|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Principals Of Managerial Accounting: Homework Chapter 3 Part 2 Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2 14.1 14.2 15.1 15.2
Learnsmart 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Final Exam 1 2 Homework Help?
A production department
in a process manufacturing system completed its work on 80,000 units of
product and transferred
them to the next department during a recent period. Of these units, 32,000 were in process at the beginning of the period. The other 48,000 units were started and completed during the period. At period-end, 17,500 units were in process. Prepare the production department’s equivalent units of production for direct materials under each of three separate assumptions using the weighted-average method for process costing. 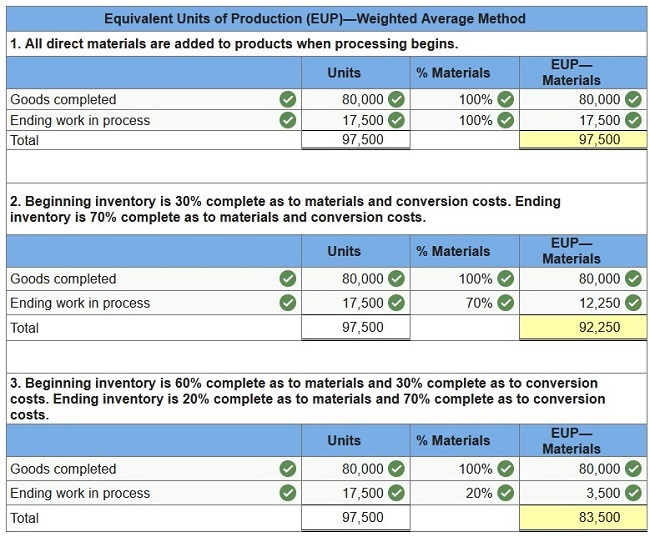
A production department in a process manufacturing system completed its work on 80,000 units of product and transferred them to the next department during a recent period. Of these units, 32,000 were in process at the beginning of the period. The other 48,000 units were started and completed during the period. At period-end, 17,500 units were in process. Prepare the department’s equivalent units of production with respect to direct materials under each of the three separate assumptions using the FIFO method for process costing. 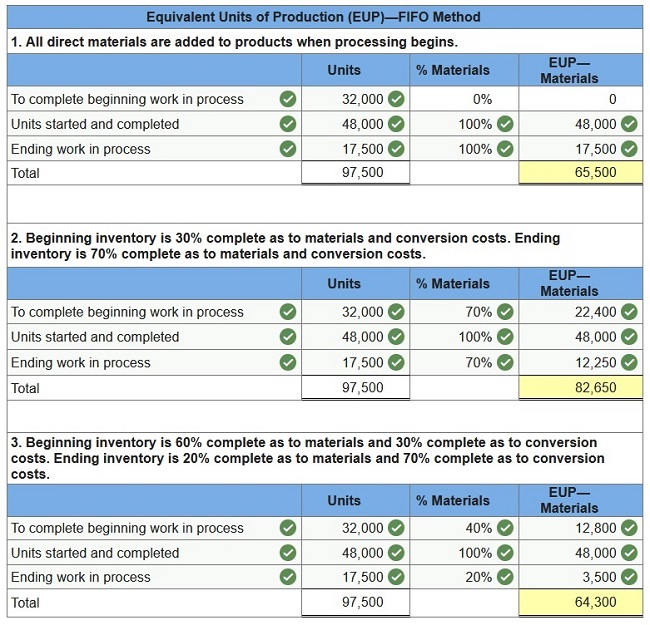
Fields Company has two manufacturing departments, forming and painting. The company uses the weighted-average method of process costing. At the beginning of the month, the forming department has 27,000 units in inventory, 70% complete as to materials and 30% complete as to conversion costs. The beginning inventory cost of $56,100 consisted of $40,000 of direct materials costs and $16,100 of conversion costs. During the month, the forming department started 320,000 units. At the end of the month, the forming department had 35,000 units in ending inventory, 80% complete as to materials and 40% complete as to conversion. Units completed in the forming department are transferred to the painting department. Cost information for the forming department follows.
1. Calculate the equivalent units of production for the forming department. 2. Calculate the costs per equivalent unit of production for the forming department. 3. Using the weighted-average method, assign costs to the forming department’s output specifically, its units transferred to painting and its ending work in process inventory. 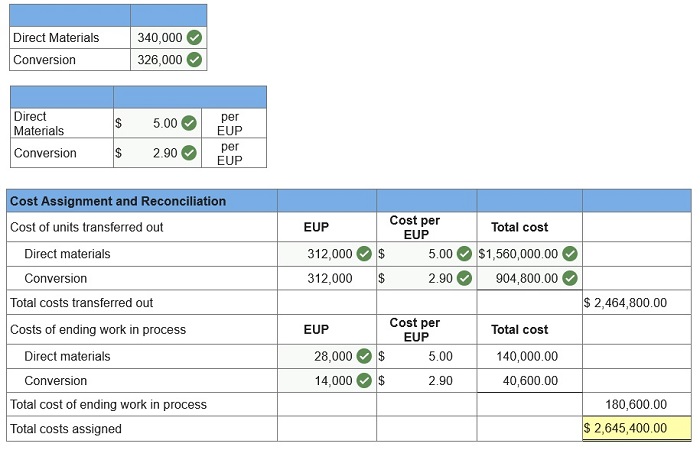
Fields Company has two manufacturing departments, forming and painting. The company uses the weighted-average method of process costing. At the beginning of the month, the forming department has 27,000 units in inventory, 70% complete as to materials and 30% complete as to conversion costs. The beginning inventory cost of $56,100 consisted of $40,000 of direct materials costs and $16,100 of conversion costs. During the month, the forming department started 320,000 units. At the end of the month, the forming department had 35,000 units in ending inventory, 80% complete as to materials and 40% complete as to conversion. Units completed in the forming department are transferred to the painting department. Cost information for the forming department follows.
Assume that Fields uses the FIFO method of process costing. 1. Calculate the equivalent units of production for the forming department. 2. Calculate the costs per equivalent unit of production for the forming department. 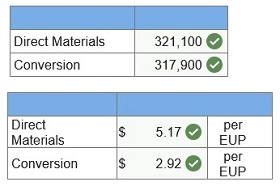
During April, the first production department of a process manufacturing system completed its work on 360,000 units of a product and transferred them to the next department. Of these transferred units, 72,000 were in process in the production department at the beginning of April and 288,000 were started and completed in April. April’s beginning inventory units were 70% complete with respect to materials and 30% complete with respect to conversion. At the end of April, 94,000 additional units were in process in the production department and were 80% complete with respect to materials and 30% complete with respect to conversion. Compute the number of equivalent units with respect to both materials used and conversion used in the first production department for April using the weighted-average method. 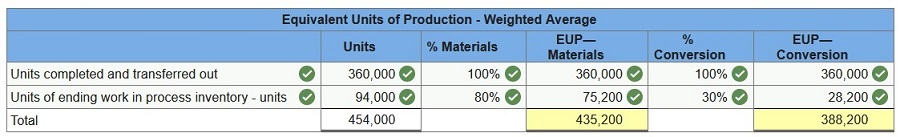
During April, the first production department of a process manufacturing system completed its work on 360,000 units of a product and transferred them to the next department. Of these transferred units, 72,000 were in process in the production department at the beginning of April and 288,000 were started and completed in April. April’s beginning inventory units were 70% complete with respect to materials and 30% complete with respect to conversion. At the end of April, 94,000 additional units were in process in the production department and were 80% complete with respect to materials and 30% complete with respect to conversion. The production department had $1,115,920 of direct materials and $777,192 of conversion costs charged to it during April. Also, its April beginning inventory of $205,948 consists of $167,920 of direct materials cost and $38,028 of conversion costs. 1. Compute the direct materials cost per equivalent unit for April. (Round “Cost per EUP” to 2 decimal places.) 2. Compute the conversion cost per equivalent unit for April. (Round “Cost per EUP” to 2 decimal places.) 3. Using the weighted-average method, assign April’s costs to the department’s output—specifically, its units transferred to the next department and its ending work in process inventory. (Round “Cost per EUP” to 2 decimal places.) 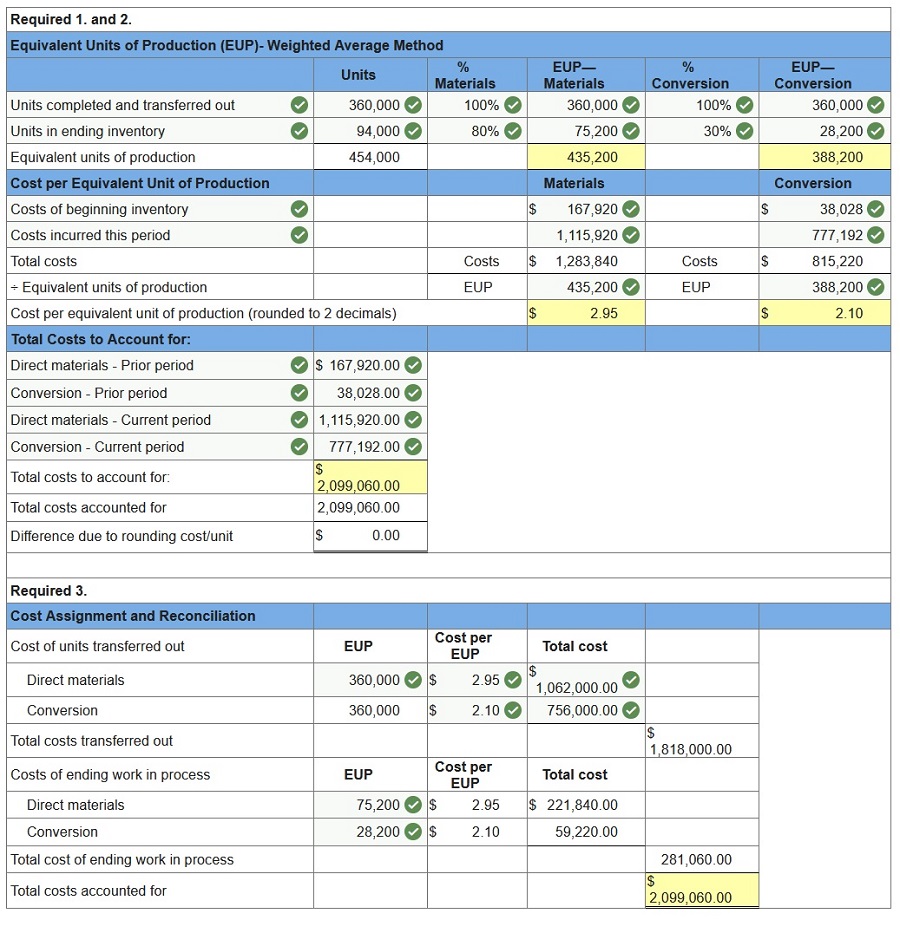
During April, the first production department of a process manufacturing system completed its work on 360,000 units of a product and transferred them to the next department. Of these transferred units, 72,000 were in process in the production department at the beginning of April and 288,000 were started and completed in April. April’s beginning inventory units were 70% complete with respect to materials and 30% complete with respect to conversion. At the end of April, 94,000 additional units were in process in the production department and were 80% complete with respect to materials and 30% complete with respect to conversion. Prepare the number of equivalent units with respect to both materials and conversion costs in the production department for April using the FIFO method. 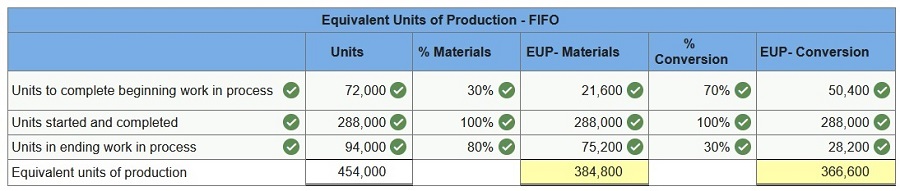
During April, the first production department of a process manufacturing system completed its work on 360,000 units of a product and transferred them to the next department. Of these transferred units, 72,000 were in process in the production department at the beginning of April and 288,000 were started and completed in April. April’s beginning inventory units were 70% complete with respect to materials and 30% complete with respect to conversion. At the end of April, 94,000 additional units were in process in the production department and were 80% complete with respect to materials and 30% complete with respect to conversion. The production department had $1,115,920 of direct materials and $777,192 of conversion costs charged to it during April. Also, its beginning inventory of $205,948 consists of $167,920 of direct materials cost and $38,028 of conversion costs. 1. Compute the direct materials cost per equivalent unit for April. (Round “Cost per EUP” to 2 decimal places.) 2. Compute the conversion cost per equivalent unit for April. (Round “Cost per EUP” to 2 decimal places.) 3. Using the FIFO method, assign April’s costs to the department’s output—specifically, its units transferred to the next department and its ending work in process inventory. (Round “Cost per EUP” to 2 decimal places.) 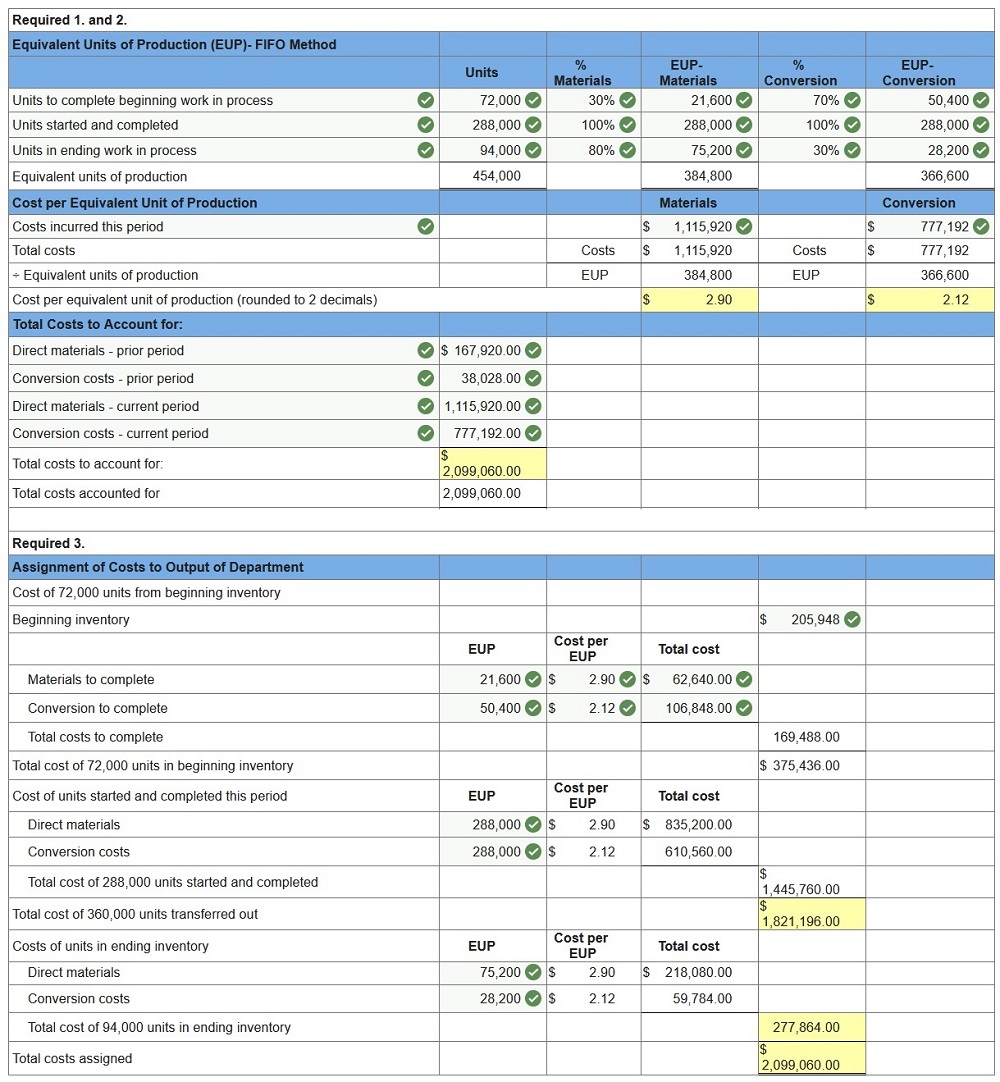
The following partially completed process cost summary describes the July production activities of the Molding department at Ashad Company. Its production output is sent to the next department. All direct materials are added to products when processing begins. Beginning work in process inventory is 20% complete with respect to conversion.
(Round “Cost per EUP” to 2 decimal places.) 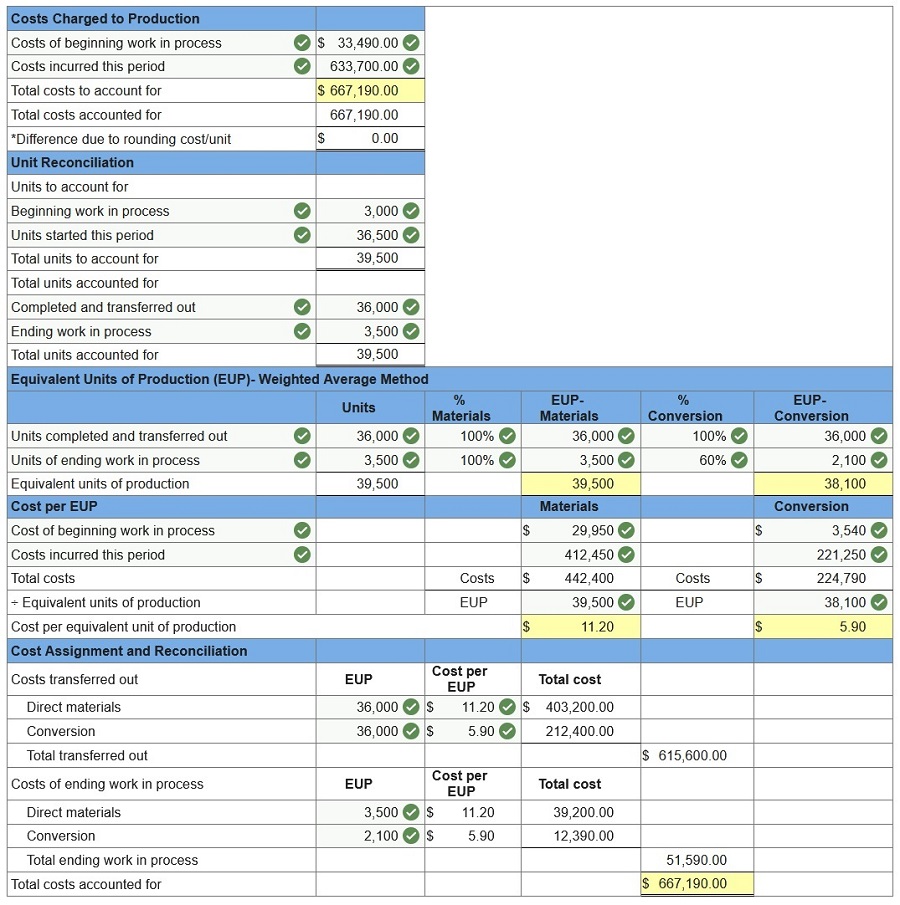
The following partially completed process cost summary describes the July production activities of the Molding department at Ashad Company. Its production output is sent to the next department. All direct materials are added to products when processing begins. Beginning work in process inventory is 20% complete with respect to conversion.
Prepare its process cost summary using the FIFO method. (Round “Cost per EUP” to 2 decimal places.) 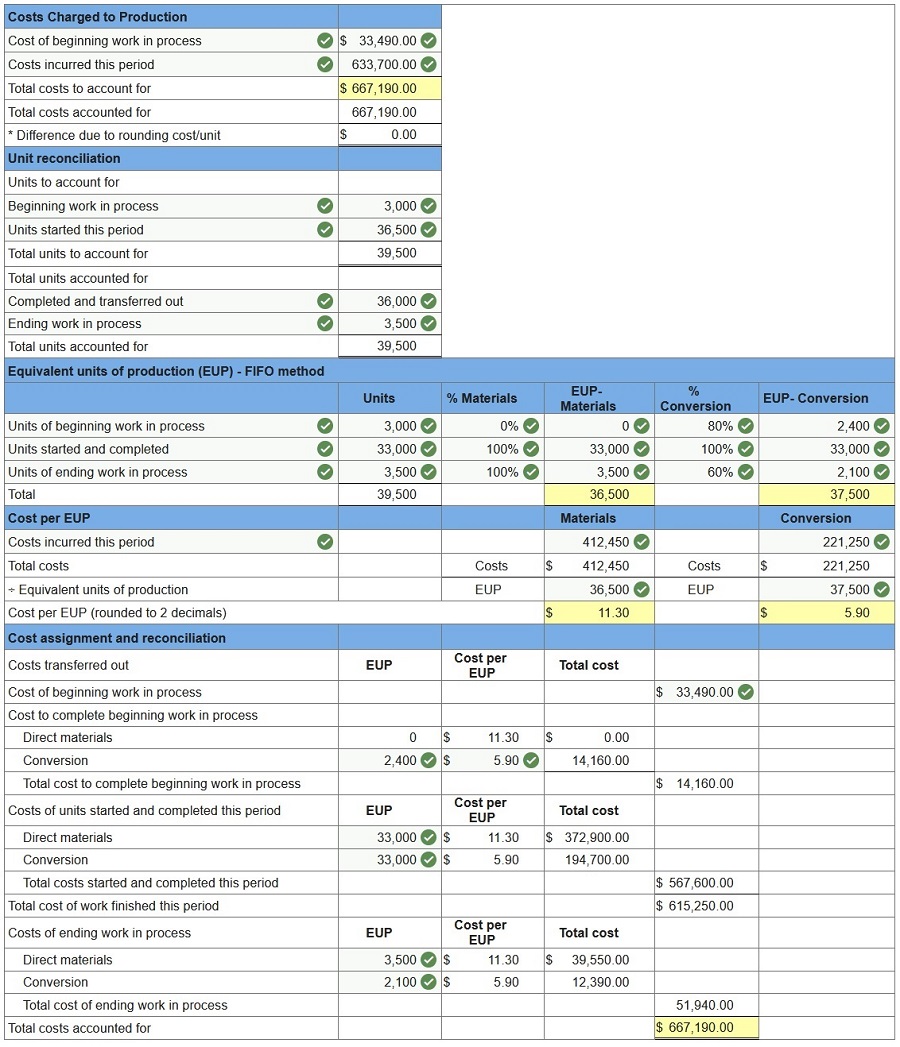
Pro-Weave manufactures stadium blankets by passing the products through a weaving department and a sewing department. The following information is available regarding its June inventories:
The following additional information describes the company’s manufacturing activities for June:
1. Compute the (a) cost of products transferred from weaving to sewing (b) cost of products transferred from sewing to finished goods (c) cost of goods sold. 2. Prepare journal entries dated June 30 to record (a) goods transferred from weaving to sewing (b) goods transferred from sewing to finished goods (c) sale of finished goods (d) cost of goods sold. 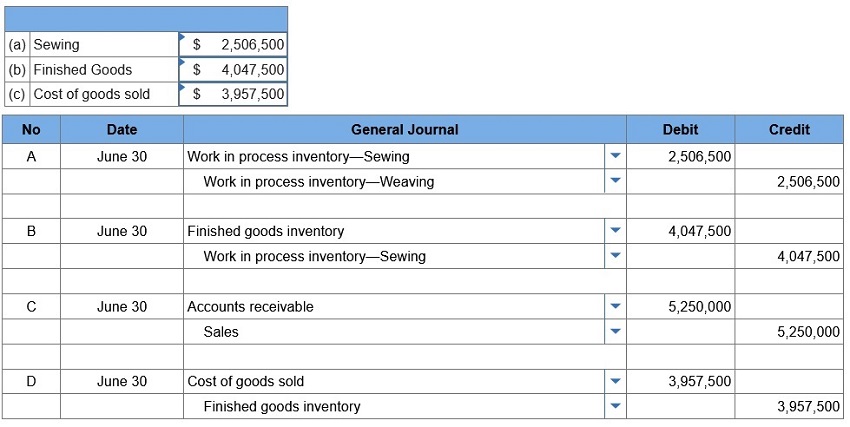
Pro-Weave manufactures stadium blankets by passing the products through a weaving department and a sewing department. The following information is available regarding its June inventories:
The following additional information describes the company’s manufacturing activities for June:
1. Prepare journal entries dated June 30 to record: (a) raw materials purchases (b) direct materials usage (c) indirect materials usage (d) direct labor usage (e) indirect labor usage (f) other overhead costs (g) overhead applied (h) payment of total payroll costs. 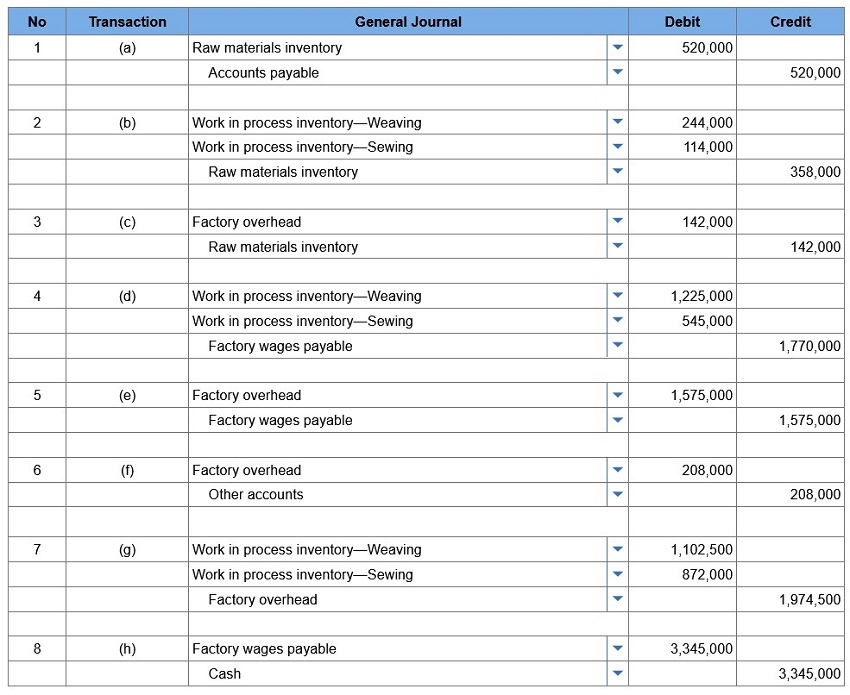
Victory Company uses weighted-average process costing to account for its production costs. Conversion cost is added evenly throughout the process. Direct materials are added at the beginning of the first process. During November, the first process transferred 785,000 units of product to the second process. Additional information for the first process follows. At the end of November, work in process inventory consists of 196,000 units that are 80% complete with respect to conversion. Beginning work in process inventory had $446,355 of direct materials and $188,360 of conversion cost. The direct material cost added in November is $2,987,145, and the conversion cost added is $3,578,840. Beginning work in process consisted of 72,000 units that were 100% complete with respect to direct materials and 80% complete with respect to conversion. Of the units completed, 72,000 were from beginning work in process and 713,000 units were started and completed during the period. Required: For the first process: 1. Determine the equivalent units of production with respect to direct materials and conversion. 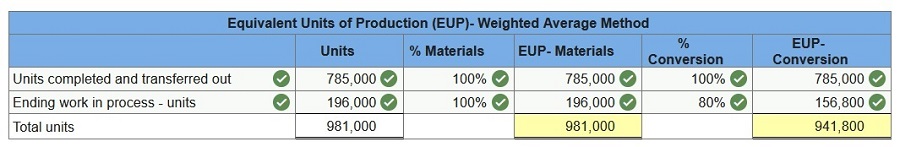
Victory Company uses weighted-average process costing to account for its production costs. Conversion cost is added evenly throughout the process. Direct materials are added at the beginning of the first process. During November, the first process transferred 785,000 units of product to the second process. Additional information for the first process follows. At the end of November, work in process inventory consists of 196,000 units that are 80% complete with respect to conversion. Beginning work in process inventory had $446,355 of direct materials and $188,360 of conversion cost. The direct material cost added in November is $2,987,145, and the conversion cost added is $3,578,840. Beginning work in process consisted of 72,000 units that were 100% complete with respect to direct materials and 80% complete with respect to conversion. Of the units completed, 72,000 were from beginning work in process and 713,000 units were started and completed during the period. 2. Compute both the direct material cost and the conversion cost per equivalent unit. 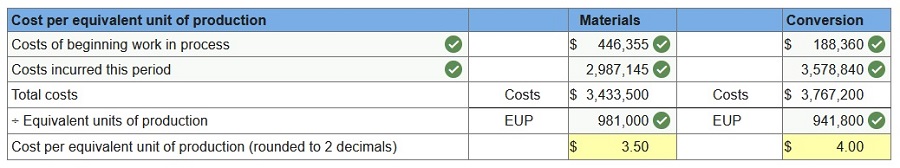
Victory Company uses weighted-average process costing to account for its production costs. Conversion cost is added evenly throughout the process. Direct materials are added at the beginning of the first process. During November, the first process transferred 785,000 units of product to the second process. Additional information for the first process follows. At the end of November, work in process inventory consists of 196,000 units that are 80% complete with respect to conversion. Beginning work in process inventory had $446,355 of direct materials and $188,360 of conversion cost. The direct material cost added in November is $2,987,145, and the conversion cost added is $3,578,840. Beginning work in process consisted of 72,000 units that were 100% complete with respect to direct materials and 80% complete with respect to conversion. Of the units completed, 72,000 were from beginning work in process and 713,000 units were started and completed during the period. 3. Compute the direct material cost and the conversion cost assigned to units completed and transferred out and ending work in process inventory. (Round “Cost per EUP” to 2 decimal places.) 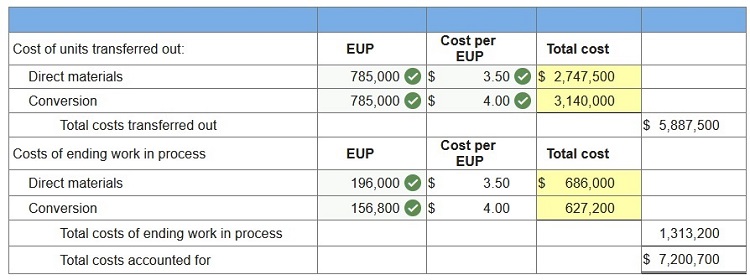
QualCo manufactures a single product in two departments: Cutting and Assembly. During May, the Cutting department completed a number of units of a product and transferred them to Assembly. Of these transferred units, 38,300 were in process in the Cutting department at the beginning of May and 158,500 were started and completed in May. May’s Cutting department beginning inventory units were 60% complete with respect to materials and 40% complete with respect to conversion. At the end of May, 52,100 additional units were in process in the Cutting department and were 60% complete with respect to materials and 20% complete with respect to conversion. The Cutting department had $533,208 of direct materials and $431,775 of conversion cost charged to it during May. Its beginning inventory included $74,875 of direct materials cost and $29,293 of conversion cost. 1. Compute the number of units transferred to Assembly. 
QualCo manufactures a single product in two departments: Cutting and Assembly. During May, the Cutting department completed a number of units of a product and transferred them to Assembly. Of these transferred units, 38,300 were in process in the Cutting department at the beginning of May and 158,500 were started and completed in May. May’s Cutting department beginning inventory units were 60% complete with respect to materials and 40% complete with respect to conversion. At the end of May, 52,100 additional units were in process in the Cutting department and were 60% complete with respect to materials and 20% complete with respect to conversion. The Cutting department had $533,208 of direct materials and $431,775 of conversion cost charged to it during May. Its beginning inventory included $74,875 of direct materials cost and $29,293 of conversion cost. 2-4. Using the FIFO method, assign May’s costs to the units transferred out and assign costs to its ending work in process inventory. (Round “Cost per EUP” to 2 decimal places.) 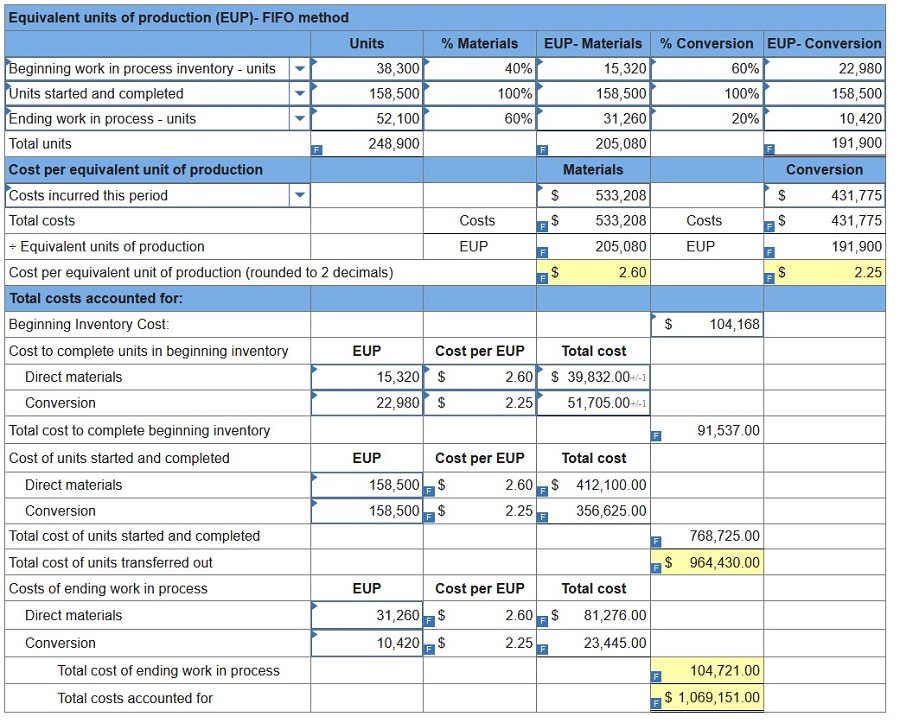
The company based its predetermined overhead rate for the current year on the following data: Total machine-hours. $ 20,000 Total fixed manufacturing overhead cost 176,000 Variable manufacturing overhead per machine-hour. 2.20 Recently, Job P505 was completed with the following characteristics: Total machine-hours 200 Direct materials. $ 540 Direct labor cost. $ 7,200 The amount of overhead applied to Job P505 is closest to: $2,200 $176,000 + ($2.20 × 20,000s) = $176,000 + $44,000 = $220,000 $220,000 ÷ 20,000 = 11 $11 × 200 = 2,200 The total job cost for Job P505 is closest to: $9,940 540 + 7,200 + 2,200 = 9,940 Lueckenhoff Corporation uses a job-order costing system with a single plantwide predetermined overhead rate based on direct labor-hours. The company based its predetermined overhead rate for the current year on total fixed manufacturing overhead cost of $497,000, variable manufacturing overhead of $2.40 per direct labor-hour, and 70,000 direct labor-hours. The company has provided the following data concerning Job T498 which was recently completed: Number of units in the job 40 Total direct labor-hours 80 Direct materials $950 Direct labor cost $2,720 The estimated total manufacturing overhead is closest to: $665,000 497,000 + ($2.40 × 70,000) = 497,000 + $168,000 = $665,000 Lister Corporation is a manufacturer that uses job-order costing. The company closes out any overapplied or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold at the end of the year. The company has supplied the following data for the just completed year: Estimated total manufacturing overhead at the beginning of the year $624,000 Estimated direct labor-hours at the beginning of the year 39,000 direct labor-hours Results of operations: Actual direct labor-hours 36,000 Manufacturing Overhead Indirect labor cost. $131,000 Other manufacturing overhead costs incurred. $543,000 The total amount of manufacturing overhead applied to production is: $576,000 624,000 ÷ 39,000 = 16.00 16.00 × 36,000 = $576,000 Leelanau Corporation uses a job-order costing system. The following data are for last year: Work in process beginning balance $ 10,500 Work in process ending balance. $ 19,000 Cost of goods manufactured $ 323,000 Direct materials $ 115,000 Direct Labor $ 78,000 Leelanau applies overhead using a predetermined rate. What amount of overhead was applied to work in process last year? 138,500 323,000 + 19,000-10500 = 331500 331,500 - 115,000 - 78,000 = 138,500 Abburi Company's manufacturing overhead is 40% of its total conversion costs. If direct labor is $105,000 and if direct materials are $21,000, the manufacturing overhead is: $70,000 Manufacturing overhead = 0.40 × Conversion cost Direct labor = $105,000 Conversion cost = Direct labor + Manufacturing overhead Conversion cost = $105,000 + Manufacturing overhead Conversion cost = $105,000 + (0.40 × Conversion cost) 0.60 × Conversion cost = $105,000 Conversion cost = $105,000 ÷ 0.60 = $175,000 Manufacturing overhead = 0.40 × Conversion cost Manufacturing overhead = 0.40 × $175,000 = $70,000 During the month of May, direct labor cost totaled $14,960 and direct labor cost was 40% of prime cost. If total manufacturing costs during May were $78,800, the manufacturing overhead was: $41,400 $14,960 ÷ 0.40 = $37,400 $78,800 - $37,400 = $41,400 In May direct labor was 30% of conversion cost. If the manufacturing overhead for the month was $114,100 and the direct materials cost was $28,200, the direct labor cost was: $48,900 1.00 – 0.30 = 0.70 $114,100 ÷ 0.70 = $163,000 0.30 × $163,000 = $48,900 A manufacturing company prepays its insurance coverage for a three-year period. The premium for the three years is $3,360 and is paid at the beginning of the first year. Seventy percent of the premium applies to manufacturing operations and thirty percent applies to selling and administrative activities. What amounts should be considered product and period costs respectively for the first year of coverage? A) $3,360, $0 B) $2,352, $1,008 C) $1,568, $672 D) $784, $336 $3,360 / 3 = $1,120 0.70 × $1,120 = $784 0.30 × $1,120 = $336 At an activity level of 9,700 machine-hours in a month, Falks Corporation's total variable production engineering cost is $810,435 and its total fixed production engineering cost is $193,050. What would be the total production engineering cost per machine-hour, both fixed and variable, at an activity level of 9,900 machine-hours in a month? Assume that this level of activity is within the relevant range. (Round intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.) $103.05 810,435 ÷ 9,700 = 83.55 193,050 ÷ 9,900 = $19.50 83.55 + 19.50 = 103.05 Paolucci Corporation's relevant range of activity is 6,300 units to 13,500 units. When it produces and sells 9,900 units, its average costs per unit are as follows: Average Cost per Unit Direct materials $ 6.75 Direct labor $ 3.65 Variable manufacturing overhead $ 1.65 Fixed manufacturing overhead $ 2.90 Fixed selling expense $ 0.95 Fixed administrative expense $ 0.65 Sales commissions $ 0.90 Variable administrative expense $ 0.55 If 8,900 units are sold, the variable cost per unit sold is closest to: $13.50 6.75 + 3.65 + 1.65 + 0.90 + 0.55 = $13.50 Schonhardt Corporation's relevant range of activity is 2,300 units to 6,500 units. When it produces and sells 4,400 units, its average costs per unit are as follows: Average Cost per Unit Direct materials $ 7.10 Direct labor $ 3.20 Variable manufacturing overhead $ 1.15 Fixed manufacturing overhead $ 3.00 Fixed selling expense $ 0.75 Fixed administrative expense $ 0.45 Sales commissions $ 0.55 Variable administrative expense $ 0.45 $13,200 4,400 x 3 = 13,200 Tirri Corporation has provided the following information: 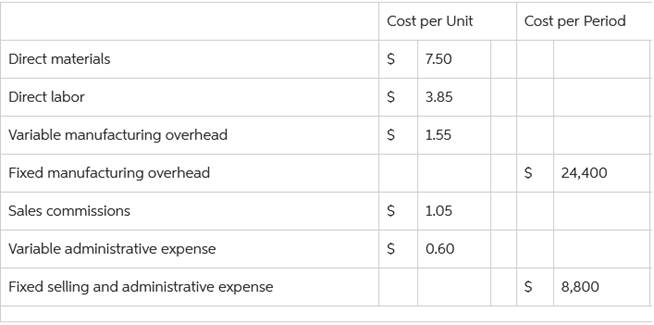 If the selling price is $28.10 per unit, the contribution margin per unit sold is closest to: $13.55 Selling price per unit = $28.10 Variable cost per unit = $7.5 + $3.85 + $1.55 + $1.05 + $0.60 = $14.55 Contribution margin per unit = $28.10 - $14.55 = $13.55 Haack Inc. is a merchandising company. Last month the company's cost of goods sold was $61,900. The company's beginning merchandise inventory was $17,600 and its ending merchandise inventory was $26,200. What was the total amount of the company's merchandise purchases for the month? $70,500 $61,900 - $17,600 + $26,200 = $70,500 Dake Corporation's relevant range of activity is 2,300 units to 6,500 units. When it produces and sells 4,400 units, its average costs per unit are as follows: Average Cost per Unit Direct materials $ 6.40 Direct labor $ 3.20 Variable manufacturing overhead $ 1.15 Fixed manufacturing overhead $ 3.00 Fixed selling expense $ 0.75 Fixed administrative expense $ 0.45 Sales commissions $ 0.55 Variable administrative expense $ 0.45 For financial reporting purposes, the total amount of product costs incurred to make 4,400 units is closest to: $60,500 6.40 + 3.20 + 1.15 = 10.75 X 4,400 = 47,300 4,400 x 3.00 = 13,200 47,300 + 13,200 = $60,500 Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2 14.1 14.2 15.1 15.2
Learnsmart 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Final Exam 1 2 Homework Help? |
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |