d) changes in input prices An increase in supply is caused by: a) suppliers' expectations of higher prices in the future. b) an increase in input prices. c) a decrease in the number of sellers in the market. d) an advancement in the technology for producing the good. a) fall. b) rise in order to clear the market. c) stay the same. d) rise. An increase in supply, with no change in demand, will lead to ________ in equilibrium quantity and ________ in equilibrium price. a) a decrease; an increase b) an increase; a decrease c) an increase; an increase d) a decrease; a decrease Which of the following would mostly likely increase the demand for gasoline? A. the expectation by consumers that gasoline prices will be higher in the future. B. the expectation by consumers that gasoline prices will be lower in the future. C. a widespread shift in car ownership from SUVs to hybrid sedans. D. a decrease in the price of public transportation. Which of the following is a characteristic of a perfectly competitive industry?: a) Firms seek to maximize profits. b) All of the answers are correct. c) There are many firms. d) Profits may be positive in the short run. If a perfectly competitive firm is producing a quantity where MC = MR, then profit: a) can be increased by decreasing production. b) can be increased by increasing production. c) is maximized. d) can be increased by decreasing the price. Figure: The Profit Maximizing Firm 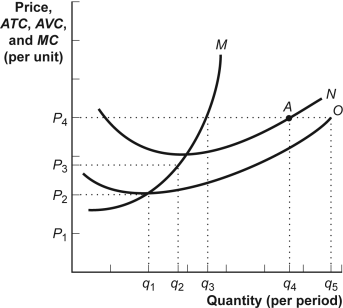
Reference: Ref 12-10 (Figure: The Profit Maximizing Firm) Look at the figure The Profit Maximizing Firm. The figure shows cost curves for a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market. Which of these curves represents the AVC curve? a) curve M b) None of the curves represents the AVC curve. c) curve N d) curve O Zoe's Bakery determines that P < ATC and P > AVC. Zoe: a) should continue to operate, as she is making an economic profit. b) has maximized her profits. c) should shut down immediately, as she is taking an economic loss. d) sells at below her beak-even price but higher than her shut-down price. The price received by a firm in a perfectly competitive market: a) is greater than the market price. b) is less than the market price. c) decreases with the quantity of output sold by the firm. d) is equal to the market price. Figure: The Profit Maximizing Firm 
Reference: Ref 12-10 (Figure: The Profit Maximizing Firm) Look at the figure The Profit Maximizing Firm. The figure shows cost curves for a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market. N is the ________ curve. a) MR b) MC c) ATC. d) AVC In the short run, if P < AVC, a perfectly competitive firm: a) produces output and incurs an economic loss. b) does not produce output and earns an economic profit. c) does not produce output and shutdown. . d) produces output and earns an economic profit. The assumptions of perfect competition imply that: a) the price will be high. b) individuals can influence the market price. c) the price will be set by the price leader. d) individuals in the market accept the market price as given. The location of the supply curve of a product depends on: A. the technology used to produce it. B. the prices of resources used in its production. C. the number of sellers in the market. D. all of these. If a local California avocado stand operates in a perfectly competitive market, that stand owner will be a: a) price-maker. b) price-maximizer. c) price-discriminator. d) price-taker. . All except one of the following are characteristics of perfect competition. Which is the exception? a) There are no obstacles to entry into or exit from the industry. b) There are many producers; one firm has a 25% market share, and all of the remaining firms have a market share less than 2% each. . c) There are many producers, and each has only a small market share. d) All firms produce the same standardized product. The land you own has the only known source of aloe needed to make anti-itch lotion. In this case, your monopoly results from which of the following? a) ownership of scarce inputs b) government restrictions c) location d) sunk costs An industry with a single producer that sells a single product with no substitutes is a: a) monopoly. b) perfect competition. c) oligopoly. d) monopolistic competition. A monopoly is a market characterized by: a) a large number of small firms. b) a product with many close substitutes. c) a single seller. d) a small number of large firms A natural monopoly exists when: a) firms naturally maximize profit regardless of market structure. b) firms enter the industry as a result of profit incentives. c) a few firms collude to make one large firm. d) increasing returns to scale provide large cost advantages to having one firm produce the industry's output. Which of the following is most likely to be an inferior good? A. fur coats B. ocean cruises C. used clothing D. steak Which of the following statements is correct? A. An increase in the price of C will decrease the demand for complementary product D. B. A decrease in income will decrease the demand for an inferior good. C. An increase in income will reduce the demand for a normal good. D. A decline in the price of X will increase the demand for substitute product Y. The law of demand states that: A. price and quantity demanded are inversely related. B. the larger the number of buyers in a market, the lower will be product price. C. price and quantity demanded are directly related. D. consumers will buy more of a given product at high prices than they will at low prices. A natural monopoly exists whenever a single firm: a) is investor owned but has been granted the exclusive right by the government to operate in a market. b) is owned and operated by the federal or local government. c) has increasing returns to scale over the entire range of production that is relevant to its market. d) has gained control over a strategic input of an important production process. If a monopolist is producing a quantity that generates MC = MR, then profit: a) is maximized. b) is maximized only if MC = P. c) can be increased by increasing production. d) can be increased by decreasing production. The demand curve facing a monopolist is: a) downward sloping. b) vertical. c) upward sloping. d) horizontal. Network externalities, one type of barriers to entry in a monopoly market, exist when a good's value to the consumer rises as: a) the number of people who use the good remains constant. b) technology improves. c) the number of people who use the good decreases. d) the number of people who use the good increases. Firms in which of the following market structures have the most market power? a) oligopoly b) monopolistic competition c) duopoly d) monopoly Control of a scarce resource or input, economies of scale, technological superiority, and government-created barriers are forms of: a) barriers to entry. b) public policy. c) market structure. d) pricing behavior. One of the earliest actions of antitrust policy was the breakup of: a) IBM. b) Bell Telephone. c) Microsoft. d) the Standard Oil Company. If the only two firms in an industry openly agree to fix the price at a given level, then this is an example of: a) contestability. b) price leadership. c) tacit collusion. d) overt collusion. Oligopoly is a market structure characterized by: a) a horizontal demand curve. b) a small number of interdependent firms. c) relatively easy entry and exit. d) independence in decision making. A market: A. reflects upsloping demand and downsloping supply curves. B. entails the exchange of goods, but not services. C. is an institution which brings together buyers and sellers. D. always entails face-to-face contact between buyer and seller An oligopoly may result from: a) low or no barriers to entry. b) the existence of increasing returns to scale in the industry. c) price-taking conditions for both buyers and sellers. d) the standardization of a product. Microsoft sets prices for their new line of computers and Dell and HP follow. This practice is known as________. a) kinked demand behavior. b) price leadership. c) price extortion. d) antitrust pricing. The most important source of oligopoly is: a) ownership of resources. b) government-created barriers. c) increasing returns to scale. d) technological superiority. Price leadership occurs if: a) competition among a large number of small firms generates a stable market price. b) two or more firms in an industry agree to fix the price at a given level. c) smaller firms in an industry silently agree to charge the same price as the largest firm. d) competition among a large number of small firms generates similar, but slightly different, prices. Attempts by the federal government to prevent the exercise of monopoly power in the United States are called ________ policy. a) fiscal b) government c) antitrust d) stabilization The industry characterized by a few interdependent firms where there are barriers to entry is called: a) monopolistic competition. b) monopoly. c) perfect competition. d) oligopoly. A field of law that attempts to limit the ability of oligopolists to collude and restrict competition is called: a) antitrust policy. b) fuel efficiency standards. c) product safety policy. d) excise tax policy. The demand curve for a firm under monopolistic competition is: a) horizontal, unlike the downward-sloping demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm. b) horizontal, the same as that facing a perfectly competitive firm. c) downward sloping, the same as that facing a perfectly competitive firm. d) downward sloping, unlike the horizontal demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm. For the monopolistically competitive seafood market, the demand curve for any individual firm is ________, and there are ________ producers of seafood. a) upward-sloping; many b) downward-sloping; a few c) vertical; a few d) downward-sloping; many Which of the following is not a characteristic of monopolistic competition? a) many competing producers b) lack of barriers to entry and exit in the long run c) tacit collusion d) product differentiation Which of the following describes a feature shared by both monopolistic competition and perfect competition? a) no barriers to entry or exit in the long run b) standardized products c) absolute market power d) small number of firms competing in the industry Monopolistic competition is an industry characterized by: a) barriers to entry and exit. b) a horizontal demand curve. c) a product with no close substitutes. d) a large number of firms. Monopolistic competition is different from perfect competition due to the fact that within monopolistic competition: a) firms experience easy entry and exit. b) products are differentiated. c) there are many firms. d) to maximize profits, a firm will produce where MR = MC. Due to the existence of a large number of similar, but not identical, substitutes in most communities, the market for chiropractors is best considered: a) a monopoly. b) perfect competition. c) monopolistic competition. d) an oligopoly. In monopolistic competition: a) there is free entry and exit in the long run. b) there are barriers to entry. c) each firm produces a standardized product. d) there are few producers. If a monopolistically competitive firm is in long-run equilibrium, we can assume that price ________. a) equals marginal revenue. b) is greater than average total cost. c) equals marginal cost. d) equals average total cost. In many cities you can stay at a Holiday Inn in the downtown area, in a suburban community, or near the airport. These Holiday Inn establishments are examples of product differentiation by: a) quality. b) location. c) style. d) type. Who are the fundamental decision-making participants of the market? households firms The law of supply indicates that: producers will offer more of a product at high prices than they will at low prices. The upward slope of the supply curve reflects the: law of supply. The supply curve shows the relationship between: price and quantity supplied. A firm's supply curve is upsloping because: beyond some point the production costs of additional units of output will Increasing marginal cost of production explains: why the supply curve is upsloping. A leftward shift of a product supply curve might be caused by: some firms leaving an industry. The location of the product supply curve depends on: production technology. An improvement in production technology will: shift the supply curve to the right. The owners of resources and they sell their resources in exchange for goods and services. households Households could be both sellers and buyers. True When an economist says that the demand for a product has increased, this means that: consumers are now willing to purchase more of this product at each possible price. By an increase in demand we mean that : the quantity demanded at each price in a set of prices is greater. The quantity demanded of a product increases as its price declines because the: demand curve is downsloping. An increase in demand means that: the demand curve has shifted to the right. Assume that the demand schedule for product C is downsloping. If the price of C falls from $2.00 to $1.75: a larger quantity of C will be demanded. Because of unseasonably cold weather, the supply of oranges has substantially decreased. This statement indicates that: the amount of oranges that will be available at various prices has declined. If producers must obtain higher prices than previously to produce various levels of output, the following has occurred: a decrease in supply. In moving along a stable supply curve which of the following is not held constant? the price of the product for which the supply curve is relevant An increase in the quantity demanded means that: price has declined and consumers therefore want to purchase more of the product. An increase in product price will cause: quantity demanded to decrease. Other things equal, if the price of a key resource used to produce product X falls, the: product supply curve of X will shift to the right. In moving along a stable demand curve which of the following is not held constant? the price of the product for which the demand curve is relevant. In which of the following statements are the terms "demand" and "quantity demanded" used correctly? When the price of ice cream rose, the quantity demanded of ice cream fell, and the demand for ice cream toppings fell. Firms could be both sellers and buyers. True Who produce goods and services? Firms When the price of oil declines significantly, the price of gasoline also declines. The latter occurs because of a(n): increase in the supply of gasoline. An increase in the excise tax on cigarettes raises the price of cigarettes by shifting the: supply curve for cigarettes leftward. A government subsidy to the producers of a product: increases product supply. Suppose that corn prices rise significantly. If farmers expect the price of corn to continue rising relative to other crops, then we would expect: the supply to increase as farmers plant more corn. If a product is in surplus supply, its price: is above the equilibrium level. A market is in equilibrium if: if the amount producers want to sell is equal to the amount consumers want to buy. At the equilibrium price: there are no pressures on price to either rise or fall. At the point where the demand and supply curves for a product intersect: the quantity that consumers want to purchase and the amount producers choose to sell are the same. The rationing function of prices refers to the: capacity of a competitive market to equate the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied. If there is a shortage of product X: the price of the product will rise. What do firms need to produce goods and services? Resources A decrease in the price of digital cameras will: shift the demand curve for memory cards to the right. A normal good is one that: the consumption of which varies directly with incomes. If the demand for steak (a normal good) shifts to the left, the most likely reason is that: consumer incomes have fallen. If consumer incomes increase, the demand for product X: may shift either to the left or right. If products A and B are complements and the price of B decreases the: demand for A will increase and the amount of B demanded will increase. If products C and D are close substitutes, an increase in the price of C will: shift the demand curve of D to the right. In constructing a stable demand curve for product X: the prices of other goods are assumed constant. An increase in the price of product A will: increase the demand for substitute product B. Where do firms buy their resources from? Households A shift to the right in the demand curve for product A can be most reasonably explained by saying that: consumer preferences have changed in favor of A so that they now want to buy more at each possible price. If L and M are complementary goods, an increase in the price of L will result in: a decrease in the sales of M. Which of the following will cause the demand curve for product A to shift to the left? an increase in money income if A is an inferior good. If X is a normal good, a rise in money income will shift the: demand curve for X to the right. If Z is an inferior good, an increase in money income will shift the: demand curve for Z to the left. An increase in consumer incomes will: increase the demand for a normal good. Tennis rackets and ballpoint pens are: independent goods. The demand for most products varies directly with changes in consumer incomes. Such products are known as: normal goods. Assume the demand curve for product X shifts to the right. This might be caused by: a decline in income if X is an inferior good. Digital cameras and memory cards are: complementary goods. Who help with the production of goods and services? households The point of view of a buyer which reflects the relationship between price and quantity demanded. law of demand Law of demand have a positive relationship. False All available quantity and all different price points that are available. quantity demanded Buying more of good and services and with each successful good it gives less and less of a satisfaction. diminishing marginal utility When a price change occurs, quantity demanded stays the same. False What will not cause a shift in the demand curve? Change in Price of the product itself When the price of a product rises, consumers shift their purchases to other products whose prices are now relatively lower. This statement describes: the substitution effect. When the price of a product falls, the purchasing power of our money income rises and thus permits consumers to purchase more of the product. This statement describes: the income effect. When product prices change, consumers are inclined to purchase larger amounts of the now cheaper products and less of the now more expensive products. This describes: the substitution effect. Suppose that tacos and pizza are substitutes, and that soda and pizza are complements. We would expect an increase in the price of pizza to: reduce the demand for soda and increase the demand for tacos. The construction of demand and supply curves assumes that the primary variable influencing decisions to produce and purchase goods is: price. One reason that the quantity demanded of a good increases when its price falls is that the: lower price increases the real incomes of buyers, enabling them to buy more. When the price of Nike soccer balls fell, Ronaldo purchased more Nike soccer balls, and fewer Adidas soccer balls. Which of the following best explains Ronaldo's decision to buy more Nike soccer balls? The substitution effect. Steve went to his favorite hamburger restaurant with $3, expecting to buy a $2 hamburger and a $1 soda. When he arrived he discovered that hamburgers were on sale for $1, so Steve bought two hamburgers and a soda. Steve's response to the decrease in the price of hamburgers is best explained by: the income effect. In the past few years, the demand for donuts has greatly increased. This increase in demand might best be explained by: a change in buyer tastes. Which of the following will not cause the demand for product K to change? A change in the price of K. On a demand curve, will it change or stay the same when price is changed? it will remain the same and the quantity demanded will change along the demand curve Price will change demand curve. False Which of the following would not shift the demand curve for beef? a reduction in the price of cattle feed An economist for a bicycle company predicts that, other things equal, a rise in consumer incomes will increase the demand for bicycles. This prediction is based on the assumption that: bicycles are normal goods. A rightward shift in the demand curve for product C might be caused by: a decrease in the price of a product that is complementary to C. If two goods are complements: a decrease in the price of one will increase the demand for the other. DVD players and DVDs are: complementary goods. If the demand curve for product B shifts to the right as the price of product A declines, then: A and B are complementary goods. If the price of product L increases, the demand curve for close-substitute product J will: shift to the right If the price of K declines, the demand curve for the complementary product J will: shift to the right. Where will a demand curve move if it have increased? towards the right Where will a demand curve move if it have decreased? towards the left What will cause a demand curve to change on a graph? non-price determinates More income and wealth, a demand for normal goods_________. Increases What does the law of demand state? states that price and quantity demanded are inversely related. Graphically, the market demand curve is: the horizontal sum of individual demand curves. The demand curve shows the relationship between what? price and quantity demanded. Economists use the term "demand" to refer to what? a schedule of various combinations of market prices and amounts demanded. The relationship between quantity supplied and price is _____ and the relationship between quantity demanded and price is _____. direct, inverse When the price of a product increases, a consumer is able to buy less of it with a given money income. This describes: the income effect. A demand curve indicates what? indicates the quantity demanded at each price in a series of prices. In presenting the idea of a demand curve, economists presume that the most important variable in determining the quantity demanded is: the price of the product itself. Why will an increase in the price of a product will reduce the amount of it purchased? consumers will substitute other products for the one whose price has risen. What do the income and substitution effects account for? the downward sloping demand curve. Less income and wealth, a demand for normal goods ___________. decrease More income and wealth, a demand for inferior goods_________. decrease Less income and wealth, a demand for inferior goods ___________. increase The amount of a product that a household would buy in a given period if it could buy all it wanted at the current market price. quantity demanded A change in any other factor affecting demand will changes the entire relationship between price and quantity. change in demand A graph illustrating how much of a given product a household would be willing to buy at different prices. demand curve "Successive units that are worth less to the consumer, the person will not be willing to pay as much for them." This is known as? diminishing marginal utility What is a market? an institution that brings together buyers and sellers. Markets explained on the basis of supply and demand assume what? assume many buyers and many sellers of a standardized product. |
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |