|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Principals Of Managerial Accounting: Homework Chapter 8 Part 1 Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2 14.1 14.2 15.1 15.2
Learnsmart 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Final Exam 1 2 Homework Help? World Company expects to operate at 80% of its productive capacity of 70,000 units per month. At this planned level, the company expects to use 25,200 standard hours of direct labor. Overhead is allocated to products using a predetermined standard rate of 0.450 direct labor hours per unit. At the 80% capacity level, the total budgeted cost includes $57,960 fixed overhead cost and $322,560 variable overhead cost. In the current month, the company incurred $386,000 actual overhead and 22,200 actual labor hours while producing 53,000 units. (1) Compute the overhead volume variance. (2) Compute the overhead controllable variance. REQ 1 Compute the overhead volume variance. Classify as favorable or unfavorable. (Round "OH costs per DL hour" to 2 decimal places.) 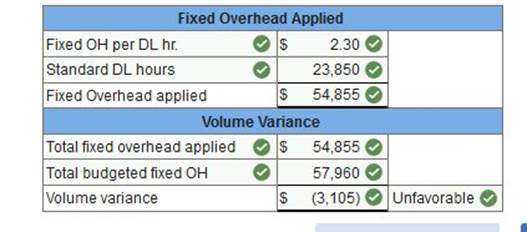
REQ 2 Compute the overhead controllable variance. Classify as favorable or unfavorable. 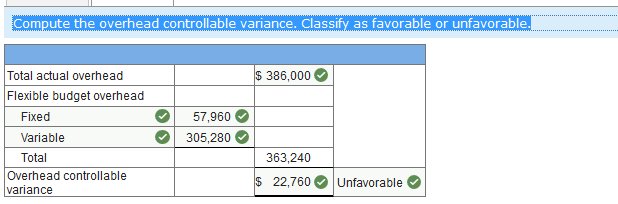
After evaluating Null Company’s manufacturing process, management decides to establish standards of 2 hours of direct labor per unit of product and $16.90 per hour for the labor rate. During October, the company uses 14,600 hours of direct labor at a $249,660 total cost to produce 7,500 units of product. In November, the company uses 23,900 hours of direct labor at a $411,080 total cost to produce 7,900 units of product. AH = Actual Hours SH = Standard Hours AR = Actual Rate SR = Standard Rate (1) Compute the direct labor rate variance, the direct labor efficiency variance, and the total direct labor cost variance for each of these two months. Classify each variance as favorable or unfavorable. SR SH SR 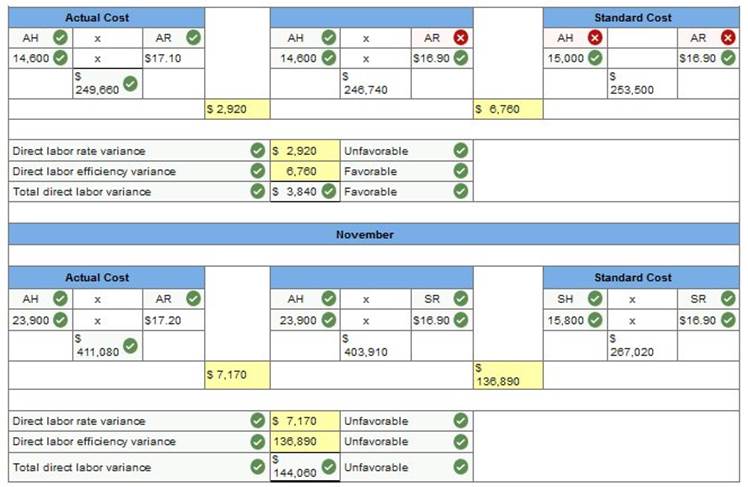
*Note Typo Incorrect answers should be (form left to right): SR SH SR Antuan Company set the following standard costs for one unit of its product.
The predetermined overhead rate ($18.50 per direct labor hour) is based on an expected volume of 75% of the factory’s capacity of 20,000 units per month. Following are the company’s budgeted overhead costs per month at the 75% capacity level.
The company incurred the following actual costs when it operated at 75% of capacity in October.
Prepare a detailed overhead variance report that shows the variances for individual items of overhead. 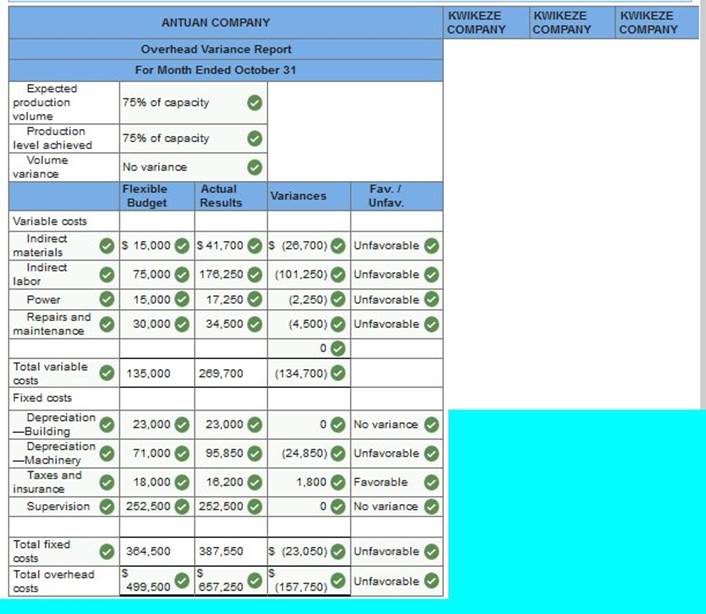
Tempo Company’s fixed budget (based on sales of 14,000 units) for the first quarter of calendar year 2017 reveals the following.
Complete the following flexible budgets for sales volumes of 12,000, 14,000, and 16,000 units. (Round cost per unit to 2 decimal places.) 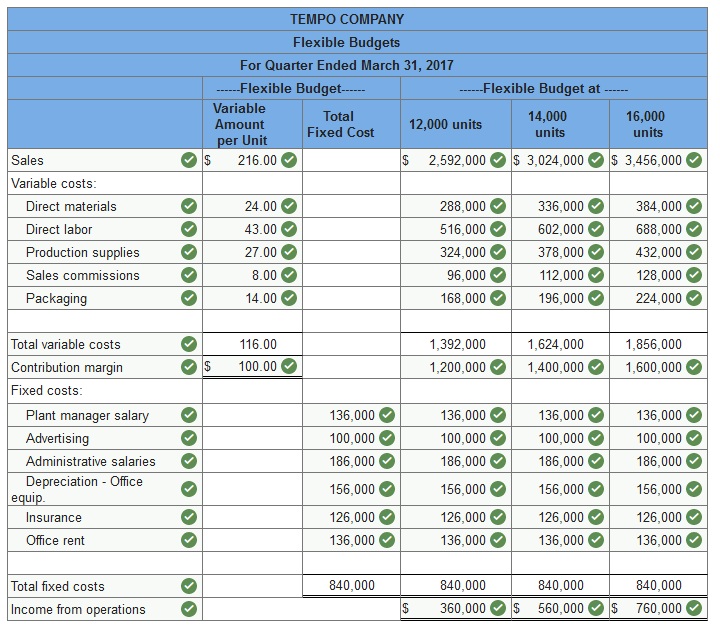
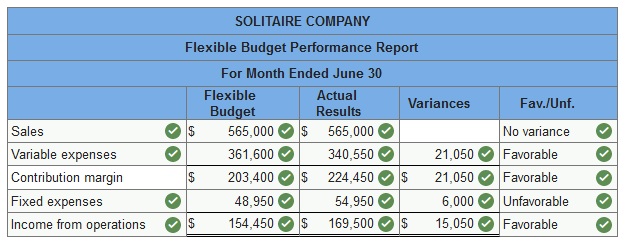
expenses and $48,950 fixed expenses. Actual expenses include $54,950 fixed expenses.
Hart Company made 3,600 bookshelves using 32,000 board feet of wood costing $332,800. The company’s direct materials standards for one bookshelf are 10 board feet of wood at $10.30 per board foot. (1) Compute the direct materials price and quantity variances incurred in manufacturing these bookshelves. AQ = Actual Quantity SQ = Standard Quantity AP = Actual Price SP = Standard Price 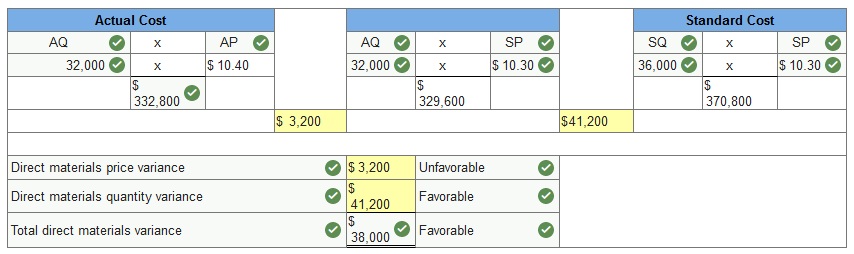
The following information describes production activities of Mercer Manufacturing for the year.
10 minutes of direct labor at $22.00 per hour. AQ = Actual Quantity SQ = Standard Quantity AP = Actual Price SP = Standard Price AH = Actual Hours SH = Standard Hours AR = Actual Rate SR = Standard Rate (1) Compute the direct materials price and quantity variances. 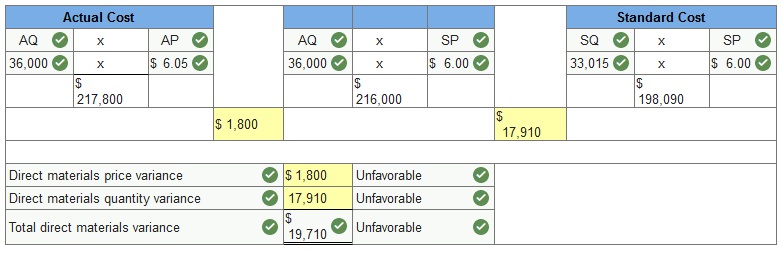
(2) Compute the direct labor rate and efficiency variances. Indicate whether each variance is favorable or unfavorable. 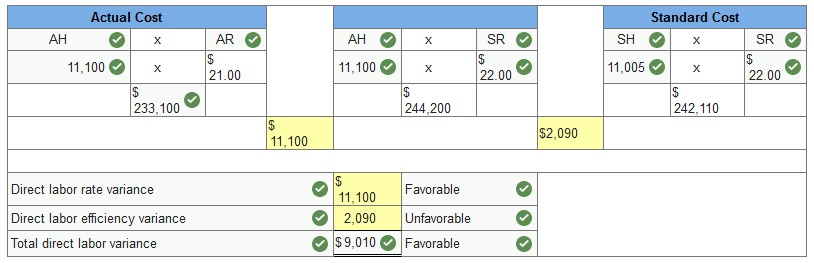
Summerlin Company budgeted 4,000 pounds of material costing $5.00 per pound to produce 2,000 units. The company actually used 4,500 pounds that cost $5.10 per pound to produce 2,000 units. What is the direct materials quantity variance? $400 unfavorable $450 unfavorable $2,500 unfavorable $2,550 unfavorable $2,950 unfavorable Use the following data to find the total direct labor cost variance if the company produced 3,500 units during the period.
$6,125 unfavorable $7,000 unfavorable $7,000 favorable $12,250 favorable $6,125 favorable The following information relating to a company’s overhead costs is available.
$2,000 favorable $6,000 favorable $2,000 unfavorable $6,000 unfavorable $1,000 favorable Overhead cost variance is: The difference between the overhead costs actually incurred and the overhead budgeted at the actual operating level. The difference between the actual overhead incurred during a period and the standard overhead applied The difference between actual and budgeted cost caused by the difference between the actual price per unit and the budgeted price per unit. The costs that should be incurred under normal conditions to produce a specific product (or component) or to perform a specific service. The difference between the total overhead cost that would have been expected if overhead cost was allocated to products using the standard rate. A flexible budget performance report compares the differences between: Actual performance and budgeted performance based on actual sales volume Actual performance over several periods. Budgeted performance over several periods. Actual performance and budgeted performance based on budgeted sales volume. Actual performance and standard costs at the budgeted sales volume. Fletcher Company collected the following data regarding production of one of its products. Compute the standard quantity allowed for the actual output.
243,000 pounds. 240,000 pounds 40,000 pounds 480,000 pounds. 80,000 pounds. Claremont Company specializes in selling refurbished copiers. During the month, the company sold 180 copiers for total sales of $540,000. The budget for the month was to sell 175 copiers at an average price of $3,200. The sales price variance for the month was: $20,000 unfavorable $20,000 favorable $36,000 unfavorable $32,000 unfavorable $36,000 favorable A company provided the following direct materials cost information. Compute the total direct materials cost variance.
$2,500 Favorable $78,250 Favorable $78,250 Unfavorable $80,750 Favorable $80,750 Unfavorable Claremont Company specializes in selling refurbished copiers. During the month, the company sold 180 copiers at an average price of $3,000 each. The budget for the month was to sell 175 copiers at an average price of $3,200. The expected total sales for 180 copiers were: $540,000 $576,000 $525,000 $560,000 $550,000 When recording the journal entry for labor, the Work in Process Inventory account is Debited for standard labor cost Debited for actual labor cost. Credited for standard labor cost. Credited for actual labor cost. Not used. A company provided the following direct materials cost information. Compute the cost variance. Standard costs assigned: Direct materials standard cost (405,000 units @ $2/unit $810,000 Actual costs Direct Materials costs incurred (403,750 units @ $2.20 /unit) $888,250 $78,250 Unfavorable Actual cost $888,250 - Standard cost $810,000 = $78,25 A company's flexible budget for 12,000 units of production showed sales, $48,000; variable costs, $18,000; and fixed costs, $16,000. The operating income expected if the company produces and sells 16,000 units is: $24,000 Selling price per unit = 48,000 / 12,000 units = 4.00 per unit Variable costs per unit = 18,000 / 12,000 = 1.50 per unit Contribution margin per unit = 4.00 - 1.50 = 2.50 per unit Expected operating income for 16,000 units: Contribution margin: 16,000 x 2.50 = 40,000 – 16,000 = 24,000 Based on predicted production of 12,000 units, a company anticipates $150,000 of fixed costs and $123,000 of variable costs. The flexible budget amounts of fixed and variable costs for 10,000 units are: $150,000 fixed and $102,500 variable Fixed costs remain at $150,000 Variable costs = (123,000 / 12,000) x 10,000 units = 102,500 Product A has a sales price of $10 per unit. Based on a 10,000-unit production level, the variable costs are $6 per unit and the fixed costs are $3 per unit. Using a flexible budget for 12,500 units, what is the budgeted operating income from Product A? $20,000 10 x 12,500 – (6 x 12,500) – (3 x 10,000) = 20,000 A company's flexible budget for 10,000 units of production reflects sales of $200,000; variable costs of $40,000; and fixed costs of $75,000. Calculate the expected level of operating income if the company produces and sells 13,000 units. $133,000 200,000 / 10,000 = 20 40,000 / 10,000 = 4 20 – 4 = 16 13,000 x 16 = 208,000 208,000 – 75,000 = 133,000 Based on a predicted level of production and sales of 12,000 units, a company anticipates reporting operating income of $26,000 after deducting variable costs of $72,000 and fixed costs of $10,000. Based on this information, the budgeted amounts of fixed and variable costs for 15,000 units would be: $10,000 of fixed costs and $90,000 of variable costs. fixed costs remain fixed at 10,000 Variable costs = (72,000 / 12,000 units) x 15,000 = 90,000 Kyle, Inc. has collected the following data on one of its products. Direct materials standard (4 lbs. @ $1/lb.) $4 per finished unit Total direct materials cost variance—unfavorable $13,750 Actual direct materials used 150.000 lbs. Actual finished units produced 30,000 units The actual cost of the direct materials used is: $133,750 (30,000 x 4) + 13,750 = 133,750 Kyle, Inc. has collected the following data on one of its products. Direct materials standard (4 lbs. @ $1/lb.) $4 per finished unit Total direct materials cost variance—unfavorable $13,750 Actual direct materials used 150.000 lbs. Actual finished units produced 30,000 units The direct materials quantity variance is: $30,000 unfavorable (150,000 x 1) – (30,000 x 4 x 1) = 30,000 Kyle, Inc. has collected the following data on one of its products. Direct materials standard (4 lbs. @ $1/lb.) $4 per finished unit Total direct materials cost variance—unfavorable $13,750 Actual direct materials used 150.000 lbs. Actual finished units produced 30,000 units The direct materials price variance is: $16,250 favorable 30,000 x 4 = 120,000 120,000 + 13,750 = 133,750 150,000 – 133,750 = 16,250 Bartels Corp. produces woodcarvings. It takes 2 hours of direct labor to produce a carving. Bartels' standard labor cost is $12 per hour. During August, Bartels produced 10,000 carvings and used 21,040 hours of direct labor at a total cost of $250,376. What is Bartels' labor rate variance for August? $2,104 favorable 21,0540 x 12 - 250,376 = 2,104 Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2 14.1 14.2 15.1 15.2
Learnsmart 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Final Exam 1 2 Homework Help? |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |