|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Principals Of Managerial Accounting: Homework Chapter 2 Part 2 Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2 14.1 14.2 15.1 15.2
Learnsmart 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Final Exam 1 2 Homework Help?
As of the end of June,
the job cost sheets at Racing Wheels, Inc., show the following total costs
accumulated on three custom jobs.
Job 102 was started in production in May, and the following costs were assigned to it in May: direct materials, $9,000 direct labor, $3,600 overhead, $1,260 Jobs 103 and 104 were started in June. Overhead cost is applied with a predetermined rate based on direct labor cost. Jobs 102 and 103 were finished in June, and Job 104 is expected to be finished in July. No raw materials were used indirectly in June. Using this information, answer the following questions. (Assume this company’s predetermined overhead rate did not change across these months.) 1 & 2. Complete the table below to calculate the cost of the raw materials requisitioned and direct labor cost incurred during June for each of the three jobs? 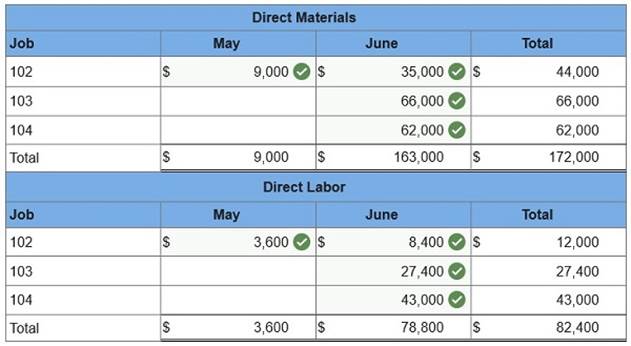
3. Using the accumulated costs of the jobs, what predetermined overhead rate is used? 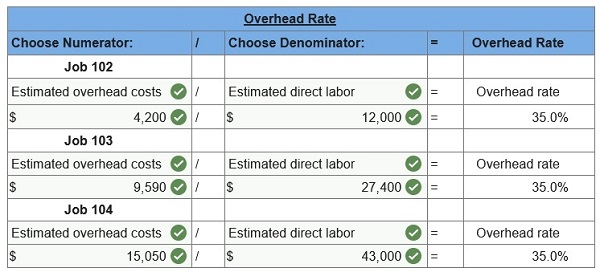 4. How much total cost is transferred to finished goods during June? 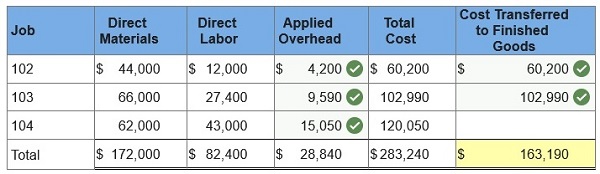
The following information is available for Lock-Tite Company, which produces special-order security products and uses a job order costing system.
Compute the following amounts for the month of May using T-accounts. Cost of direct materials used. Cost of direct labor used. Cost of goods manufactured. Cost of goods sold.* Gross profit. Overapplied or underapplied overhead. *Do not consider any underapplied or overapplied overhead. 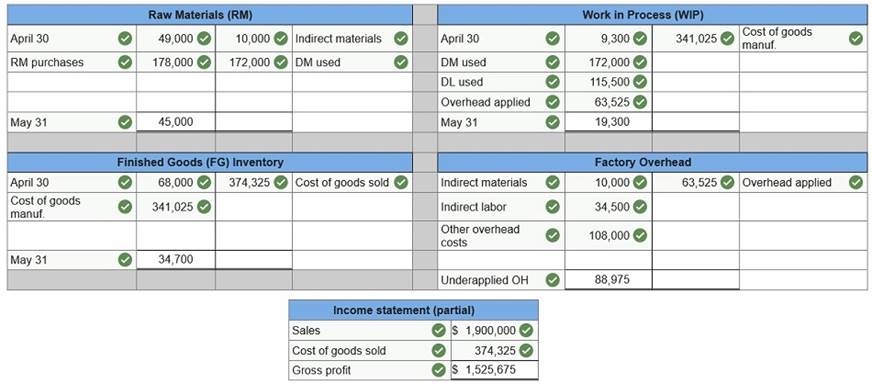
The following information is available for Lock-Tite Company, which produces special-order security products and uses a job order costing system.
Raw materials purchases for cash. Direct materials usage. Indirect materials usage. Prepare journal entries for the above transactions for the month of May. 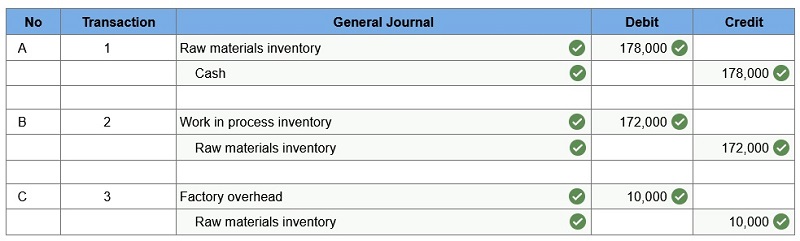
The following information is available for Lock-Tite Company, which produces special-order security products and uses a job order costing system.
Direct labor usage. Indirect labor usage. Total payroll paid in cash. Prepare journal entries for the above transactions for the month of May. 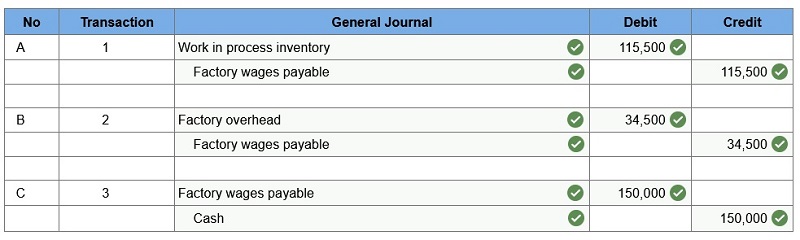
The following information is available for Lock-Tite Company, which produces special-order security products and uses a job order costing system.
Incurred other overhead costs (record credit to Other Accounts). Applied overhead to work in process. Prepare journal entries for the above transactions for the month of May. 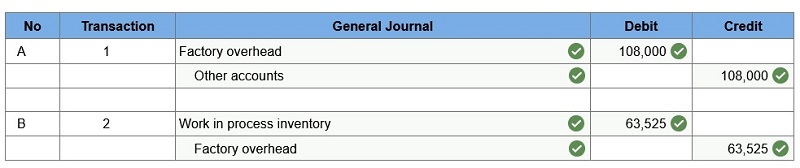
Lorenzo Company applies overhead to jobs on the basis of direct materials cost. At year-end, the Work in Process Inventory account shows the following.
1. Determine the predetermined overhead rate used (based on direct materials cost). 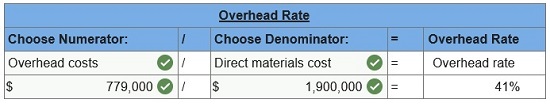 2. Only one job remained in work in process inventory at December 31. Its direct materials cost is $39,000. How much direct labor cost and overhead cost are assigned to this job? 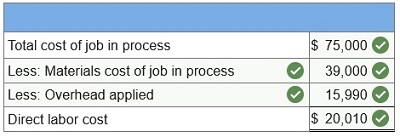
The following information is available for Lock-Tite Company, which produces special-order security products and uses a job order costing system.
Determine whether there is over or underapplied overhead. Prepare the journal entry to allocate (close) overapplied or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold. 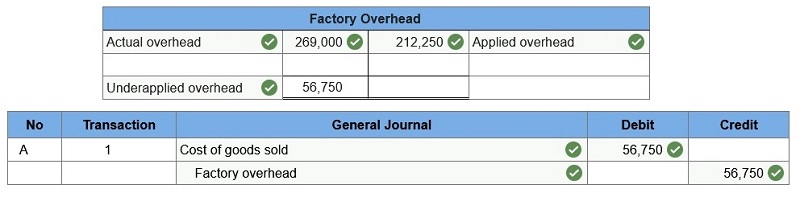
Storm Concert Promotions Determine whether overhead is overapplied or underapplied. Prepare the journal entry to allocate (close) overapplied or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold. 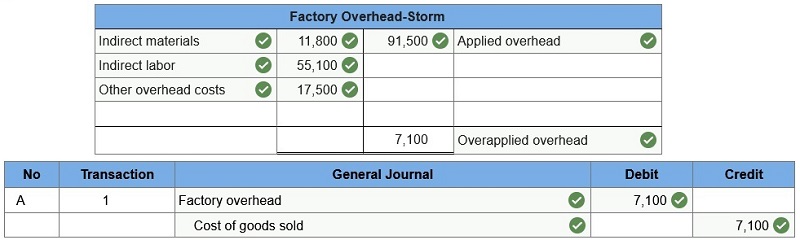
Valle Home Builders Determine whether overhead is overapplied or underapplied. Prepare the journal entry to allocate (close) overapplied or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold. 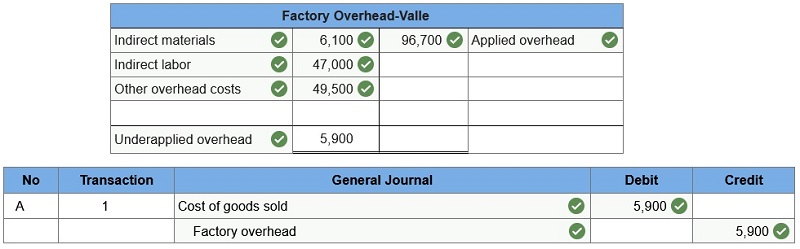
At the beginning of the year, Custom Mfg. established its predetermined overhead rate by using the following cost predictions: overhead costs, $340,000, and direct materials costs, $200,000. At year-end, the company’s records show that actual overhead costs for the year are $877,800. Actual direct materials cost had been assigned to jobs as follows.
1. Determine the predetermined overhead rate.  2 & 3. Enter the overhead costs incurred and the amounts applied to jobs during the year using the predetermined overhead rate and determine whether overhead is overapplied or underapplied. 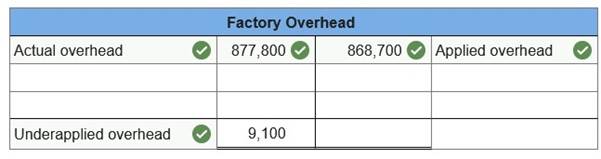 4. Prepare the adjusting entry to allocate any over- or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold. 
At the beginning of the year, Infodeo established its predetermined overhead rate for movies produced during the year by using the following cost predictions: overhead costs, $1,400,000,and direct labor costs, $400,000. At year-end, the company’s records show that actual overhead costs for the year are $1,900,700. Actual direct labor cost had been assigned to jobs as follows.
1. Determine the predetermined overhead rate for the year. 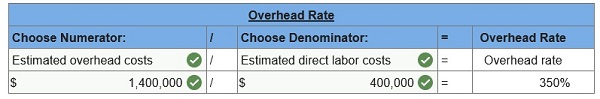 2 & 3. Enter the overhead costs incurred and the amounts applied to movies during the year using the predetermined overhead rate and determine whether overhead is overapplied or underapplied. 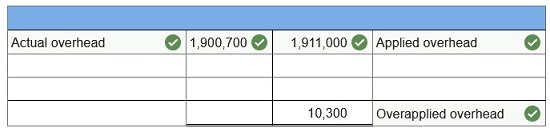 4. Prepare the adjusting entry to allocate any over- or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold. 
Q14. Marcelino Co.’s March 31 inventory of raw materials is $82,000. Raw materials purchases in April are $530,000, and factory payroll cost in April is $380,000. Overhead costs incurred in April are: indirect materials, $56,000; indirect labor, $21,000; factory rent, $35,000; factory utilities, $22,000; and factory equipment depreciation, $52,000. The predetermined overhead rate is 50% of direct labor cost. Job 306 is sold for $640,000 cash in April. Costs of the three jobs worked on in April follow.
Required: 1. Determine the total of each production cost incurred for April (direct labor, direct materials, and applied overhead), and the total cost assigned to each job (including the balances from March 31). 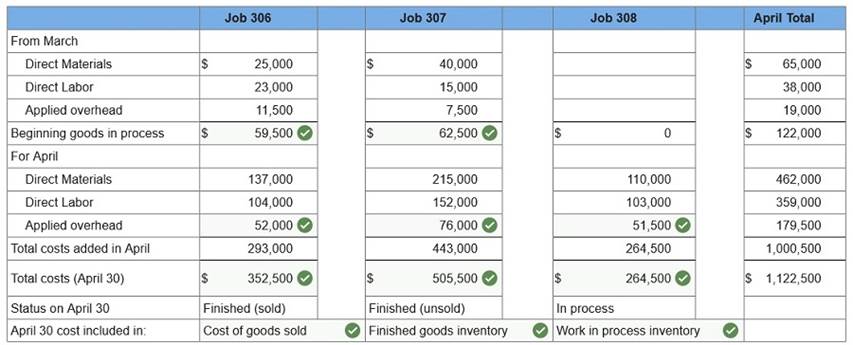
Marcelino Co.’s March 31 inventory of raw materials is $82,000. Raw materials purchases in April are $530,000, and factory payroll cost in April is $380,000. Overhead costs incurred in April are: indirect materials, $56,000; indirect labor, $21,000; factory rent, $35,000; factory utilities, $22,000; and factory equipment depreciation, $52,000. The predetermined overhead rate is 50% of direct labor cost. Job 306 is sold for $640,000 cash in April. Costs of the three jobs worked on in April follow.
Materials purchases (on credit). Direct materials used in production. Direct labor paid and assigned to Work in Process Inventory. Indirect labor paid and assigned to Factory Overhead. Overhead costs applied to Work in Process Inventory. Actual overhead costs incurred, including indirect materials. (Factory rent and utilities are paid in cash.) Transfer of Jobs 306 and 307 to Finished Goods Inventory. Cost of goods sold for Job 306. Revenue from the sale of Job 306. Assignment of any underapplied or overapplied overhead to the Cost of Goods Sold account. (The amount is not material.) 2. Prepare journal entries for the month of April to record the above transactions. 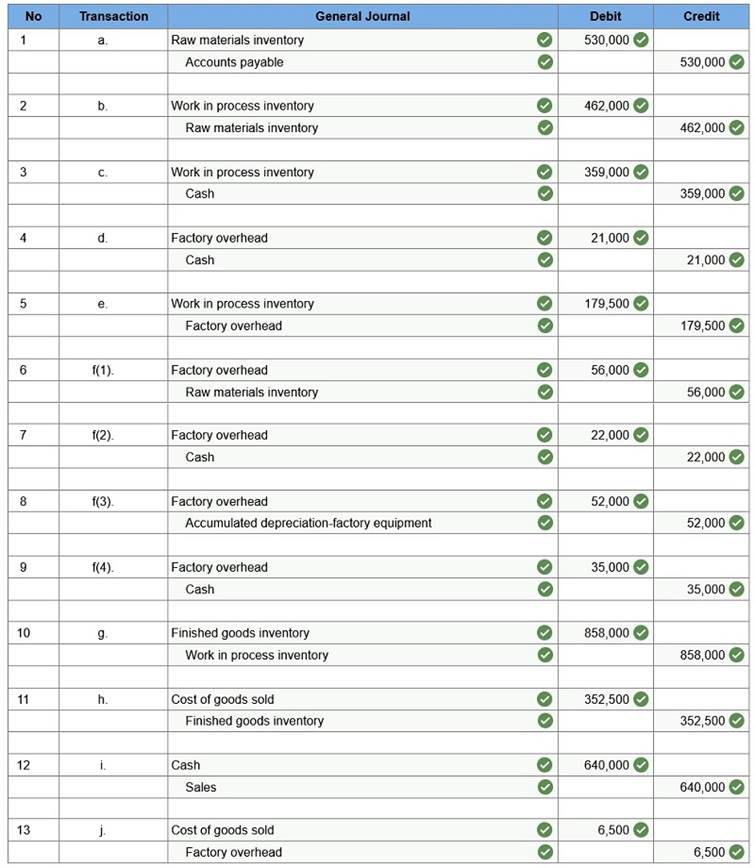
Marcelino Co.’s March 31 inventory of raw materials is $82,000. Raw materials purchases in April are $530,000, and factory payroll cost in April is $380,000. Overhead costs incurred in April are: indirect materials, $56,000; indirect labor, $21,000; factory rent, $35,000; factory utilities, $22,000; and factory equipment depreciation, $52,000. The predetermined overhead rate is 50% of direct labor cost. Job 306 is sold for $640,000 cash in April. Costs of the three jobs worked on in April follow.
3. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured. 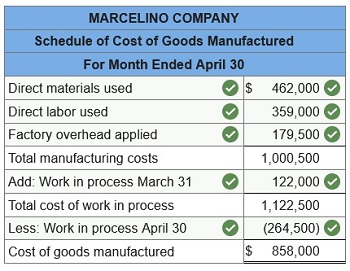
Marcelino Co.’s March 31 inventory of raw materials is $82,000. Raw materials purchases in April are $530,000, and factory payroll cost in April is $380,000. Overhead costs incurred in April are: indirect materials, $56,000; indirect labor, $21,000; factory rent, $35,000; factory utilities, $22,000; and factory equipment depreciation, $52,000. The predetermined overhead rate is 50% of direct labor cost. Job 306 is sold for $640,000 cash in April. Costs of the three jobs worked on in April follow.
4-b. Show how to present the inventories on the April 30 balance sheet. 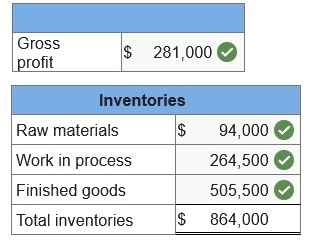
A. Manufacturing equipment depreciation. B. Property taxes on corporate headquarters. C. Direct materials costs. D. Electrical costs to light the production facility. E. Sales commissions. Which of the following costs would be variable with respect to the number of cones sold at a Baskins & Robbins shop? (There may be more than one correct answer.) A. The cost of lighting the store. B. The wages of the store manager. C. The cost of ice cream. D. The cost of napkins for customers. If your fixed monthly utility charge is $40, your variable cost is $0.03 per kilowatt hour, and your monthly activity level is 2,000 kilowatt hours, what is the amount of your utility bill? $100 Y = a + bX Y = $40 + ($0.03 × 2,000) Y = 100 Sales salaries and commissions are $10,000 when 80,000 units are sold, and $14,000 when 120,000 units are sold. Using the high-low method, what is the variable portion of sales salaries and commission? a. $0.08 per unit b. $0.10 per unit c. $0.12 per unit d. $0.125 per unit 14,000 – 10,000 / 120,000 – 80,000 Sales salaries and commissions are $10,000 when 80,000 units are sold, and $14,000 when 120,000 units are sold. Using the high-low method, what is the fixed portion of sales salaries and commissions? a. $ 2,000 b. $ 4,000 c. $10,000 d. $12,000 Total cost = Total fixed cost + Total variable cost $14,000 = Total fixed cost + ($0.10 _ 120,000 units) Total fixed cost = $14,000 - $12,000 Total fixed cost = $2,000 Suppose that your car could be sold now for $5,000. Is this a sunk cost? A. Yes, it is a sunk cost. B. No, it is not a sunk cost Job-order costing systems are used when: Many different products are produced each period. Products are manufactured to order. The unique nature of each order requires tracing or allocating costs to each job, and maintaining cost records for each job. PearCo estimates that it will require 160,000 direct labor-hours to meet the coming period's estimated production level. In addition, the company estimates total fixed manufacturing overhead at $200,000, and variable manufacturing overhead costs of $2.75 per direct labor hour. Find POHR Y = a + bX Y = $200,000 + ($2.75 per direct labor-hour × 160,000 direct labor-hours) Y = $200,000 + $440,000 Y = $640,000 640,000 / 160000 is 4 so there POHR is $4.00 Job WR53 at NW Fab, Inc. required $200 of direct materials and 10 direct labor hours at $15 per hour. Estimated total overhead for the year was $760,000 and estimated direct labor hours were 20,000. What would be recorded as the cost of job WR53? a. $200. b. $350. c. $380. d. $730. POHR = $760,000/20,000 = 38 Direct materials $200 Direct labor $15 x 10 hours $150 Manufacturing overhead $38 x 10 hours $380 200 + 150 + 380 = $730 Process costing is used for products that are: a. Different and produced continuously. b. Similar and produced continuously. c. Individual units produced to customer specifications. d. Purchased from vendors. For the current period, Jones started 15,000 units and completed 10,000 units, leaving 5,000 units in process 30 percent complete. How many equivalent units of production did Jones have for the period? a. 10,000 b. 11,500 c. 13,500 d. 15,000 10,000 + 5,000(.3) = 11,500 Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2 14.1 14.2 15.1 15.2
Learnsmart 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Final Exam 1 2 Homework Help? |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |