|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Principals Of Managerial Accounting: Homework Chapter 7 Part 1 Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2 14.1 14.2 15.1 15.2
Learnsmart 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Final Exam 1 2 Homework Help? Use the following information to prepare the September cash budget for PTO Manufacturing Co. The following information relates to expected cash receipts and cash payments for the month ended September 30. Beginning cash balance, September 1, $46,000. Budgeted cash receipts from sales in September, $263,000. Raw materials are purchased on account. Purchase amounts are: August (actual), $78,000, and September (budgeted), $105,000. Payments for direct materials are made as follows: 70% in the month of purchase and 30% in the month following purchase. Budgeted cash payments for direct labor in September, $36,000. Budgeted depreciation expense for September, $3,300. Other cash expenses budgeted for September, $59,000. Accrued income taxes payable in September, $10,300. Bank loan interest payable in September, $1,400. 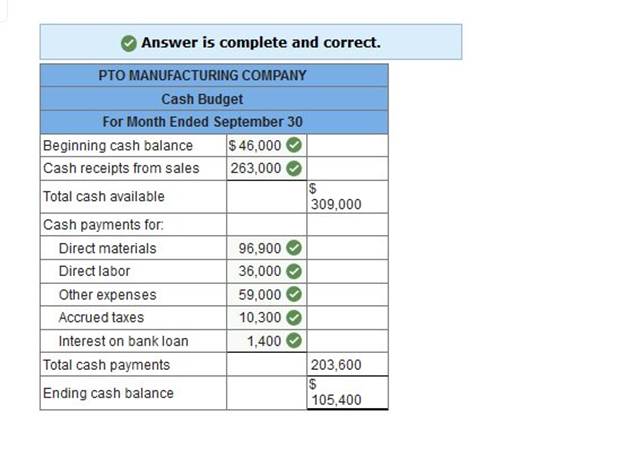
Jasper Company has sales on account and for cash. Specifically, 59% of its sales are on account and 41% are for cash. Credit sales are collected in full in the month following the sale. The company forecasts sales of $525,000 for April, $535,000 for May, and $560,000 for June. The beginning balance of Accounts Receivable is $306,200 on April 1. Prepare a schedule of budgeted cash receipts for April, May, and June. 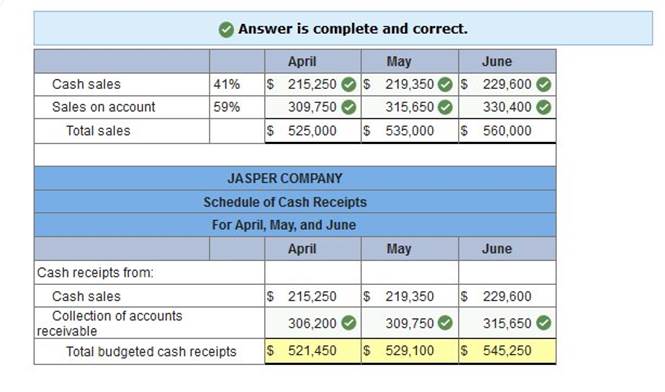
Ruiz Co. provides the following sales forecast for the next four months: April May June July Sales (units) 580 660 610 700 The company wants to end each month with ending finished goods inventory equal to 30% of next month’s forecasted sales. Finished goods inventory on April 1 is 174 units. Assume July’s budgeted production is 610 units. In addition, each finished unit requires six pounds (lbs.) of raw materials and the company wants to end each month with raw materials inventory equal to 30% of next month’s production needs. Beginning raw materials inventory for April was 1,087 pounds. Assume direct materials cost $4 per pound. Prepare a production budget for the months of April, May, and June. 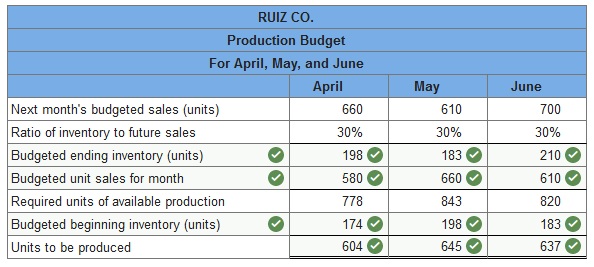
Ruiz Co. provides the following sales forecast for the next four months: April May June July Sales (units) 670 750 700 790 The company wants to end each month with ending finished goods inventory equal to 30% of next month’s forecasted sales. Finished goods inventory on April 1 is 201 units. Assume July’s budgeted production is 700 units. In addition, each finished unit requires four pounds (lbs.) of raw materials and the company wants to end each month with raw materials inventory equal to 30% of next month’s production needs. Beginning raw materials inventory for April was 833 pounds. Assume direct materials cost $5 per pound. Prepare a direct materials budget for April, May, and June. (Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) 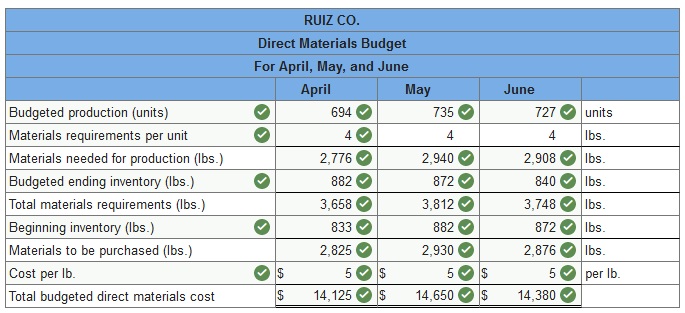
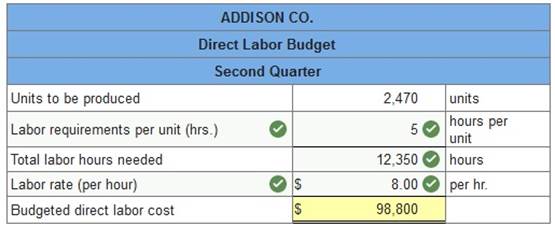
2. Prepare a factory overhead budget. 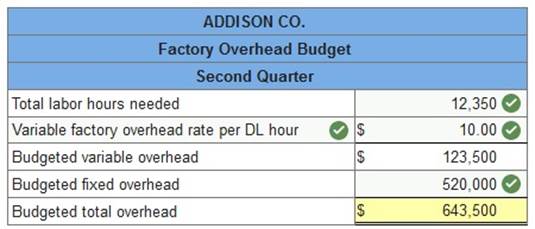
Kayak Co. budgeted the following cash receipts (excluding cash receipts from loans received) and cash payments (excluding cash payments for loan principal and interest payments) for the first three months of next year.
According to a credit agreement with the company’s bank, Kayak promises to have a minimum cash balance of $30,000 at each month-end. In return, the bank has agreed that the company can borrow up to $150,000 at a monthly interest rate of 1%, paid on the last day of each month. The interest is computed based on the beginning balance of the loan for the month. The company repays loan principal with any cash in excess of $30,000 on the last day of each month. The company has a cash balance of $30,000 and a loan balance of $60,000 at January 1. Prepare monthly cash budgets for January, February, and March. (Negative balances and Loan repayment amounts (if any) should be indicated with minus sign.) 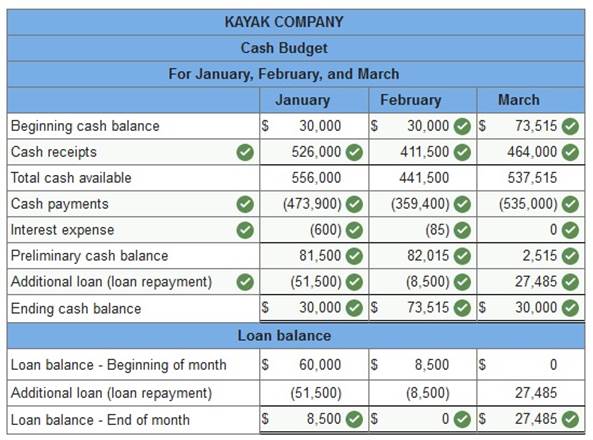
Jasper Company has sales on account and for cash. Specifically, 59% of its sales are on account and 41% are for cash. Credit sales are collected in full in the month following the sale. The company forecasts sales of $519,000 for April, $529,000 for May, and $554,000 for June. The beginning balance of Accounts Receivable is $300,100 on April 1. Prepare a schedule of budgeted cash receipts for April, May, and June 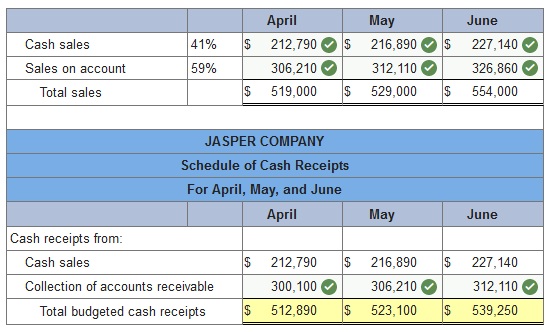
The company wants to end each month with ending finished goods inventory equal to 30% of next month’s forecasted sales. Finished goods inventory on April 1 is 207 units. Prepare a production budget for the months of April, May, and June. 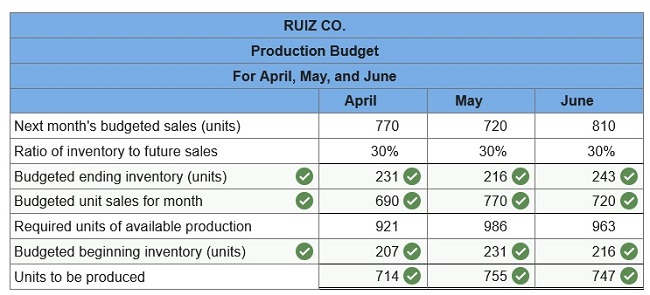
Each finished unit requires four pounds of raw materials and the company wants to end each month with raw materials inventory equal to 20% of next month’s production needs. Beginning raw materials inventory for April was 483 pounds. Assume direct materials cost $5 per pound. Prepare a direct materials budget for April, May, and June. (Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) 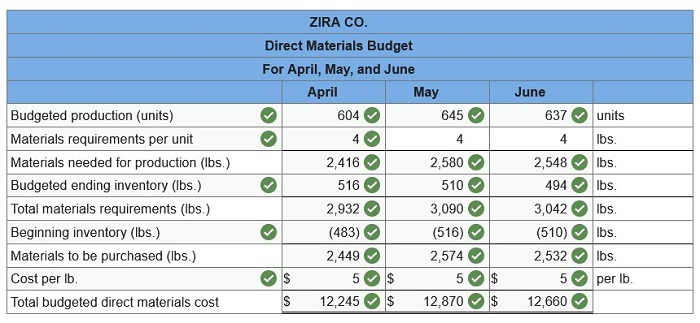
Electro Company manufactures an innovative automobile transmission for electric cars. Management predicts that ending finished goods inventory for the first quarter will be 238,200 units. The following unit sales of the transmissions are expected during the rest of the year: second quarter, 397,000 units third quarter, 286,000 units fourth quarter, 216,000 units Company policy calls for the ending finished goods inventory of a quarter to equal 60% of the next quarter’s budgeted sales. Prepare a production budget for both the second and third quarters that shows the number of transmissions to manufacture. 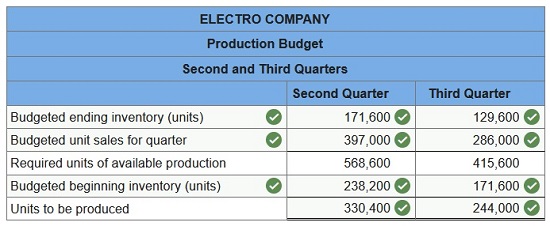
at a rate of $15 per hour. Variable manufacturing overhead is charged at a rate of $2 per direct labor hour. Fixed manufacturing overhead is $16,000 per month. The company’s policy is to end each month with direct materials inventory equal to 30% of the next month’s materials requirement. At the end of August the company had 2,980 pounds of direct materials in inventory. The company’s production budget reports the following.
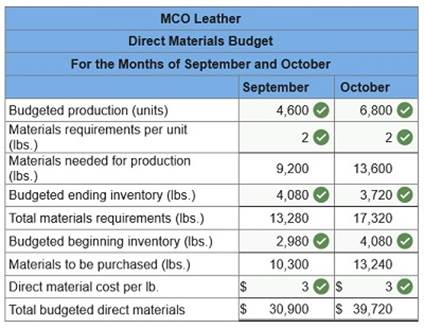 (2) Prepare direct labor budgets for September and October. 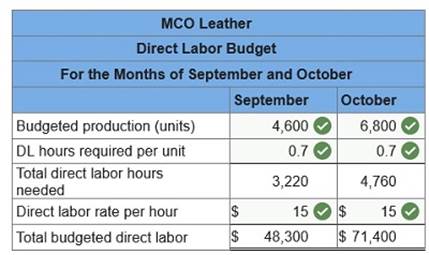 (3) Prepare factory overhead budgets for September and October. 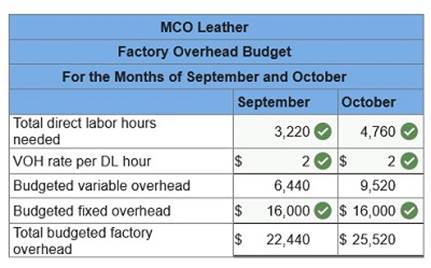
$280,000 $297,000 $271,600 $288,400 $364,000 Budgeted ending inventory. Budgeted beginning inventory. Budgeted sales. Budgeted overhead Ratio of inventory to future sales. Zhang Industries is preparing a cash budget for June. The company has $25,000 cash at the beginning of June and anticipates $95,000 in cash receipts and $111,290 in cash disbursements during June. The company has no loans outstanding on June 1. Compute the amount the company must borrow, if any, to maintain a $20,000 cash balance. $28,710 $12,290 $16,290 $11,290 $6,290 Which of the following budgets is not a budget that a manufacturer would include in its master budget? Sales budget. Direct materials budget. Production budget. Merchandise purchases budget Cash budget. Frankie’s Chocolate Co. reports the following information from its sales budget:
Cash sales are normally 25% of total sales and all credit sales are expected to be collected in the month following the date of sale. The total amount of cash expected to be received from customers in September is: $30,000 $78,000 $108,000 $120,000 $130,500 Q6. Junior Snacks reports the following information from its sales budget:
All sales are on credit and are expected to be collected 40% in the month of sale and 60% in the month following sale. The total amount of cash expected to be received from customers in November is: $146,200 $85,800 $151,000 $236,800 $60,400 Flagstaff Company has budgeted production units for July of 7,900 units. Variable factory overhead is $1.20 per unit. Budgeted fixed factory overhead is $19,000, which includes $3,000 of factory equipment depreciation. Compute the total budgeted overhead to be reported on the factory overhead budget for the month. $25,480 $19,000 $23,900 $28,480 $9,480 Boulware Company’s budgeted production calls for 5,000 units in October and 8,000 units in November. Each unit requires 8 pounds (lbs.) of raw material A. Each month’s ending inventory of raw materials should equal 20% of the following month’s budgeted materials requirements. The October 1 inventory for this material is 8,000 pounds. What is the budgeted materials purchases for this key material in pounds for October? 40,000 lbs 44,800 lbs 52,800 lbs 60,800 lbs 35,200 lbs Ratchet Manufacturing anticipates total sales for August, September, and October of $200,000, $210,000, and $220,500 respectively. Cash sales are normally 25% of total sales and the remaining sales are on credit. All credit sales are collected in the first month after the sale. Compute the amount of accounts receivable to be reported on the company’s budgeted balance sheet for August. $150,000 $50,000 $157,500 $52,500 $200,000 Fortune Company’s direct materials budget shows the following cost of materials to be purchased for the coming three months:
Payments for purchases are expected to be made 50% in the month of purchase and 50% in the month following purchase. The December Accounts Payable balance is $6,500. The budgeted cash payments for materials in January are: $6,500 $9,270 $12,520 $13,095 $18,540 Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2 14.1 14.2 15.1 15.2
Learnsmart 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Final Exam 1 2 Homework Help? |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |