|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Principals Of Managerial Accounting: Homework Chapter 4 Part 1 Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2 14.1 14.2 15.1 15.2
Learnsmart 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Final Exam 1 2 Homework Help?
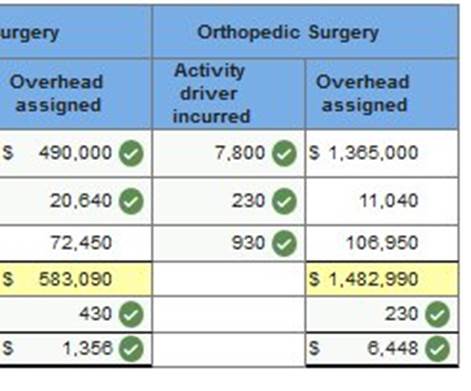
Surgery Center is an
outpatient surgical clinic that was profitable for many years,
but Medicare has cut its reimbursements by as much as 40%. As a result, the clinic wants to better understand its costs. It decides to prepare an activity-based cost analysis, including an estimate of the average cost of both general surgery and orthopedic surgery. The clinic’s three activity cost pools and their cost drivers follow.
The two main surgical units and their related data follow.
* Orthopedic surgery requires more space for patients, supplies, and equipment. Required: 1. & 2. Compute the cost per cost driver for each of the three activity cost pools. Use the results to allocate costs to both the general surgery and the orthopedic surgery units. Compute total cost and average cost per patient for both the general surgery and the orthopedic surgery units. 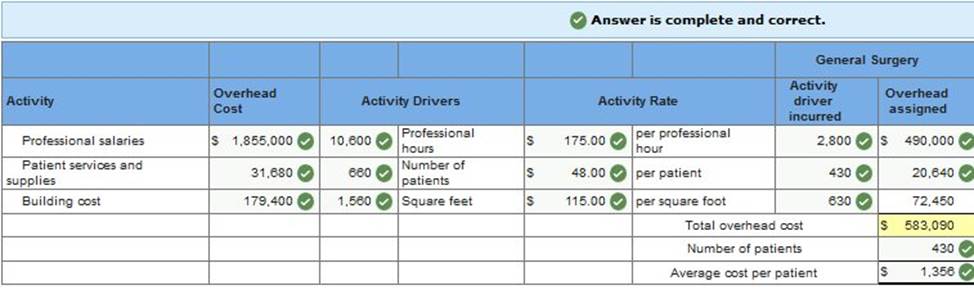
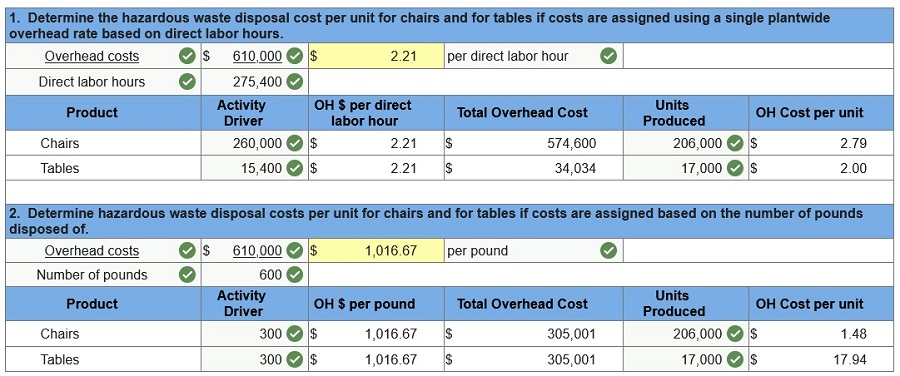
Exercise 4-4 Plantwide overhead rate LO P1 Textra Plastics produces parts for a variety of small machine manufacturers. Most products go through two operations, molding and trimming, before they are ready for packaging. Expected costs and activities for the molding department and for the trimming department for 2017 follow.
Data for two special order parts to be manufactured by the company in 2017 follow.
Required 1. Compute the plantwide overhead rate using direct labor hours as the base. 2. Determine the overhead cost assigned to each product line using the plantwide rate computed in requirement 1. Compute the plantwide overhead rate using direct labor hours as the base. 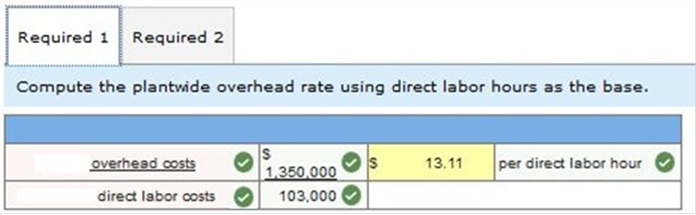
Determine the overhead cost assigned to each product line using the plantwide rate computed in requirement 1. (Round "OH rate" to 2 decimal places.) 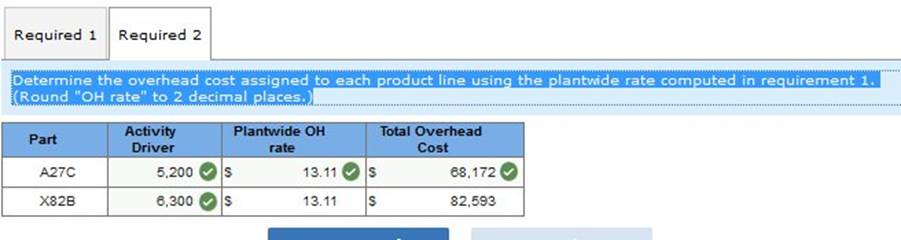
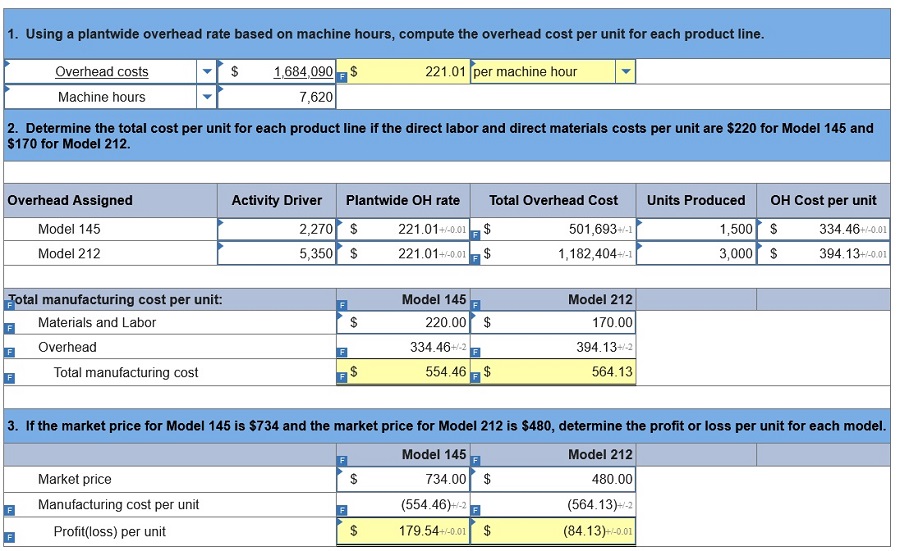
Exercise 4-8 Using departmental overhead rates to assess prices LO P2 Way Cool produces two different models of air conditioners. The company produces the mechanical systems in their components department. The mechanical systems are combined with the housing assembly in its finishing department. The activities, costs, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the production support process follow.
Additional production information concerning its two product lines follows.
Required 1 Determine departmental overhead rates and compute the overhead cost per unit for each product line. Base your overhead assignment for the components department on machine hours. Use welding hours to assign overhead costs to the finishing department. Assign costs to the support department based on number of purchase orders. (Round your intermediate calculations and per unit cost answers to 2 decimal places.) 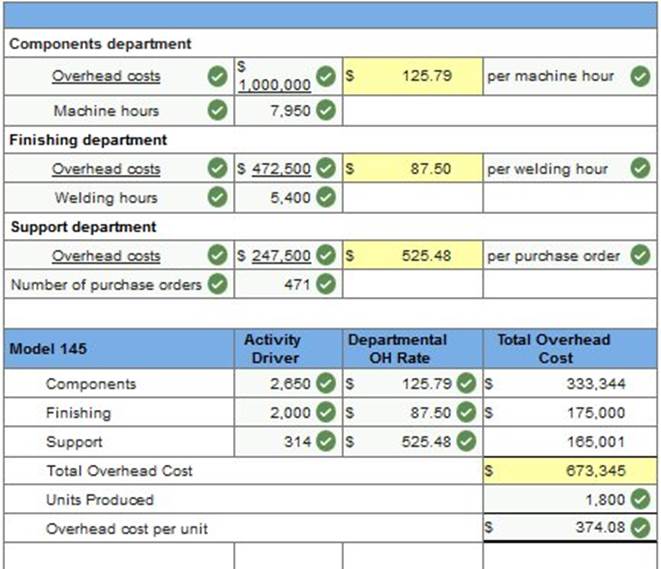
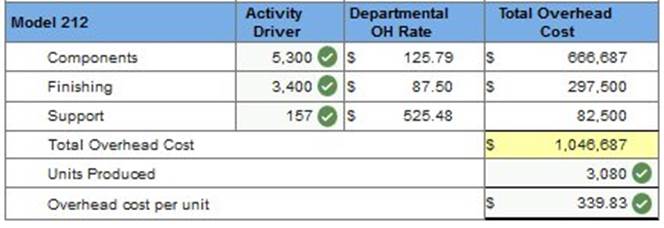
Required 2: Determine the total cost per unit for each product line if the direct labor and direct materials costs per unit are $250 for Model 145 and $200 for Model 212. (Round your intermediate calculations and cost per unit answers to 2 decimal places.) 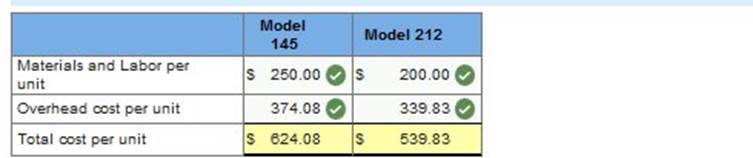
Required 3: Determine departmental overhead rates and compute the overhead cost per unit for each product line. Base your overhead assignment for the components department on machine hours. Use welding hours to assign overhead costs to the finishing department. Assign costs to the support department based on number of purchase orders. Determine the total cost per unit for each product line if the direct labor and direct materials costs per unit are: $250 for Model 145 and $200 for Model 212. If the market price for Model 145 is $1,400 and the market price for Model 212 is $280, determine the profit or loss per unit for each model. 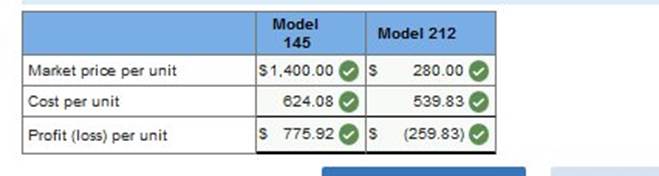
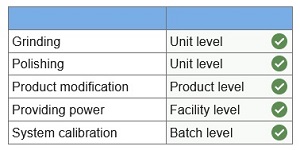
Required information Problem 4-3A Applying activity-based costing LO P1, P3, A1, A2, C3 [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Craft Pro Machining produces machine tools for the construction industry. The following details about overhead costs were taken from its company records.
Additional information on the drivers for its production activities follows.
Required: 1. Classify each activity as unit level, batch level, product level, or facility level. 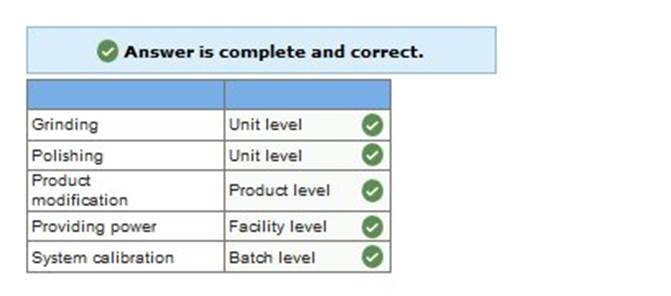
Required information Problem 4-3A Applying activity-based costing LO P1, P3, A1, A2, C3 [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Craft Pro Machining produces machine tools for the construction industry. The following details about overhead costs were taken from its company records.
Additional information on the drivers for its production activities follows.
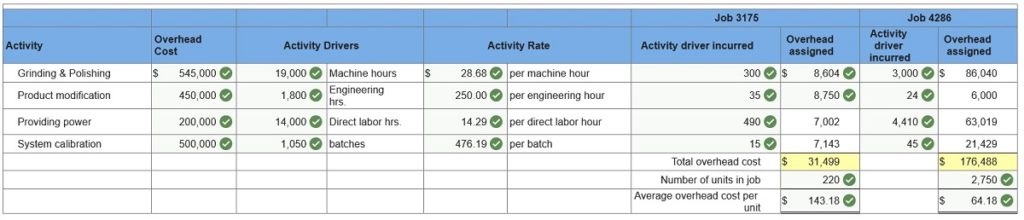
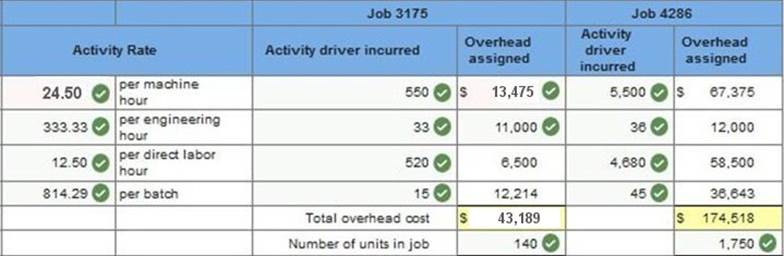
Problem 4-3A Parts 2, 3 & 4 2, 3 & 4. Compute the activity overhead rates using ABC. Combine the grinding and polishing activities into a single cost pool. Determine overhead costs to assign to the following jobs using ABC. What is the overhead cost per unit for Job 3175? What is the overhead cost per unit for Job 4286? (Round your activity rate and average overhead cost per unit to 2 decimal places. Round "overhead assigned" to the nearest whole dollar.) 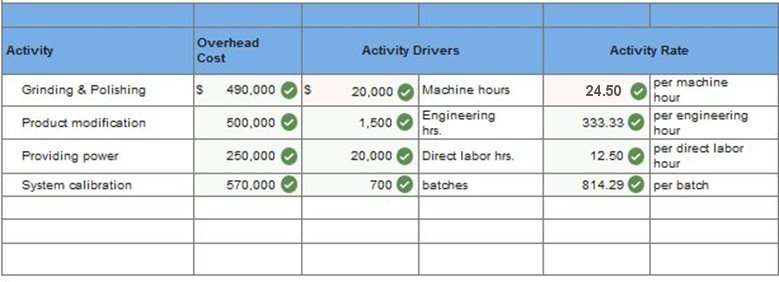
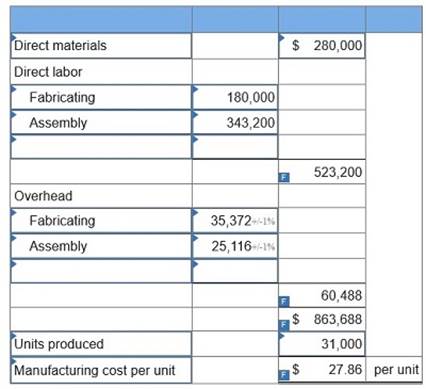
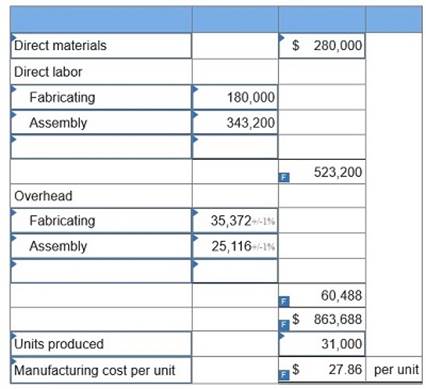
Laval produces lamps and home lighting fixtures. Its most popular product is a brushed aluminum desk lamp. This lamp is made from components shaped in the fabricating department and assembled in the assembly department. Information related to the 31,000 desk lamps produced annually follows.
1. Determine the plantwide overhead rate for Laval using direct labor hours as a base. 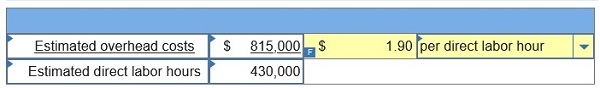
2. Determine the total manufacturing cost per unit for the aluminum desk lamp using the plantwide overhead rate. 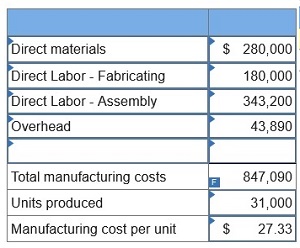
3. Compute departmental overhead rates based on machine hours in the fabricating department and direct labor hours in the assembly department. 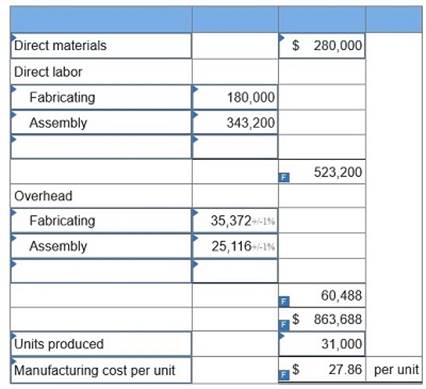
4. Use departmental overhead rates from requirement 3 to determine the total manufacturing cost per unit for the aluminum desk lamps. 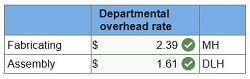
Way Cool produces two different models of air conditioners. The company produces the mechanical systems in its components department. The mechanical systems are combined with the housing assembly in its finishing department. The activities, costs, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the production support process follow. (Loss amounts should be indicated with a minus sign. Round your intermediate calculations and round “Cost per unit and OH rate” answers to 2 decimal places.)
Additional production information concerning its two product lines follows.
Way Cool produces two different models of air conditioners. The company produces the mechanical systems in its components department. The mechanical systems are combined with the housing assembly in its finishing department. The activities, costs, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the production support process follow.
Additional production information concerning its two product lines follows.
Required: 1. Determine departmental overhead rates and compute the overhead cost per unit for each product line. Base your overhead assignment for the components department on machine hours. Use welding hours to assign overhead costs to the finishing department. Assign costs to the support department based on number of purchase orders. 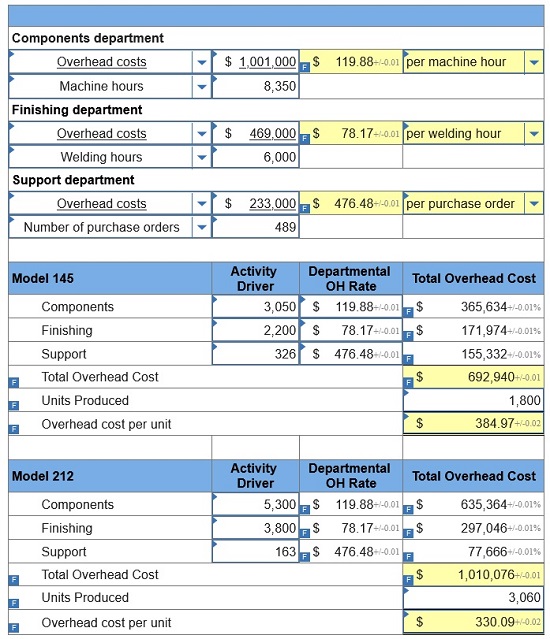
2. Determine the total cost per unit for each product line if the direct labor and direct materials costs per unit are $210 for Model 145 and $190 for Model 212. 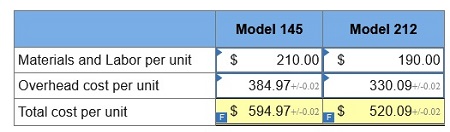
3. If the market price for Model 145 is $1,925 and the market price for Model 212 is $320, determine the profit or loss per unit for each model. 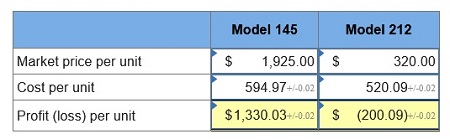
Way Cool produces two different models of air conditioners. The company produces the mechanical systems in its components department. The mechanical systems are combined with the housing assembly in its finishing department. The activities, costs, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the production support process follow.
Additional production information concerning its two product lines follows.
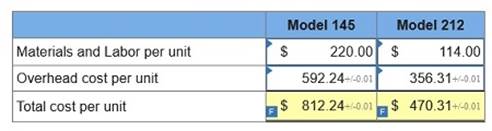
Required: 1. Using ABC, compute the overhead cost per unit for each product line. 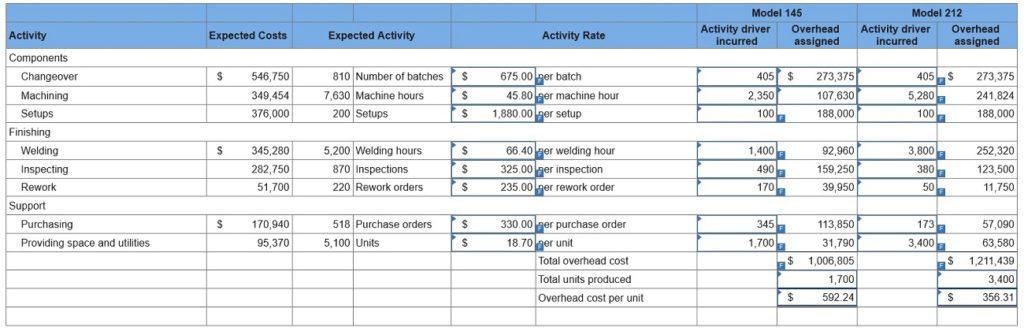
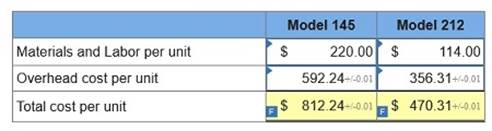
2. Determine the total cost per unit for each product line if the direct labor and direct materials costs per unit are $220 for Model 145 and $114 for Model 212. 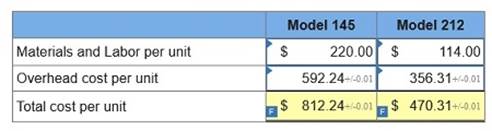
3. If the market price for Model 145 is $812.90 and the market price for Model 212 is $470.67, determine the profit or loss per unit for each model. 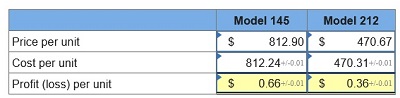
Q5. Consider the following data for two products of Gitano Manufacturing. (Loss amounts should be indicated with a minus sign. Round your intermediate calculations and “OH rate and cost per unit” answers to 2 decimal places.)
Based on your results in part 4, should the profit or loss per unit for each product influence company strategy? Yes Required: 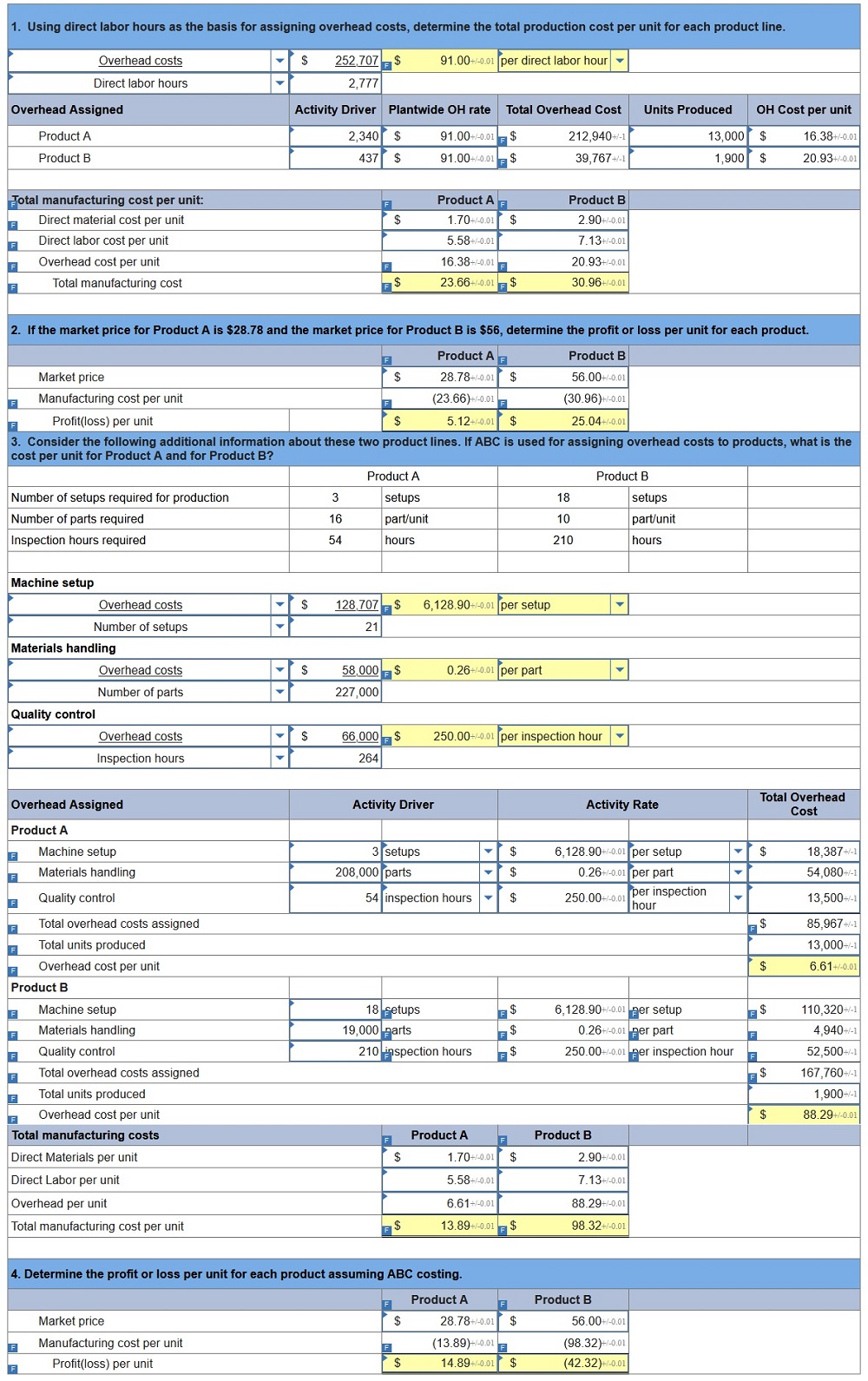
Cardiff and Delp is an architectural firm that provides services for residential construction projects. The following data pertain to a recent reporting period.
Required: 1. & 2. Using ABC, compute the firm’s activity overhead rates. Form activity cost pools where appropriate. Assign costs to a 7,600-square-foot job that requires 480 contact hours, 348 design hours, and 135 days to complete. (Round activity rate answers to 2 decimal places.) 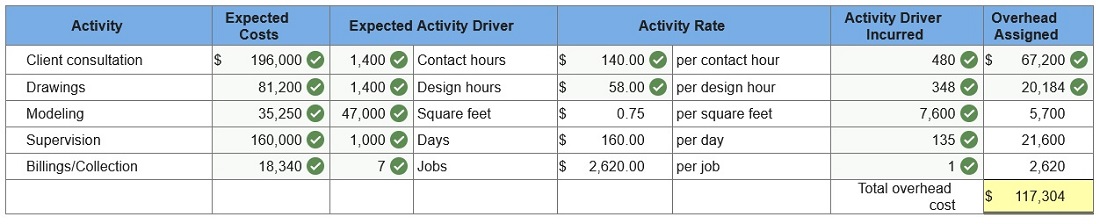
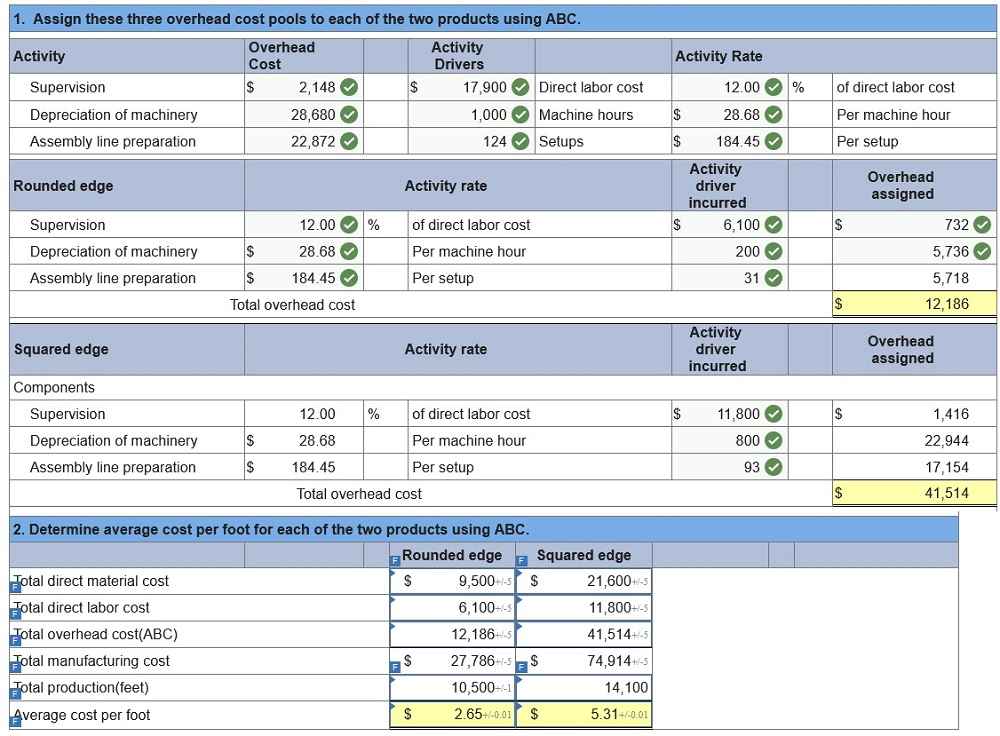
Glassworks Inc. produces two types of glass shelving, rounded edge and squared edge, on the same production line. For the current period, the company reports the following data.
Glassworks’s controller wishes to apply activity-based costing (ABC) to allocate the $53,700 of overhead costs incurred by the two product lines to see whether cost per foot would change markedly from that reported above. She has collected the following information.
She has also collected the following information about the cost drivers for each category (cost pool) and the amount of each driver used by the two product lines. (Round activity rate and cost per unit answers to 2 decimal places.)
Smythe Co. makes furniture. The following data are taken from its production plans for the year.
Required:
Craft Pro Machining produces machine tools for the construction industry. The following details about overhead costs were taken from its company records.
Production Activity Indirect Labor Indirect Materials Other Overhead Grinding $ 400,000 Polishing $ 145,000 Product modification 450,000 Providing power $200,000 System calibration 500,000
Additional information on the drivers for its production activities follows.
Required:
Craft Pro Machining produces machine tools for the construction industry. The following details about overhead costs were taken from its company records.
Additional information on the drivers for its production activities follows.
Required: 2, 3 & 4. Compute the activity overhead rates using ABC. Combine the grinding and polishing activities into a single cost pool. Determine overhead costs to assign to the above jobs using ABC. What is the overhead cost per unit for Job 3175? What is the overhead cost per unit for Job 4286? (Round your activity rate and average overhead cost per unit to 2 decimal places. Round “overhead assigned” to the nearest whole dollar.)
Craft Pro Machining produces machine tools for the construction industry. The following details about overhead costs were taken from its company records.
Additional information on the drivers for its production activities follows.
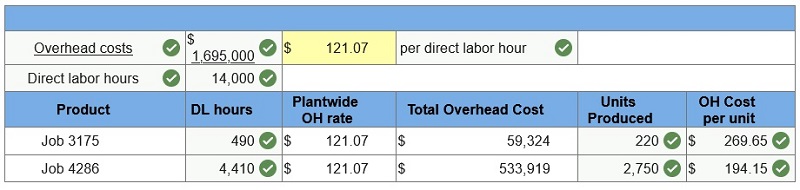
Required: 5. If the company uses a plantwide overhead rate based on direct labor hours, what is the overhead cost for each unit of Job 3175? Of Job 4286? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round “OH Cost per unit” answers to 2 decimal places.)
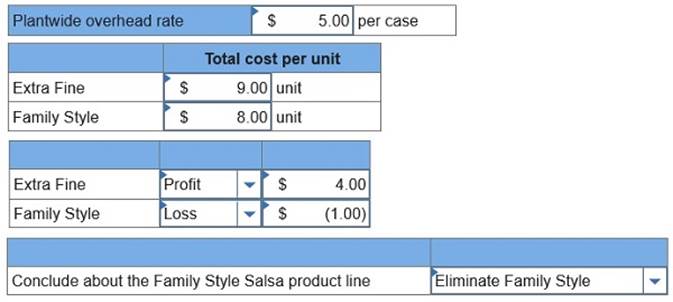
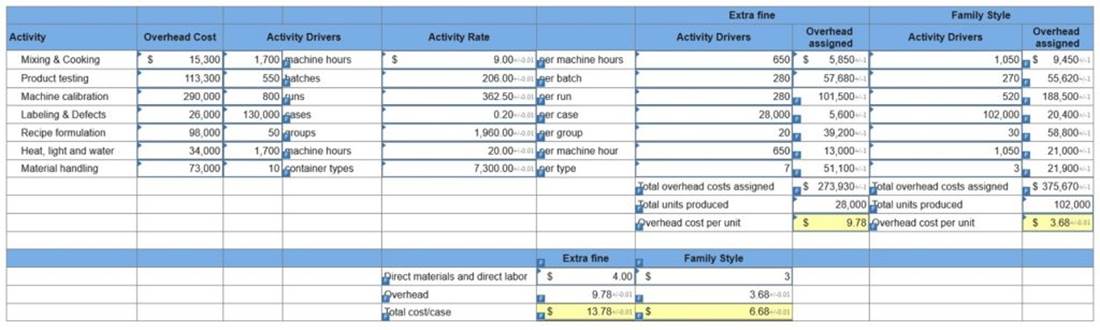
Sara’s Salsa Company produces its condiments in two types: Extra Fine for restaurant customers and Family Style for home use. Salsa is prepared in department 1 and packaged in department 2. The activities, overhead costs, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the company’s production support activities follow.
Additional production information about its two product lines follows.
Required: Extra Fine Salsa and each case of Family Style Salsa.
$4 per case of Extra Fine and $3 per case of Family Style.
determine the gross profit per case for each product.
Sara’s Salsa Company produces its condiments in two types: Extra Fine for restaurant customers and Family Style for home use. Salsa is prepared in department 1 and packaged in department 2. The activities, overhead costs, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the company’s production support activities follow.
Additional production information about its two product lines follows.
4. Using ABC, compute the total cost per case for each product type if the direct labor and direct materials cost is $4 per case of Extra Fine and $3 per case of Family Style. (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places. Round “Activity Rate” and “Overhead cost per unit” answers to 2 decimal places.)
Sara’s Salsa Company produces its condiments in two types: Extra Fine for restaurant customers and Family Style for home use. Salsa is prepared in department 1 and packaged in department 2. The activities, overhead costs, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the company’s production support activities follow.
Additional production information about its two product lines follows.
5. If the market price is $13 per case of Extra Fine and $7 per case of Family Style, determine the gross profit per case for each product. (Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.)
Laval produces lamps and home lighting fixtures. Its most popular product is a brushed aluminum desk lamp. This lamp is made from components shaped in the fabricating department and assembled in the assembly department. Information related to the 31,000 desk lamps produced annually follows.
Expected overhead cost and related data for the two production departments follow.
Required 1. Determine the plantwide overhead rate for Laval using direct labor hours as a base.
2. Determine the total manufacturing cost per unit for the aluminum desk lamp using the plantwide overhead rate.
3. Compute departmental overhead rates based on machine hours in the fabricating department and direct labor hours in the assembly department.
4. Use departmental overhead rates from requirement 3 to determine the total manufacturing cost per unit for the aluminum desk lamps.
Way Cool produces two different models of air conditioners. The company produces the mechanical systems in its components department. The mechanical systems are combined with the housing assembly in its finishing department. The activities, costs, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the production support process follow. (Loss amounts should be indicated with a minus sign. Round your intermediate calculations and round “Cost per unit and OH rate” answers to 2 decimal places.)
Additional production information concerning its two product lines follows.
Required:
Way Cool produces two different models of air conditioners. The company produces the mechanical systems in its components department. The mechanical systems are combined with the housing assembly in its finishing department. The activities, costs, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the production support process follow.
Additional production information concerning its two product lines follows.
Required:
Base your overhead assignment for the components department on machine hours. Use welding hours to assign overhead costs to the finishing department. Assign costs to the support department based on number of purchase orders.
2. Determine the total cost per unit for each product line if the direct labor and direct materials costs per unit are $210 for Model 145 and $190 for Model 212.
3. If the market price for Model 145 is $1,925 and the market price for Model 212 is $320, determine the profit or loss per unit for each model.
Way Cool produces two different models of air conditioners. The company produces the mechanical systems in its components department. The mechanical systems are combined with the housing assembly in its finishing department. The activities, costs, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the production support process follow.
Additional production information concerning its two product lines follows.
Required:
2. Determine the total cost per unit for each product line if the direct labor and direct materials costs per unit are $220 for Model 145 and $114 for Model 212.
3. If the market price for Model 145 is $812.90 and the market price for Model 212 is $470.67, determine the profit or loss per unit for each model.
Q5. Consider the following data for two products of Gitano Manufacturing. (Loss amounts should be indicated with a minus sign. Round your intermediate calculations and “OH rate and cost per unit” answers to 2 decimal places.)
Based on your results in part 4, should the profit or loss per unit for each product influence company strategy? Yes Required:
Cardiff and Delp is an architectural firm that provides services for residential construction projects. The following data pertain to a recent reporting period.
Required: 1. & 2. Using ABC, compute the firm’s activity overhead rates. Form activity cost pools where appropriate. Assign costs to a 7,600-square-foot job that requires 480 contact hours, 348 design hours, and 135 days to complete. (Round activity rate answers to 2 decimal places.)
Glassworks Inc. produces two types of glass shelving, rounded edge and squared edge, on the same production line. For the current period, the company reports the following data.
Glassworks’s controller wishes to apply activity-based costing (ABC) to allocate the $53,700 of overhead costs incurred by the two product lines to see whether cost per foot would change markedly from that reported above. She has collected the following information.
She has also collected the following information about the cost drivers for each category (cost pool) and the amount of each driver used by the two product lines. (Round activity rate and cost per unit answers to 2 decimal places.)
Required:
Smythe Co. makes furniture. The following data are taken from its production plans for the year.
Required:
Craft Pro Machining produces machine tools for the construction industry. The following details about overhead costs were taken from its company records.
Production Activity Indirect Labor Indirect Materials Other Overhead Grinding $ 400,000 Polishing $ 145,000 Product modification 450,000 Providing power $200,000 System calibration 500,000
Additional information on the drivers for its production activities follows.
Required:
Craft Pro Machining produces machine tools for the construction industry. The following details about overhead costs were taken from its company records.
Additional information on the drivers for its production activities follows.
Required: 2, 3 & 4. Compute the activity overhead rates using ABC. Combine the grinding and polishing activities into a single cost pool. Determine overhead costs to assign to the above jobs using ABC. What is the overhead cost per unit for Job 3175? What is the overhead cost per unit for Job 4286? (Round your activity rate and average overhead cost per unit to 2 decimal places. Round “overhead assigned” to the nearest whole dollar.)
Craft Pro Machining produces machine tools for the construction industry. The following details about overhead costs were taken from its company records.
Additional information on the drivers for its production activities follows.
Required: 5. If the company uses a plantwide overhead rate based on direct labor hours, what is the overhead cost for each unit of Job 3175? Of Job 4286? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round “OH Cost per unit” answers to 2 decimal places.)
Sara’s Salsa Company produces its condiments in two types: Extra Fine for restaurant customers and Family Style for home use. Salsa is prepared in department 1 and packaged in department 2. The activities, overhead costs, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the company’s production support activities follow.
Additional production information about its two product lines follows.
Required: Extra Fine Salsa and each case of Family Style Salsa.
$4 per case of Extra Fine and $3 per case of Family Style.
determine the gross profit per case for each product.
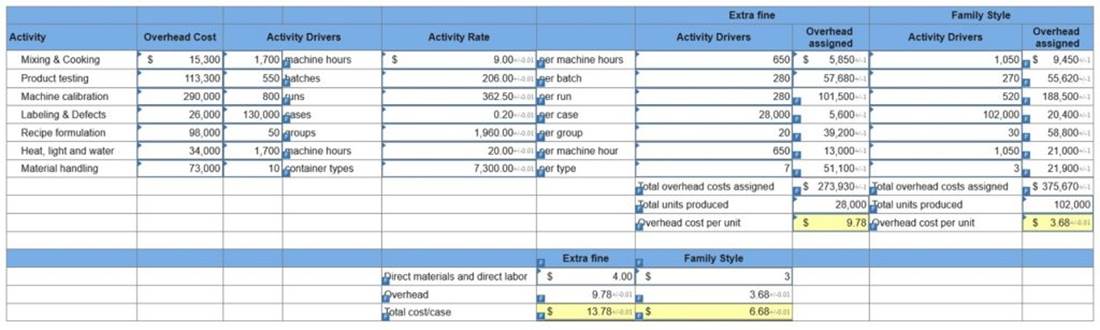
Sara’s Salsa Company produces its condiments in two types: Extra Fine for restaurant customers and Family Style for home use. Salsa is prepared in department 1 and packaged in department 2. The activities, overhead costs, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the company’s production support activities follow.
Additional production information about its two product lines follows.
4. Using ABC, compute the total cost per case for each product type if the direct labor and direct materials cost is $4 per case of Extra Fine and $3 per case of Family Style. (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places. Round “Activity Rate” and “Overhead cost per unit” answers to 2 decimal places.)
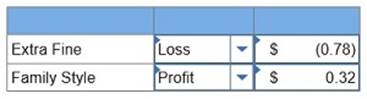
Sara’s Salsa Company produces its condiments in two types: Extra Fine for restaurant customers and Family Style for home use. Salsa is prepared in department 1 and packaged in department 2. The activities, overhead costs, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the company’s production support activities follow.
Additional production information about its two product lines follows.
5. If the market price is $13 per case of Extra Fine and $7 per case of Family Style, determine the gross profit per case for each product. (Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.)
Laval produces lamps and home lighting fixtures. Its most popular product is a brushed aluminum desk lamp. This lamp is made from components shaped in the fabricating department and assembled in the assembly department. Information related to the 31,000 desk lamps produced annually follows.
Expected overhead cost and related data for the two production departments follow.
Required 1. Determine the plantwide overhead rate for Laval using direct labor hours as a base.
2. Determine the total manufacturing cost per unit for the aluminum desk lamp using the plantwide overhead rate.
3. Compute departmental overhead rates based on machine hours in the fabricating department and direct labor hours in the assembly department.
4. Use departmental overhead rates from requirement 3 to determine the total manufacturing cost per unit for the aluminum desk lamps.
Way Cool produces two different models of air conditioners. The company produces the mechanical systems in its components department. The mechanical systems are combined with the housing assembly in its finishing department. The activities, costs, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the production support process follow. (Loss amounts should be indicated with a minus sign. Round your intermediate calculations and round “Cost per unit and OH rate” answers to 2 decimal places.)
Additional production information concerning its two product lines follows.
Required:
Way Cool produces two different models of air conditioners. The company produces the mechanical systems in its components department. The mechanical systems are combined with the housing assembly in its finishing department. The activities, costs, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the production support process follow.
Additional production information concerning its two product lines follows.
Required:
Base your overhead assignment for the components department on machine hours. Use welding hours to assign overhead costs to the finishing department. Assign costs to the support department based on number of purchase orders.
2. Determine the total cost per unit for each product line if the direct labor and direct materials costs per unit are $210 for Model 145 and $190 for Model 212.
3. If the market price for Model 145 is $1,925 and the market price for Model 212 is $320, determine the profit or loss per unit for each model.
Way Cool produces two different models of air conditioners. The company produces the mechanical systems in its components department. The mechanical systems are combined with the housing assembly in its finishing department. The activities, costs, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the production support process follow.
Additional production information concerning its two product lines follows.
Required:
2. Determine the total cost per unit for each product line if the direct labor and direct materials costs per unit are $220 for Model 145 and $114 for Model 212.
3. If the market price for Model 145 is $812.90 and the market price for Model 212 is $470.67, determine the profit or loss per unit for each model.
Q5. Consider the following data for two products of Gitano Manufacturing. (Loss amounts should be indicated with a minus sign. Round your intermediate calculations and “OH rate and cost per unit” answers to 2 decimal places.)
Based on your results in part 4, should the profit or loss per unit for each product influence company strategy? Yes Required:
Cardiff and Delp is an architectural firm that provides services for residential construction projects. The following data pertain to a recent reporting period.
Required: 1. & 2. Using ABC, compute the firm’s activity overhead rates. Form activity cost pools where appropriate. Assign costs to a 7,600-square-foot job that requires 480 contact hours, 348 design hours, and 135 days to complete. (Round activity rate answers to 2 decimal places.)
Glassworks Inc. produces two types of glass shelving, rounded edge and squared edge, on the same production line. For the current period, the company reports the following data.
Glassworks’s controller wishes to apply activity-based costing (ABC) to allocate the $53,700 of overhead costs incurred by the two product lines to see whether cost per foot would change markedly from that reported above. She has collected the following information.
She has also collected the following information about the cost drivers for each category (cost pool) and the amount of each driver used by the two product lines. (Round activity rate and cost per unit answers to 2 decimal places.)
Required:
Smythe Co. makes furniture. The following data are taken from its production plans for the year.
Required:
Craft Pro Machining produces machine tools for the construction industry. The following details about overhead costs were taken from its company records.
Production Activity Indirect Labor Indirect Materials Other Overhead Grinding $ 400,000 Polishing $ 145,000 Product modification 450,000 Providing power $200,000 System calibration 500,000
Additional information on the drivers for its production activities follows.
Required:
Craft Pro Machining produces machine tools for the construction industry. The following details about overhead costs were taken from its company records.
Additional information on the drivers for its production activities follows.
Required: 2, 3 & 4. Compute the activity overhead rates using ABC. Combine the grinding and polishing activities into a single cost pool. Determine overhead costs to assign to the above jobs using ABC. What is the overhead cost per unit for Job 3175? What is the overhead cost per unit for Job 4286? (Round your activity rate and average overhead cost per unit to 2 decimal places. Round “overhead assigned” to the nearest whole dollar.)
Craft Pro Machining produces machine tools for the construction industry. The following details about overhead costs were taken from its company records.
Additional information on the drivers for its production activities follows.
Required: 5. If the company uses a plantwide overhead rate based on direct labor hours, what is the overhead cost for each unit of Job 3175? Of Job 4286? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round “OH Cost per unit” answers to 2 decimal places.)
Sara’s Salsa Company produces its condiments in two types: Extra Fine for restaurant customers and Family Style for home use. Salsa is prepared in department 1 and packaged in department 2. The activities, overhead costs, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the company’s production support activities follow.
Additional production
information about its two product lines follows.
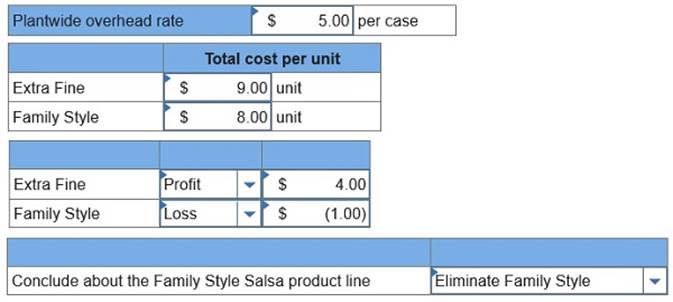
Required: 1. Using a plantwide overhead rate based on cases, compute the overhead cost that is assigned to each case of Extra Fine Salsa and each case of Family Style Salsa. 2. Using the plantwide overhead rate, determine the total cost per case for the two products if the direct materials and direct labor cost is $4 per case of Extra Fine and $3 per case of Family Style. 3.a. If the market price of Extra Fine Salsa is $13 per case and the market price of Family Style Salsa is $7 per case, determine the gross profit per case for each product. 3.b. What might management conclude about the Family Style Salsa product line? 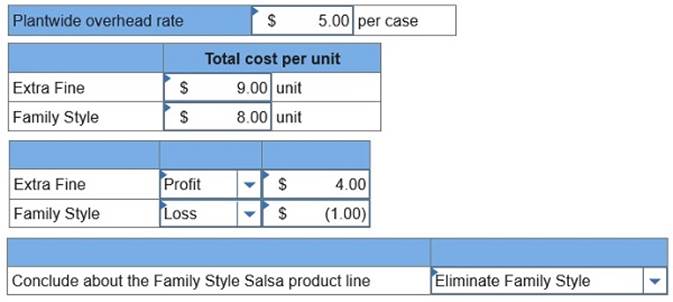
Sara’s Salsa Company produces its condiments in two types: Extra Fine for restaurant customers and Family Style for home use. Salsa is prepared in department 1 and packaged in department 2. The activities, overhead costs, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the company’s production support activities follow.
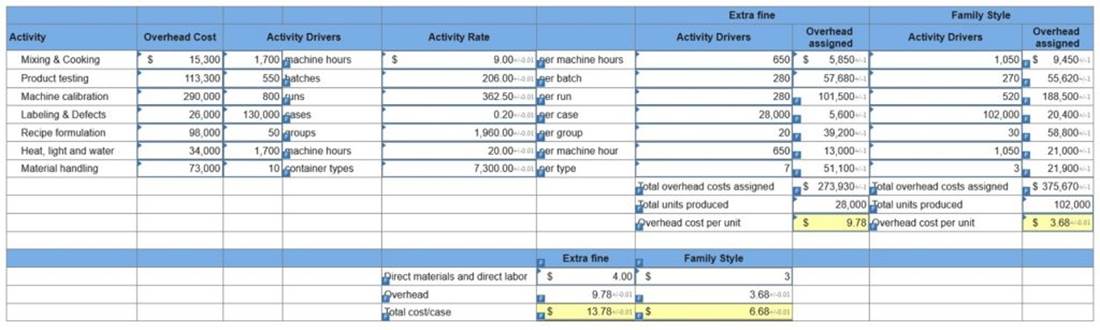
4. Using ABC, compute the total cost per case for each product type if the direct labor and direct materials cost is $4 per case of Extra Fine and $3 per case of Family Style. (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places. Round “Activity Rate” and “Overhead cost per unit” answers to 2 decimal places.)
Sara’s Salsa Company produces its condiments in two types: Extra Fine for restaurant customers and Family Style for home use. Salsa is prepared in department 1 and packaged in department 2. The activities, overhead costs, and drivers associated with these two manufacturing processes and the company’s production support activities follow.
Additional production information about its two product lines follows.
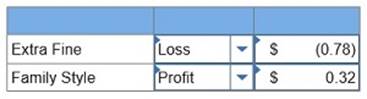
5. If the market price is $13 per case of Extra Fine and $7 per case of Family Style, determine the gross profit per case for each product. (Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.) 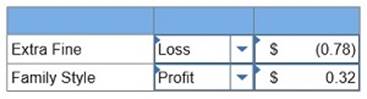
Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2 14.1 14.2 15.1 15.2
Learnsmart 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Final Exam 1 2 Homework Help? |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |