|
Principals Of Managerial Accounting: Homework Chapter 8 Part 2
Tempo
Company’s fixed budget (based on sales of 14,000 units) for the first quarter
reveals the following.
|
Fixed Budget
|
|
Sales (14,000 units × $210 per unit)
|
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
2,940,000
|
|
|
Cost of goods sold
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Direct materials
|
|
$
|
336,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Direct labor
|
|
|
602,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Production supplies
|
|
|
378,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Plant manager salary
|
|
|
136,000
|
|
|
|
1,452,000
|
|
|
Gross profit
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,488,000
|
|
|
Selling expenses
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sales commissions
|
|
|
98,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Packaging
|
|
|
210,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Advertising
|
|
|
100,000
|
|
|
|
408,000
|
|
|
Administrative expenses
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Administrative salaries
|
|
|
186,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation—office equip.
|
|
|
156,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Insurance
|
|
|
126,000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Office rent
|
|
|
136,000
|
|
|
|
604,000
|
|
|
Income from operations
|
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
476,000
|
|
|
|
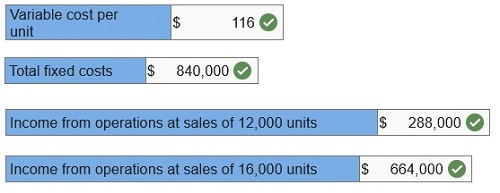
(1)
Compute the total variable cost per unit.
(2) Compute the total fixed costs.
(3) Compute the income from operations for sales volume of 12,000 units.
(4) Compute the income from operations for sales volume of 16,000 units.
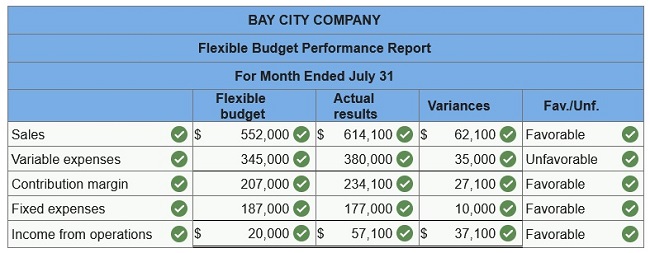
Bay
City Company’s fixed budget performance report for July follows. The $587,000
budgeted total expenses include $400,000 variable expenses and $187,000 fixed
expenses. Actual expenses include $177,000 fixed expenses.
|
Fixed Budget
|
Actual Results
|
Variances
|
|
Sales (in units)
|
|
8,000
|
|
|
6,900
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sales (in dollars)
|
$
|
640,000
|
|
$
|
614,100
|
|
$
|
25,900
|
U
|
|
Total expenses
|
|
587,000
|
|
|
557,000
|
|
|
30,000
|
F
|
|
Income from operations
|
$
|
53,000
|
|
$
|
57,100
|
|
$
|
4,100
|
U
|
|
Prepare
a flexible budget performance report that shows any variances between budgeted
results and actual results. List fixed and variable expenses separately.
(Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting for favorable,
unfavorable, and no variance. Do not round your intermediate calculations.
Round your final answers to whole dollars.)
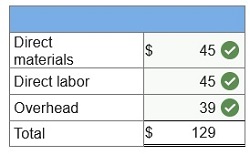
A
manufactured product has the following information for June.
|
Standard
|
Actual
|
|
Direct materials
|
5 lbs. @ $9 per lb.
|
|
42,000
|
lbs. @ $9.10 per lb.
|
|
Direct labor
|
3 hrs. @ $15 per hr.
|
|
24,600
|
hrs. @ $15.40 per hr.
|
|
Overhead
|
3 hrs. @ $13 per hr.
|
$
|
329,400
|
|
|
Units manufactured
|
|
|
8,300
|
|
|
|
(1)
Compute the standard cost per unit.
(2) Compute the total cost variance for June.
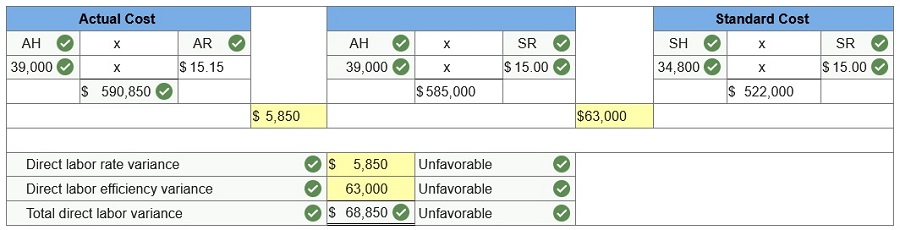
Reed
Corp. has set the following standard direct materials and direct labor costs
per unit for the product it manufactures.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Direct materials (15 lbs. @ $4 per
lb.)
|
|
|
$60
|
|
|
Direct labor (4 hrs. @ $15 per hr.)
|
|
|
60
|
|
|
|
During June the company incurred the following actual costs to
produce 8,700 units.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Direct materials (132,700 lbs. @ $3.75
per lb.)
|
|
$
|
497,625
|
|
|
Direct labor (39,000 hrs. @ $15.15 per
hr.).
|
|
|
590,850
|
|
|
|
AH = Actual Hours
SH = Standard Hours
AR = Actual Rate
SR = Standard Rate
AQ = Actual Quantity
SQ = Standard Quantity
AP = Actual Price
SP = Standard Price
(1) Compute the direct
materials price and quantity variances.
(Indicate the effect of
each variance by selecting for favorable, unfavorable, and no variance.)
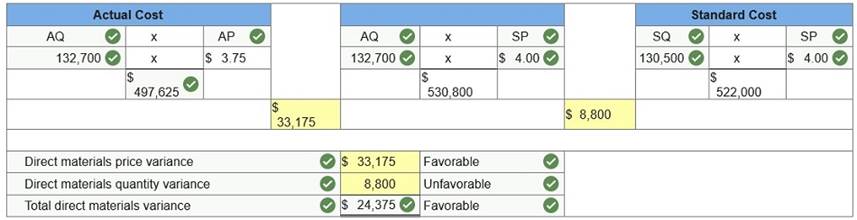
(2) Compute the direct
labor rate variance and the direct labor efficiency variance.
(Indicate the effect of
each variance by selecting for favorable, unfavorable, and no variance.)
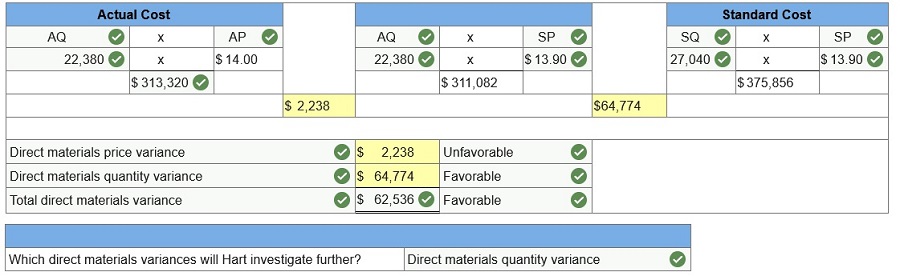
Hart
Company made 3,380 bookshelves using 22,380 board feet of wood costing $313,320.
The company’s direct materials
standards for one bookshelf are 8 board feet of
wood at $13.90 per board foot.
AQ
= Actual Quantity
SQ = Standard Quantity
AP = Actual Price
SP = Standard Price
(1)
Compute the direct materials price and quantity variances and classify each as
favorable or unfavorable.
(2) Hart applies management by exception by investigating direct materials
variances of more than 5% of actual direct materials costs.
Which
direct materials variances will Hart investigate further?
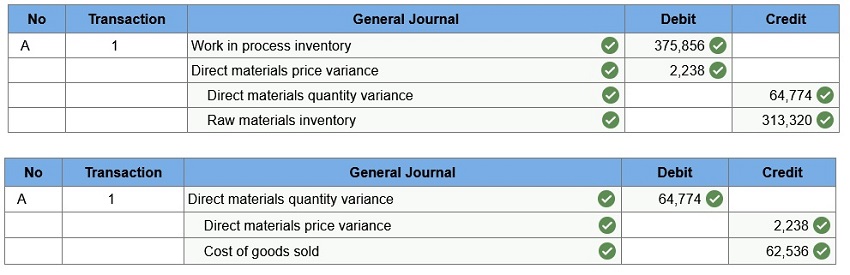
Hart
Company made 3,380 bookshelves using 22,380 board feet of wood costing
$313,320. The company’s direct materials standards for one bookshelf are 8
board feet of wood at $13.90 per board foot.
Hart
Company uses a standard costing system.
(1)
Prepare the journal entry to charge direct materials costs to Work in Process
Inventory and record the materials variances.
(2) Assume that Hart’s materials variances are the only variances accumulated
in the accounting period and that they are immaterial. Prepare the adjusting
journal entry to close the variance accounts at period-end.
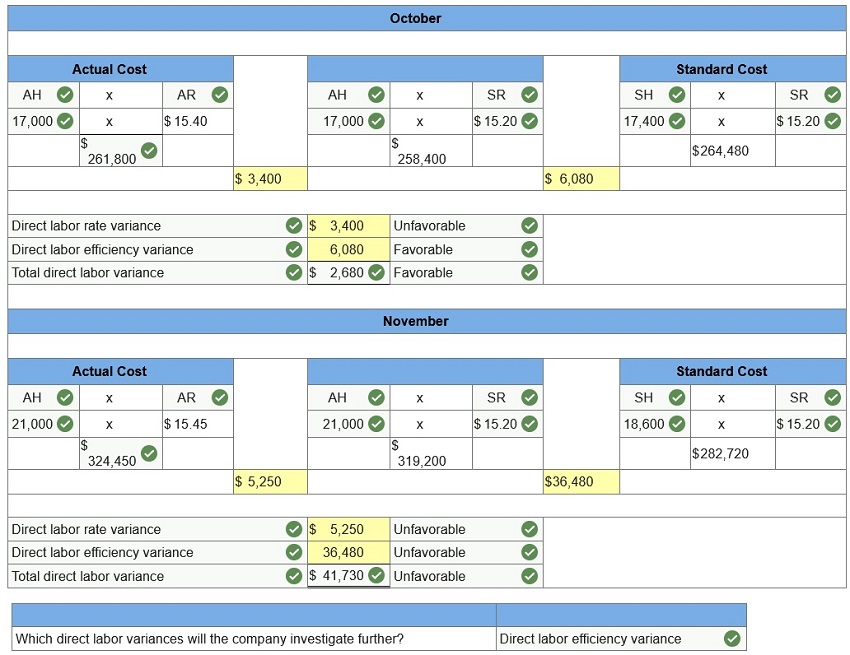
Javonte
Co. set standards of 3 hours of direct labor per unit of product and $15.20 per
hour for the labor rate. During October, the company uses 17,000 hours of
direct labor at a $261,800 total cost to produce 5,800 units of product. In
November, the company uses 21,000 hours of direct labor at a $324,450 total
cost to produce 6,200 units of product.
AH
= Actual Hours
SH = Standard Hours
AR = Actual Rate
SR = Standard Rate
(1)
Compute the direct labor rate variance, the direct labor efficiency variance,
and the total direct labor cost variance for each of these two months. Classify
each variance as favorable or unfavorable.
(2) Javonte investigates variances of more than 5% of actual direct labor cost.
Which direct labor variances will the company investigate further?
Sedona
Company set the following standard costs for one unit of its product for this
year.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Direct material (30 Ibs. @ $2.30 per
Ib.)
|
|
$
|
69.00
|
|
|
Direct labor (20 hrs. @ $4.30 per hr.)
|
|
|
86.00
|
|
|
Variable overhead (20 hrs. @ $2.30 per
hr.)
|
|
|
46.00
|
|
|
Fixed overhead (20 hrs. @ $1.20 per
hr.)
|
|
|
24.00
|
|
|
Total standard cost
|
|
$
|
225.00
|
|
|
|
The
$3.50 ($2.30 + $1.20) total overhead rate per direct labor hour is based on an
expected operating level equal to 60%
of the factory’s capacity of 69,000 units
per month. The following monthly flexible budget information is also available.
|
|
Operating Levels (% of capacity)
|
|
|
Flexible Budget
|
|
|
55%
|
|
|
|
60%
|
|
|
|
65%
|
|
|
Budgeted output (units)
|
|
|
37,950
|
|
|
|
41,400
|
|
|
|
44,850
|
|
|
Budgeted labor (standard hours)
|
|
|
759,000
|
|
|
|
828,000
|
|
|
|
897,000
|
|
|
Budgeted overhead (dollars)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Variable overhead
|
|
$
|
1,745,700
|
|
|
$
|
1,904,400
|
|
|
$
|
2,063,100
|
|
|
Fixed overhead
|
|
|
993,600
|
|
|
|
993,600
|
|
|
|
993,600
|
|
|
Total overhead
|
|
$
|
2,739,300
|
|
|
$
|
2,898,000
|
|
|
$
|
3,056,700
|
|
|
|
During
the current month, the company operated at 55% of capacity, employees worked
731,000 hours, and the following
actual overhead costs were incurred.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Variable overhead costs
|
|
$
|
1,710,000
|
|
|
Fixed overhead costs
|
|
|
1,031,500
|
|
|
Total overhead costs
|
|
$
|
2,741,500
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sedona
Company set the following standard costs for one unit of its product for this
year.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Direct material (30 Ibs. @ $2.30 per Ib.)
|
|
$
|
69.00
|
|
|
Direct labor (20 hrs. @ $4.30 per hr.)
|
|
|
86.00
|
|
|
Variable overhead (20 hrs. @ $2.30 per
hr.)
|
|
|
46.00
|
|
|
Fixed overhead (20 hrs. @ $1.20 per
hr.)
|
|
|
24.00
|
|
|
Total standard cost
|
|
$
|
225.00
|
|
|
|
The
$3.50 ($2.30 + $1.20) total overhead rate per direct labor hour is based on an
expected operating level equal to
60% of the factory’s capacity of 69,000 units
per month. The following monthly flexible budget information is also available.
|
|
Operating Levels (% of capacity)
|
|
|
Flexible Budget
|
|
|
55%
|
|
|
|
60%
|
|
|
|
65%
|
|
|
Budgeted output (units)
|
|
|
37,950
|
|
|
|
41,400
|
|
|
|
44,850
|
|
|
Budgeted labor (standard hours)
|
|
|
759,000
|
|
|
|
828,000
|
|
|
|
897,000
|
|
|
Budgeted overhead (dollars)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Variable overhead
|
|
$
|
1,745,700
|
|
|
$
|
1,904,400
|
|
|
$
|
2,063,100
|
|
|
Fixed overhead
|
|
|
993,600
|
|
|
|
993,600
|
|
|
|
993,600
|
|
|
Total overhead
|
|
$
|
2,739,300
|
|
|
$
|
2,898,000
|
|
|
$
|
3,056,700
|
|
|
|
During
the current month, the company operated at 55% of capacity, employees worked
731,000 hours,
and the following actual overhead costs were incurred.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Variable overhead costs
|
|
$
|
1,710,000
|
|
|
Fixed overhead costs
|
|
|
1,031,500
|
|
|
Total overhead costs
|
|
$
|
2,741,500
|
|
|
|
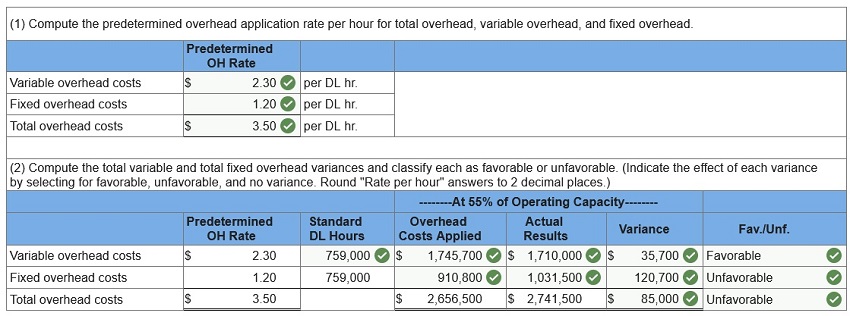
AH
= Actual Hours
SH = Standard Hours
AVR = Actual Variable Rate
SVR = Standard Variable Rate
1. Compute the variable overhead spending and efficiency variances.
2. Compute the fixed overhead spending and volume variances and classify each
as favorable or unfavorable.
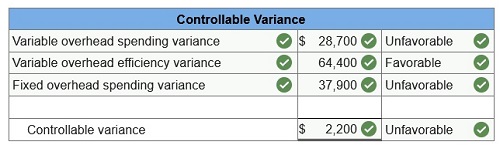
3. Compute the controllable variance.
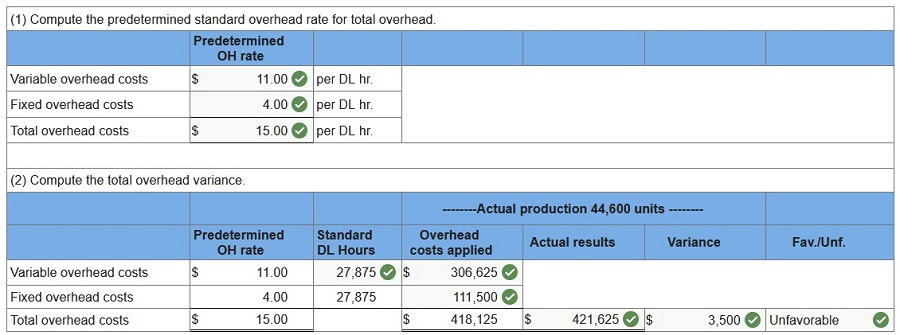
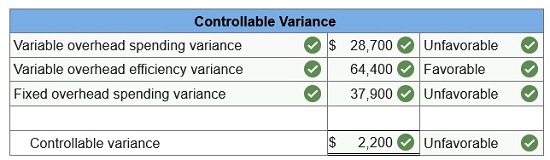 Q10.
World Company expects to operate at 70% of its productive capacity of 38,000
units per month. At this planned level, the
Q10.
World Company expects to operate at 70% of its productive capacity of 38,000
units per month. At this planned level, the
company expects to use 16,625
standard hours of direct labor. Overhead is allocated to products using a
predetermined standard
rate of 0.625 direct labor hour per unit. At the 70%
capacity level, the total budgeted cost includes $66,500 fixed overhead cost
and
$182,875 variable overhead cost. In the current month, the company incurred
$421,625 actual overhead and 16,405 actual labor
hours while producing 44,600
units. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting for favorable,
unfavorable, and no variance.
Do not round intermediate calculations. Round “OH
costs per DL hour” to 2 decimal places.)
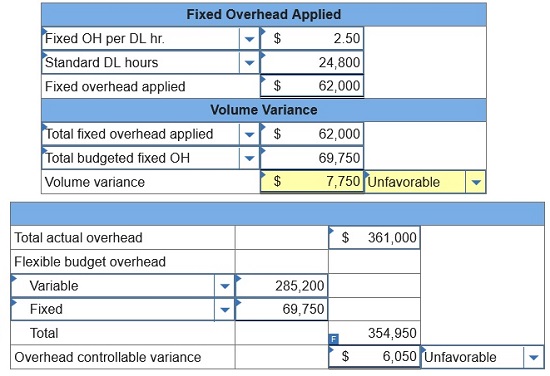
World
Company expects to operate at 80% of its productive capacity of 56,250 units
per month. At this planned level, the company expects to use 27,900 standard
hours of direct labor. Overhead is allocated to products using a predetermined
standard rate of 0.620 direct labor hour per unit. At the 80% capacity level,
the total budgeted cost includes $69,750 fixed overhead cost and $320,850
variable overhead cost. In the current month, the company incurred $361,000
actual overhead and 24,900 actual labor hours while producing 40,000 units.
(1)
Compute the overhead volume variance. Classify each as favorable or
unfavorable.
(2) Compute the overhead controllable variance. Classify each as favorable or
unfavorable.
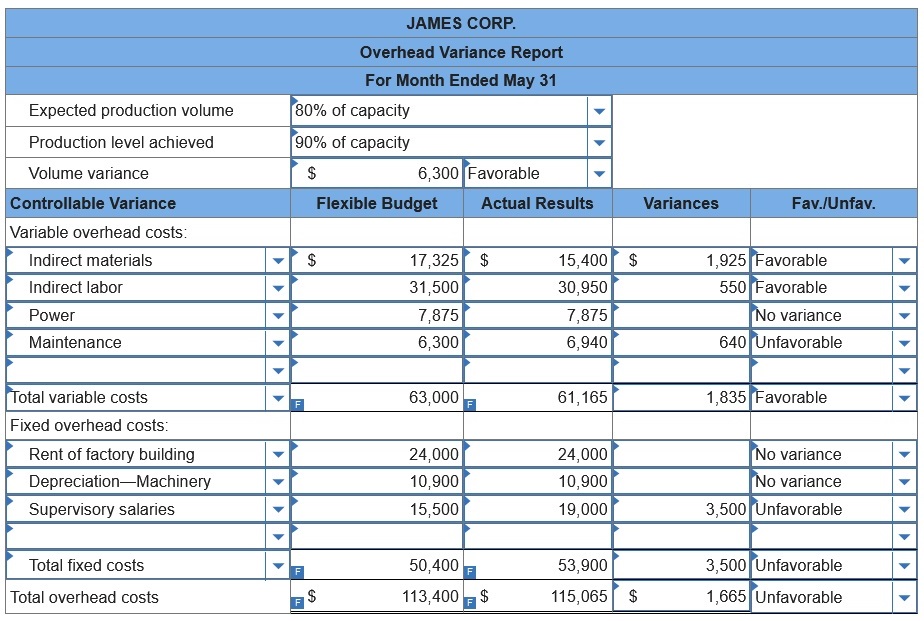
James
Corp. applies overhead on the basis of direct labor hours. For the month of
May, the company planned production of
10,000 units (80% of its production
capacity of 12,500 units) and prepared the following overhead budget:
|
Operating Levels
|
|
Overhead Budget
|
80%
|
|
Production in units
|
|
10,000
|
|
|
Standard direct labor hours
|
|
28,000
|
|
|
Budgeted overhead
|
|
|
|
|
Variable overhead costs
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect materials
|
$
|
15,400
|
|
|
Indirect labor
|
|
28,000
|
|
|
Power
|
|
7,000
|
|
|
Maintenance
|
|
5,600
|
|
|
Total variable costs
|
|
56,000
|
|
|
Fixed overhead costs
|
|
|
|
|
Rent of factory building
|
|
24,000
|
|
|
Depreciation—Machinery
|
|
10,900
|
|
|
Supervisory salaries
|
|
15,500
|
|
|
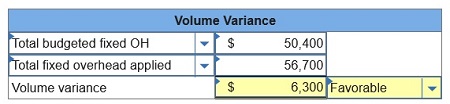
Total fixed costs
|
|
50,400
|
|
|
Total overhead costs
|
$
|
106,400
|
|
|
|
During
May, the company operated at 90% capacity (11,250 units) and incurred the
following actual overhead costs:
|
Overhead costs (actual)
|
|
Indirect materials
|
$
|
15,400
|
|
|
Indirect labor
|
|
30,950
|
|
|
Power
|
|
7,875
|
|
|
Maintenance
|
|
6,940
|
|
|
Rent of factory building
|
|
24,000
|
|
|
Depreciation—Machinery
|
|
10,900
|
|
|
Supervisory salaries
|
|
19,000
|
|
|
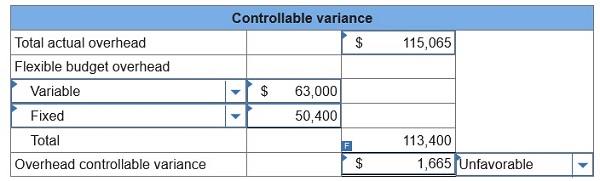
Total actual overhead costs
|
$
|
115,065
|
|
|
|
1. Compute the overhead
controllable variance and classify it as favorable or unfavorable.
2. Compute the overhead
volume variance and classify it as favorable or unfavorable.
3. Prepare an overhead variance report at the actual activity level of 11,250
units.
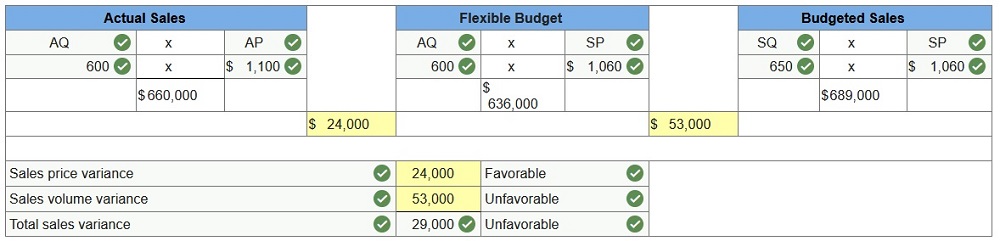
Comp Wiz sells computers.
During May, it sold 600 computers at a $1,100 average price each.
The May fixed budget
included sales of 650 computers at an average price of $1,060 each.
AQ = Actual Quantity
SQ = Standard Quantity
AP = Actual Price
SP = Standard Price
1&2. Compute the sales
price variance and the sales volume variance for May.
Classify it as favorable
or unfavorable. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting for
favorable, unfavorable, and no variance.)
Antuan
Company set the following standard costs for one unit of its product.
|
|
|
|
Direct materials (4.0 Ibs. @ $4.00 per
Ib.)
|
$
|
16.00
|
|
Direct labor (1.6 hrs. @ $11.00 per
hr.)
|
|
17.60
|
|
Overhead (1.6 hrs. @ $18.50 per hr.)
|
|
29.60
|
|
Total standard cost
|
$
|
63.20
|
|
|
The predetermined overhead
rate ($18.50 per direct labor hour) is based on an expected volume of 75% of
the factory’s capacity
of 20,000 units per month. Following are the company’s
budgeted overhead costs per month at the 75% capacity level.
|
Overhead Budget (75% Capacity)
|
|
Variable overhead costs
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect materials
|
$
|
15,000
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect labor
|
|
75,000
|
|
|
|
|
Power
|
|
15,000
|
|
|
|
|
Repairs and maintenance
|
|
30,000
|
|
|
|
|
Total variable overhead costs
|
|
|
|
$
|
135,000
|
|
Fixed overhead costs
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation—Building
|
|
24,000
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation—Machinery
|
|
71,000
|
|
|
|
|
Taxes and insurance
|
|
17,000
|
|
|
|
|
Supervision
|
|
197,000
|
|
|
|
|
Total fixed overhead costs
|
|
|
|
|
309,000
|
|
Total overhead costs
|
|
|
|
$
|
444,000
|
|
|
The
company incurred the following actual costs when it operated at 75% of capacity
in October.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Direct materials (61,000 Ibs. @ $4.10
per lb.)
|
|
|
|
$
|
250,100
|
|
Direct labor (20,000 hrs. @ $11.20 per
hr.)
|
|
|
|
|
224,000
|
|
Overhead costs
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect materials
|
$
|
41,600
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect labor
|
|
176,450
|
|
|
|
|
Power
|
|
17,250
|
|
|
|
|
Repairs and maintenance
|
|
34,500
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation—Building
|
|
24,000
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation—Machinery
|
|
95,850
|
|
|
|
|
Taxes and insurance
|
|
15,300
|
|
|
|
|
Supervision
|
|
197,000
|
|
|
601,950
|
|
Total costs
|
|
|
|
$
|
1,076,050
|
|
|
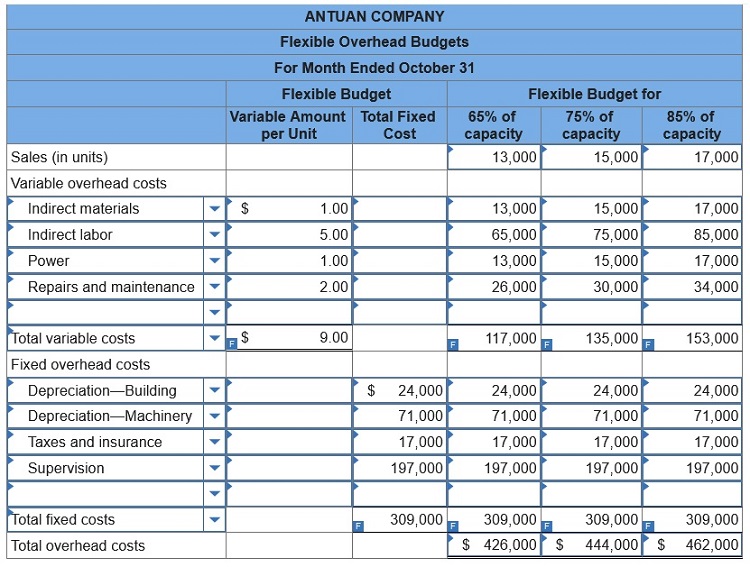
Required:
1&2. Prepare flexible overhead budgets for October showing the amounts of
each variable and fixed cost at the 65%, 75%,
and 85% capacity levels and
classify all items listed in the fixed budget as variable or fixed.
Antuan Company set the
following standard costs for one unit of its product.
|
|
|
|
Direct materials (4.0 Ibs. @ $4.00 per
Ib.)
|
$
|
16.00
|
|
Direct labor (1.6 hrs. @ $11.00 per
hr.)
|
|
17.60
|
|
Overhead (1.6 hrs. @ $18.50 per hr.)
|
|
29.60
|
|
Total standard cost
|
$
|
63.20
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The
predetermined overhead rate ($18.50 per direct labor hour) is based on an
expected volume of 75% of the factory’s capacity
of 20,000 units per month.
Following are the company’s budgeted overhead costs per month at the 75%
capacity level.
|
Overhead Budget (75% Capacity)
|
|
Variable overhead costs
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect materials
|
$
|
15,000
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect labor
|
|
75,000
|
|
|
|
|
Power
|
|
15,000
|
|
|
|
|
Repairs and maintenance
|
|
30,000
|
|
|
|
|
Total variable overhead costs
|
|
|
|
$
|
135,000
|
|
Fixed overhead costs
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation—Building
|
|
24,000
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation—Machinery
|
|
71,000
|
|
|
|
|
Taxes and insurance
|
|
17,000
|
|
|
|
|
Supervision
|
|
197,000
|
|
|
|
|
Total fixed overhead costs
|
|
|
|
|
309,000
|
|
Total overhead costs
|
|
|
|
$
|
444,000
|
|
|
The
company incurred the following actual costs when it operated at 75% of capacity
in October.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Direct materials (61,000 Ibs. @ $4.10
per lb.)
|
|
|
|
$
|
250,100
|
|
Direct labor (20,000 hrs. @ $11.20 per
hr.)
|
|
|
|
|
224,000
|
|
Overhead costs
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect materials
|
$
|
41,600
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect labor
|
|
176,450
|
|
|
|
|
Power
|
|
17,250
|
|
|
|
|
Repairs and maintenance
|
|
34,500
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation—Building
|
|
24,000
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation—Machinery
|
|
95,850
|
|
|
|
|
Taxes and insurance
|
|
15,300
|
|
|
|
|
Supervision
|
|
197,000
|
|
|
601,950
|
|
Total costs
|
|
|
|
$
|
1,076,050
|
|
|
3.
Compute the direct materials cost variance, including its price and quantity
variances. (Indicate the effect of each
variance by selecting for
favorable, unfavorable, and No variance.)
Antuan
Company set the following standard costs for one unit of its product.
|
|
|
|
Direct materials (4.0 Ibs. @ $4.00 per
Ib.)
|
$
|
16.00
|
|
Direct labor (1.6 hrs. @ $11.00 per
hr.)
|
|
17.60
|
|
Overhead (1.6 hrs. @ $18.50 per hr.)
|
|
29.60
|
|
Total standard cost
|
$
|
63.20
|
|
|
The
predetermined overhead rate ($18.50 per direct labor hour) is based on an
expected volume of 75% of the factory’s capacity
of 20,000 units per month.
Following are the company’s budgeted overhead costs per month at the 75%
capacity level.
|
Overhead Budget (75% Capacity)
|
|
Variable overhead costs
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect materials
|
$
|
15,000
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect labor
|
|
75,000
|
|
|
|
|
Power
|
|
15,000
|
|
|
|
|
Repairs and maintenance
|
|
30,000
|
|
|
|
|
Total variable overhead costs
|
|
|
|
$
|
135,000
|
|
Fixed overhead costs
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation—Building
|
|
24,000
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation—Machinery
|
|
71,000
|
|
|
|
|
Taxes and insurance
|
|
17,000
|
|
|
|
|
Supervision
|
|
197,000
|
|
|
|
|
Total fixed overhead costs
|
|
|
|
|
309,000
|
|
Total overhead costs
|
|
|
|
$
|
444,000
|
|
|
The
company incurred the following actual costs when it operated at 75% of capacity
in October.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Direct materials (61,000 Ibs. @ $4.10
per lb.)
|
|
|
|
$
|
250,100
|
|
Direct labor (20,000 hrs. @ $11.20 per
hr.)
|
|
|
|
|
224,000
|
|
Overhead costs
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect materials
|
$
|
41,600
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect labor
|
|
176,450
|
|
|
|
|
Power
|
|
17,250
|
|
|
|
|
Repairs and maintenance
|
|
34,500
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation—Building
|
|
24,000
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation—Machinery
|
|
95,850
|
|
|
|
|
Taxes and insurance
|
|
15,300
|
|
|
|
|
Supervision
|
|
197,000
|
|
|
601,950
|
|
Total costs
|
|
|
|
$
|
1,076,050
|
|
|
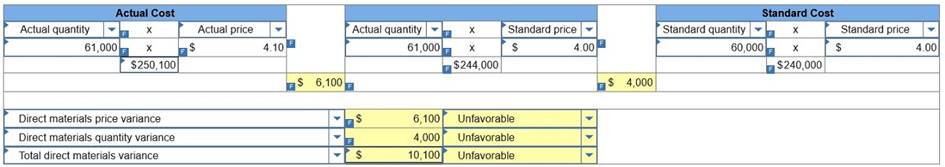
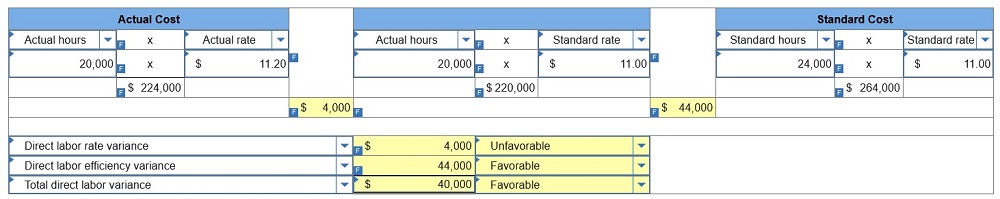
4.
Compute the direct labor cost variance, including its rate and efficiency
variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting for
favorable, unfavorable, and No variance. Round “Rate per hour” answers to two
decimal places.)
Antuan Company set the
following standard costs for one unit of its product.
|
|
|
|
Direct materials (4.0 Ibs. @ $4.00 per
Ib.)
|
$
|
16.00
|
|
Direct labor (1.6 hrs. @ $11.00 per
hr.)
|
|
17.60
|
|
Overhead (1.6 hrs. @ $18.50 per hr.)
|
|
29.60
|
|
Total standard cost
|
$
|
63.20
|
|
|
The
predetermined overhead rate ($18.50 per direct labor hour) is based on an
expected volume of 75% of the factory’s
capacity of 20,000 units per month.
Following are the company’s budgeted overhead costs per month at the 75%
capacity level.
|
Overhead Budget (75% Capacity)
|
|
Variable overhead costs
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect materials
|
$
|
15,000
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect labor
|
|
75,000
|
|
|
|
|
Power
|
|
15,000
|
|
|
|
|
Repairs and maintenance
|
|
30,000
|
|
|
|
|
Total variable overhead costs
|
|
|
|
$
|
135,000
|
|
Fixed overhead costs
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation—Building
|
|
24,000
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation—Machinery
|
|
71,000
|
|
|
|
|
Taxes and insurance
|
|
17,000
|
|
|
|
|
Supervision
|
|
197,000
|
|
|
|
|
Total fixed overhead costs
|
|
|
|
|
309,000
|
|
Total overhead costs
|
|
|
|
$
|
444,000
|
|
|
The
company incurred the following actual costs when it operated at 75% of capacity
in October.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Direct materials (61,000 Ibs. @ $4.10 per lb.)
|
|
|
|
$
|
250,100
|
|
Direct labor (20,000 hrs. @ $11.20 per hr.)
|
|
|
|
|
224,000
|
|
Overhead costs
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect materials
|
$
|
41,600
|
|
|
|
|
Indirect labor
|
|
176,450
|
|
|
|
|
Power
|
|
17,250
|
|
|
|
|
Repairs and maintenance
|
|
34,500
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation—Building
|
|
24,000
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation—Machinery
|
|
95,850
|
|
|
|
|
Taxes and insurance
|
|
15,300
|
|
|
|
|
Supervision
|
|
197,000
|
|
|
601,950
|
|
Total costs
|
|
|
|
$
|
1,076,050
|
|
|
Spot Company's master budget shows expected sales of
10,000 units and expected production of 11,000 units for the month of March.
Each unit requires 1/2 hour of direct labor. The direct labor rate is $15.00
per hour. Calculate the expected total direct labor cost for t
he month of March:
$82,000
11,000 x 1/2 x 15 = 82,500
Carter Production Inc required production for the
first six month of the year is as follows
Jan 50,000
Feb 70,000
Mar 85,000
Apr 105,000
May 110,000
Jun 120,000
Each unit requires two pounds of material. Given a desired ending inventory of
20% of the next month's
production needs, the pounds of material to be
purchased in April is:
212,000 pounds
(105,000 x 2) + (110,000 x 2 x .20) 44,000 -
(.20% x 105,000) = 212,000
A company's flexible budget for
15,000 units of production showed sales, $90,000; variable costs,
$37,500; and
fixed costs, $25,000. The sales expected if the company produces and sells
19,000 units is:
$114,000
90,000
/ 15,000 units = 6.00
6.00
× 19,000 units = 114,000
|



















