|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Principals Of Managerial Accounting: Homework Chapter 7 Part 2 Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2 14.1 14.2 15.1 15.2
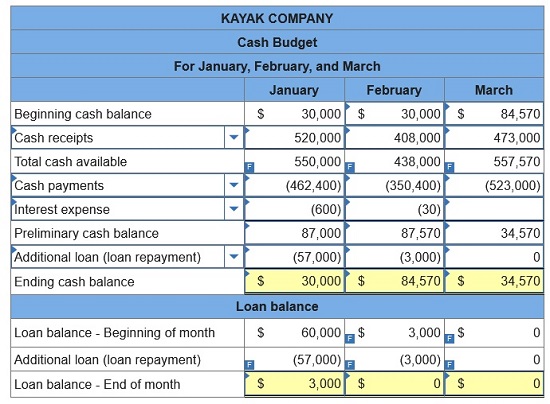
Learnsmart 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Final Exam 1 2 Homework Help? Kayak Co. budgeted the following cash receipts (excluding cash receipts from loans received) and cash payments (excluding cash payments for loan principal and interest payments) for the first three months of next year.
According to a credit agreement with its bank, Kayak requires a minimum cash balance of $30,000 at each month-end. In return, the bank has agreed that the company can borrow up to $140,000 at a monthly interest rate of 1%, paid on the last day of each month. The interest is computed based on the beginning balance of the loan for the month. The company repays loan principal with any cash in excess of $30,000 on the last day of each month. The company has a cash balance of $30,000 and a loan balance of $60,000 at January 1. Prepare monthly cash budgets for January, February, and March. (Negative balances and Loan repayment amounts (if any) should be indicated with minus sign.)
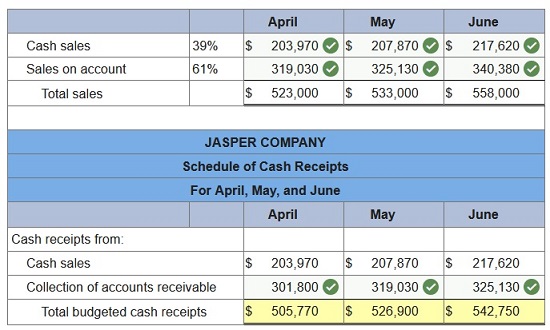
Jasper Company has sales on account and for cash. Specifically, 61% of its sales are on account and 39% are for cash. Credit sales are collected in full in the month following the sale. The company forecasts sales of $523,000 for April, $533,000 for May, and $558,000 for June. The beginning balance of Accounts Receivable is $301,800 on April 1. Prepare a schedule of budgeted cash receipts for April, May, and June.
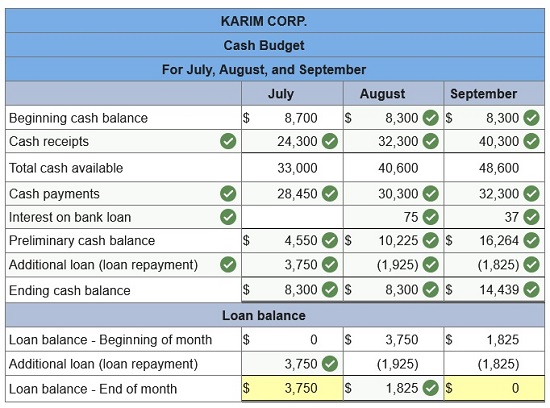
Karim Corp. requires a minimum $8,300 cash balance. Loans taken to meet this requirement cost 2% interest per month (paid monthly). Any excess cash is used to repay loans at month-end. The cash balance on July 1 is $8,700, and the company has no outstanding loans. Forecasted cash receipts (other than for loans received) and forecasted cash payments (other than for loan or interest payments) follow.
Prepare a cash budget for July, August, and September. (Negative balances and Loan repayment amounts (if any) should be indicated with minus sign. Round your final answers to the nearest whole dollar.)
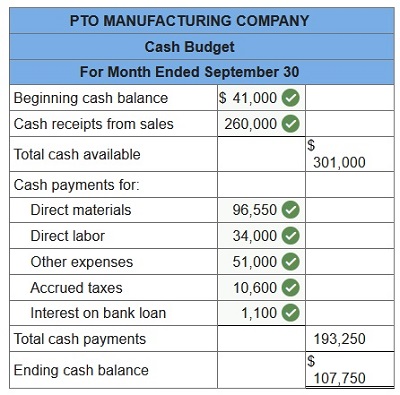
Use the following information to prepare the September cash budget for PTO Co. The following information relates to expected cash receipts and cash payments for the month ended September 30. Beginning cash balance, September 1, $41,000. Budgeted cash receipts from sales in September, $260,000. Raw materials are purchased on account. Purchase amounts are August (actual), $79,000, and September (budgeted), $106,000. Payments for direct materials are made as follows: 65% in the month of purchase and 35% in the month following purchase. Budgeted cash payments for direct labor in September, $34,000. Budgeted depreciation expense for September, $3,200. Other cash expenses budgeted for September, $51,000. Accrued income taxes payable in September, $10,600. Bank loan interest payable in September, $1,100.
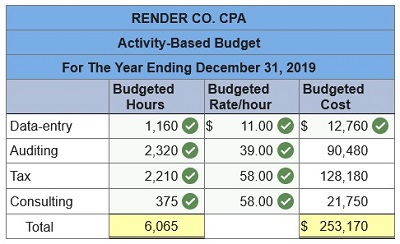
Render Co. CPA is preparing activity-based budgets for 2019. The partners expect the firm to generate billable hours for the year as follows:
The company pays $11 per hour to data-entry clerks, $39 per hour to audit personnel, $58 per hour to tax personnel, and $58 per hour to consulting personnel. Prepare a schedule of budgeted labor costs for 2019 using activity-based budgeting.
The management of Zigby Manufacturing prepared the following estimated balance sheet for March 2019.
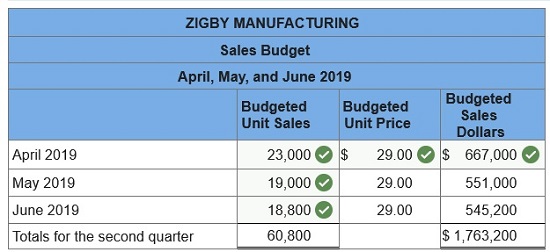
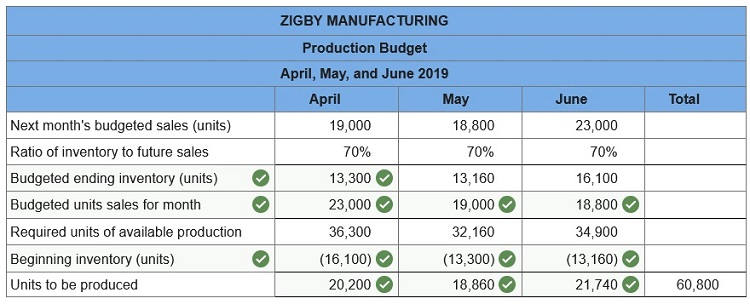
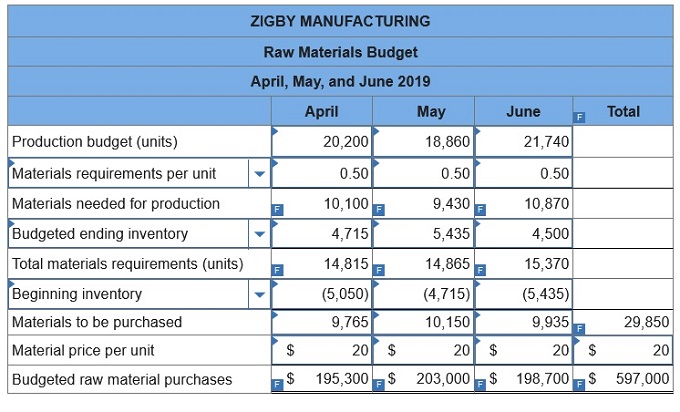
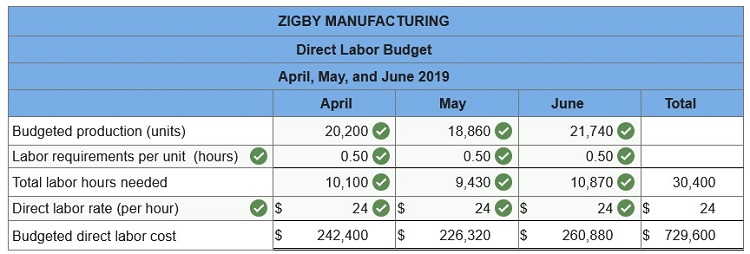
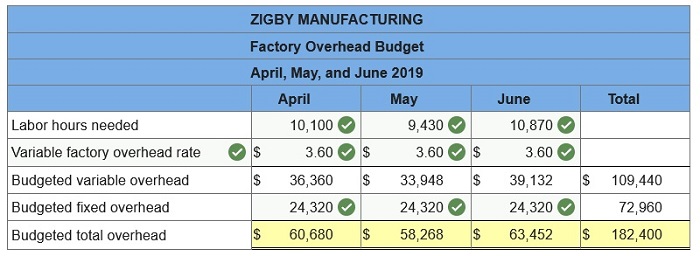
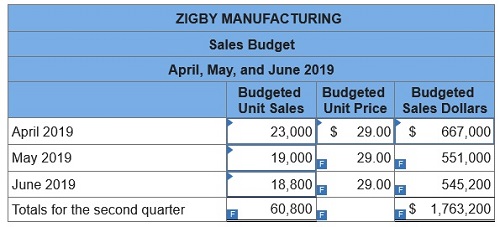
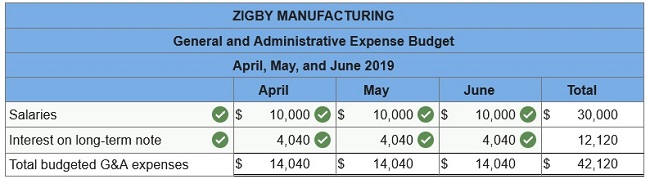
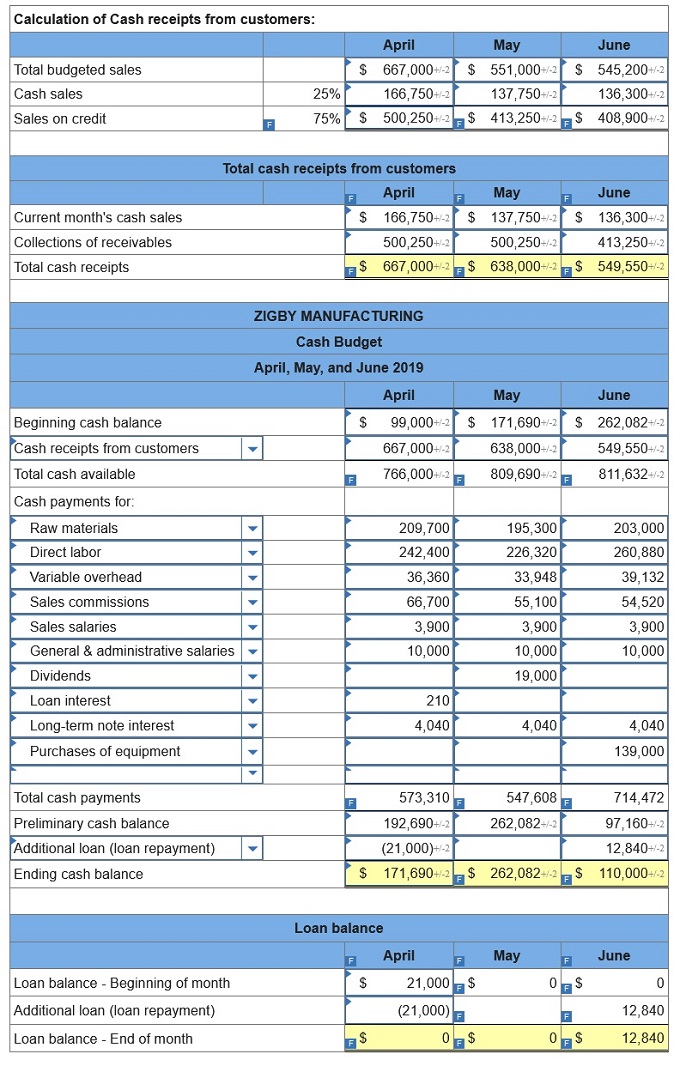
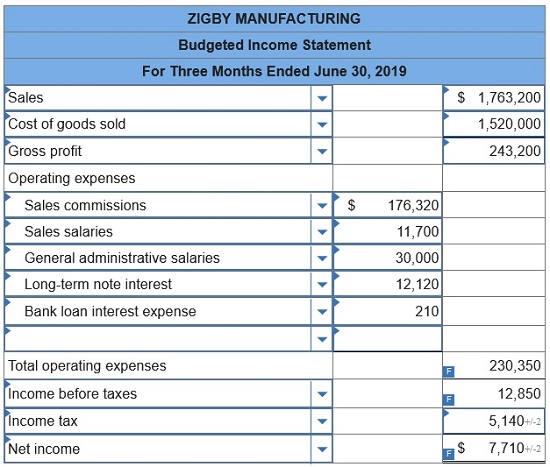
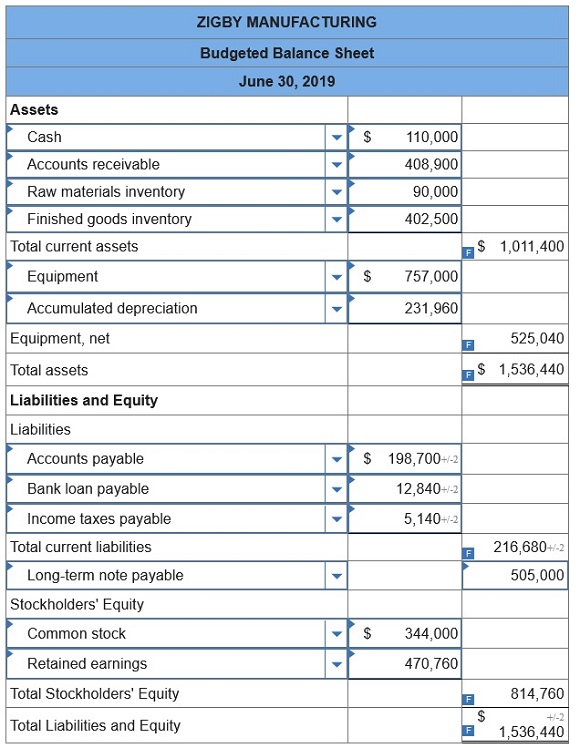
To prepare a master budget for April, May, and June of 2019, management gathers the following information. Sales for March total 23,000 units. Forecasted sales in units are as follows: April, 23,000; May, 19,000; June, 18,800; and July, 23,000. Sales of 249,000 units are forecasted for the entire year. The product’s selling price is $29.00 per unit and its total product cost is $25.00 per unit. Company policy calls for a given month’s ending raw materials inventory to equal 50% of the next month’s materials requirements. The March 31 raw materials inventory is 5,050 units, which complies with the policy. The expected June 30 ending raw materials inventory is 4,500 units. Raw materials cost $20 per unit. Each finished unit requires 0.50 units of raw materials. Company policy calls for a given month’s ending finished goods inventory to equal 70% of the next month’s expected unit sales. The March 31 finished goods inventory is 16,100 units, which complies with the policy. Each finished unit requires 0.50 hours of direct labor at a rate of $24 per hour. Overhead is allocated based on direct labor hours. The predetermined variable overhead rate is $3.60 per direct labor hour. Depreciation of $24,320 per month is treated as fixed factory overhead. Sales representatives’ commissions are 10% of sales and are paid in the month of the sales. The sales manager’s monthly salary is $3,900. Monthly general and administrative expenses include $10,000 administrative salaries and 0.8% monthly interest on the long-term note payable. The company expects 25% of sales to be for cash and the remaining 75% on credit. Receivables are collected in full in the month following the sale (none are collected in the month of the sale). All raw materials purchases are on credit, and no payables arise from any other transactions. One month’s raw materials purchases are fully paid in the next month. The minimum ending cash balance for all months is $110,000. If necessary, the company borrows enough cash using a short-term note to reach the minimum. Short-term notes require an interest payment of 1% at each month-end (before any repayment). If the ending cash balance exceeds the minimum, the excess will be applied to repaying the short-term notes payable balance. Dividends of $19,000 are to be declared and paid in May. No cash payments for income taxes are to be made during the second calendar quarter. Income tax will be assessed at 40% in the quarter and paid in the third calendar quarter. Equipment purchases of $139,000 are budgeted for the last day of June.
Required: All budgets and other financial information should be prepared for the second calendar quarter, except as otherwise noted below. (Round calculations up to the nearest whole dollar, except for the amount of cash sales, which should be rounded down to the nearest whole dollar.):
1. Sales budget.
2. Production budget.
3. Raw materials budget.
4. Direct labor budget.
5. Factory overhead budget.
6. Selling expense budget.
7. General and administrative expense budget.
8. Cash budget.
9. Budgeted income statement for the entire second quarter (not for each month separately).
10. Budgeted balance sheet.
Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2 14.1 14.2 15.1 15.2
Learnsmart 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Final Exam 1 2 Homework Help? |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |