|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Principals Of Managerial Accounting: Homework Chapter 2 Part 1 Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2 14.1 14.2 15.1 15.2
Learnsmart 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Final Exam 1 2 Homework Help?
Exercise 2-14 Adjusting
factory overhead LO P4
Storm Concert Promotions Determine whether overhead is overapplied or underapplied. Prepare the journal entry to allocate (close) overapplied or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold. Valle Home Builders Determine whether overhead is overapplied or underapplied. Prepare the journal entry to allocate (close) overapplied or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Factory OH Storm Determine whether overhead is overapplied or underapplied. 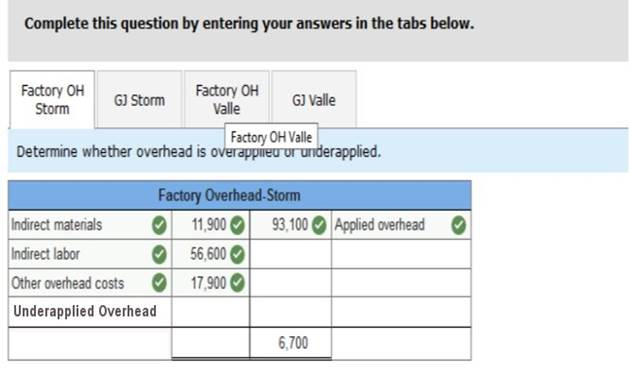
GJ Storm Prepare the journal entry to allocate (close) overapplied or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold. 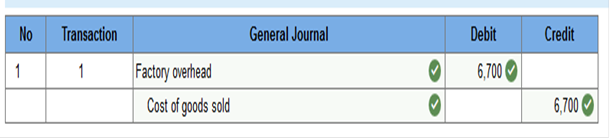
Factory OH Valle Determine whether overhead is overapplied or underapplied. 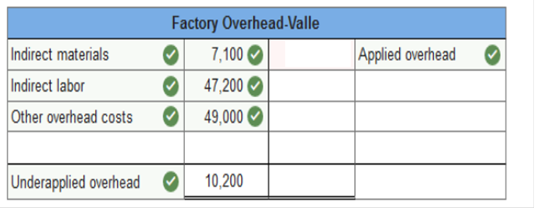
Exercise 2-12 Analysis of costs assigned to work in process LO P3 Lorenzo Company uses a job order costing system that charges overhead to jobs on the basis of direct materials cost. At year-end, the Work in Process Inventory account shows the following.
1. Determine the predetermined overhead rate used (based on direct materials cost). 2. Only one job remained in work in process inventory at December 31, 2017. Its direct materials cost is $40,000. How much direct labor cost and overhead cost are assigned to this job? Required 1 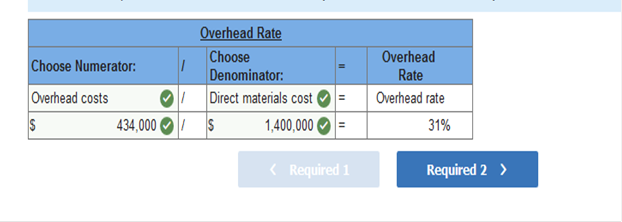
Required 2 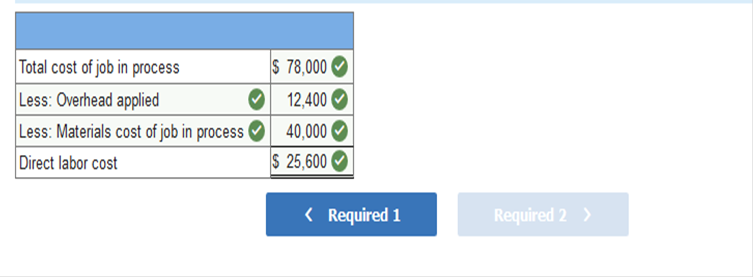
Exercise 2-3 Analysis of cost flows LO C2 As of the end of June, the job cost sheets at Racing Wheels, Inc., show the following total costs accumulated on three custom jobs.
Job 102 was started in production in May and the following costs were assigned to it in May: direct materials, $9,000; direct labor, $3,000; and overhead, $1,410. Jobs 103 and 104 were started in June. Overhead cost is applied with a predetermined rate based on direct labor cost. Jobs 102 and 103 were finished in June, and Job 104 is expected to be finished in July. No raw materials were used indirectly in June. Using this information, answer the following questions. (Assume this company’s predetermined overhead rate did not change across these months.) 1 & 2. Complete the table below to calculate the cost of the raw materials requisitioned and direct labor cost incurred during June for each of the three jobs? 3. Using the accumulated costs of the jobs, what predetermined overhead rate is used? 4. How much total cost is transferred to finished goods during June? Req 1 and 2 Complete the table below to calculate the cost of the raw materials requisitioned and direct labor cost incurred during June for each of the three jobs? 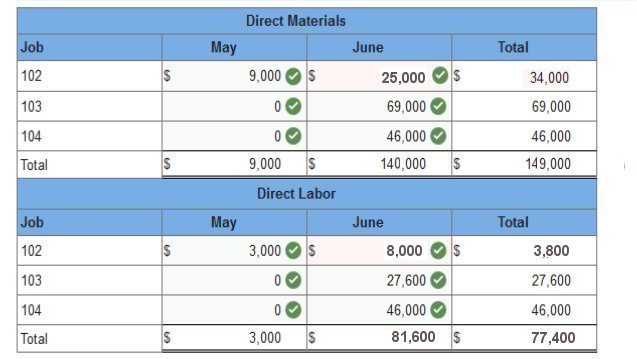
Req 3 Using the accumulated costs of the jobs, what predetermined overhead rate is used? 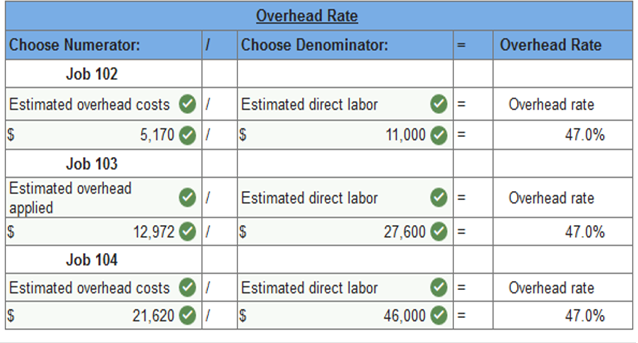
Req 4 How much total cost is transferred to finished goods during June? 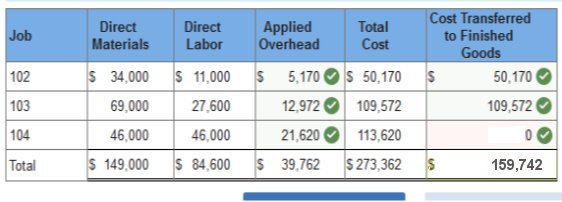
Problem 2-3A Source documents, journal entries, and accounts in job order costing LO P1, P2, P3 [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Widmer Watercraft’s predetermined overhead rate for the year 2017 is 200% of direct labor. Information on the company’s production activities during May 2017 follows. Purchased raw materials on credit, $220,000. Materials requisitions record use of the following materials for the month.
Paid $15,750 cash to a computer consultant to reprogram factory equipment. Time tickets record use of the following labor for the month. These wages were paid in cash.
Applied overhead to Jobs 136, 138, and 139. Transferred Jobs 136, 138, and 139 to Finished Goods. Sold Jobs 136 and 138 on credit at a total price of $545,000. The company incurred the following overhead costs during the month (credit Prepaid Insurance for expired factory insurance).
Applied overhead at month-end to the Work in Process Inventory account (Jobs 137 and 140) using the predetermined overhead rate of 200% of direct labor cost. Problem 2-3A Part 1 Required: 1. Prepare a job cost sheet for each job worked on during the month. 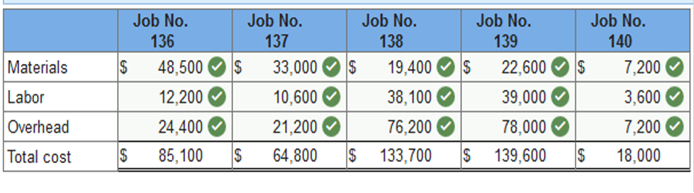
Required information 5. Required information Problem 2-3A Source documents, journal entries, and accounts in job order costing LO P1, P2, P3 [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Widmer Watercraft’s predetermined overhead rate for the year 2017 is 200% of direct labor. Information on the company’s production activities during May 2017 follows. a. Purchased raw materials on credit, $220,000. b. Materials requisitions record use of the following materials for the month.
c. Paid $15,750 cash to a computer consultant to reprogram factory equipment. d. Time tickets record use of the following labor for the month. These wages were paid in cash.
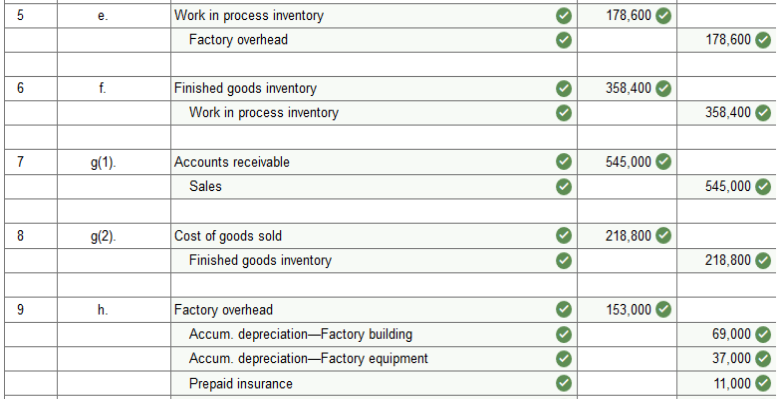
e. Applied overhead to Jobs 136, 138, and 139. f. Transferred Jobs 136, 138, and 139 to Finished Goods. g. Sold Jobs 136 and 138 on credit at a total price of $545,000. h. The company incurred the following overhead costs during the month (credit Prepaid Insurance for expired factory insurance).
Applied overhead at month-end to the Work in Process Inventory account (Jobs 137 and 140) using the predetermined overhead rate of 200% of direct labor cost. Problem 2-3A Part 2 2. Prepare journal entries to record the events and transactions a through i. 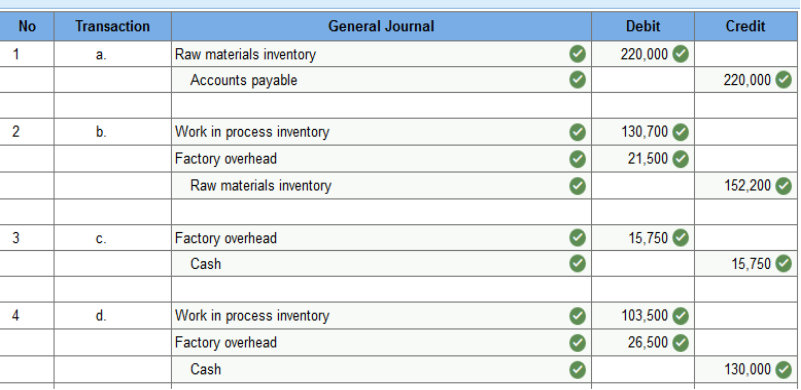

Starr Company reports the following information for August.
· Prepare journal entries to record the following events. · Raw materials purchased. · Direct materials used in production. · Direct labor used in production. · Applied overhead. 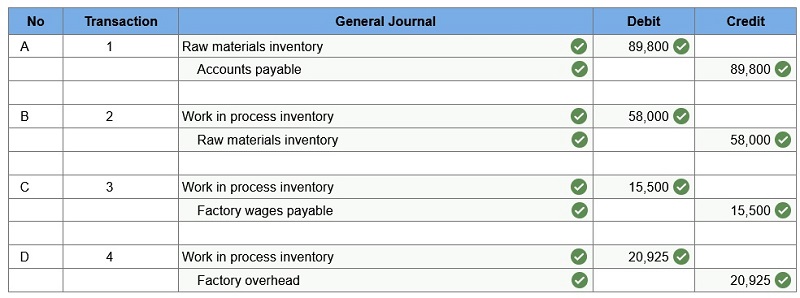
Custom Cabinetry has one job in process (Job 120) as of June 30; at that time, its job cost sheet reports direct materials of $7,600, direct labor of $3,800, and applied overhead of $3,230. Custom Cabinetry applies overhead at the rate of 85% of direct labor cost. During July, Job 120 is sold (on account) for $28,500, Job 121 is started and completed, and Job 122 is started and still in process at the end of the month. Custom Cabinetry incurs the following costs during July.
1. Prepare journal entries for the following in July. Direct materials used in production. Direct labor used in production. Overhead applied. The sale of Job 120. Cost of goods sold for Job 120. 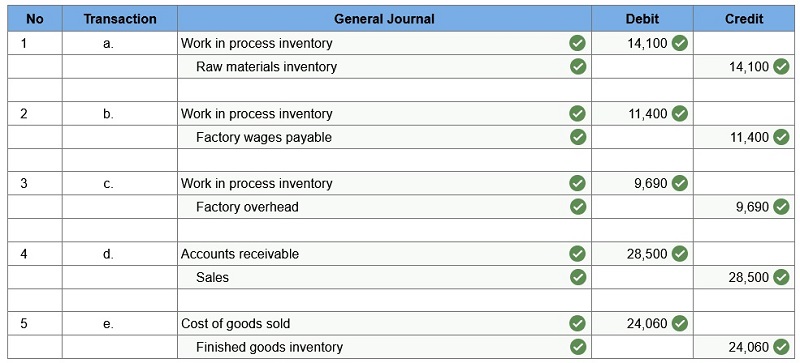
2. Compute the July 31 balances of the Work in Process Inventory and the Finished Goods Inventory accounts. (Assume there are no jobs in Finished Goods Inventory as of June 30.) 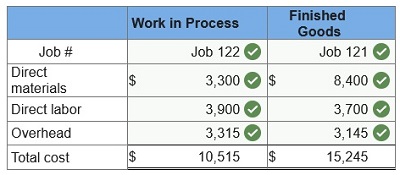
Prepare summary journal entries to record the following transactions for a company in its first month of operations. Raw materials purchased on account, $80,000. Direct materials used in production, $37,000. Indirect materials used in production, $12,000. Paid cash for factory payroll, $35,000. Of this total, $25,000 is for direct labor and $10,000 is for indirect labor. Paid cash for other actual overhead costs, $7,000. Applied overhead at the rate of 120% of direct labor cost. Transferred cost of jobs completed to finished goods, $50,470. Jobs that had a cost of $50,470 were sold. Sold jobs on account for $72,100. 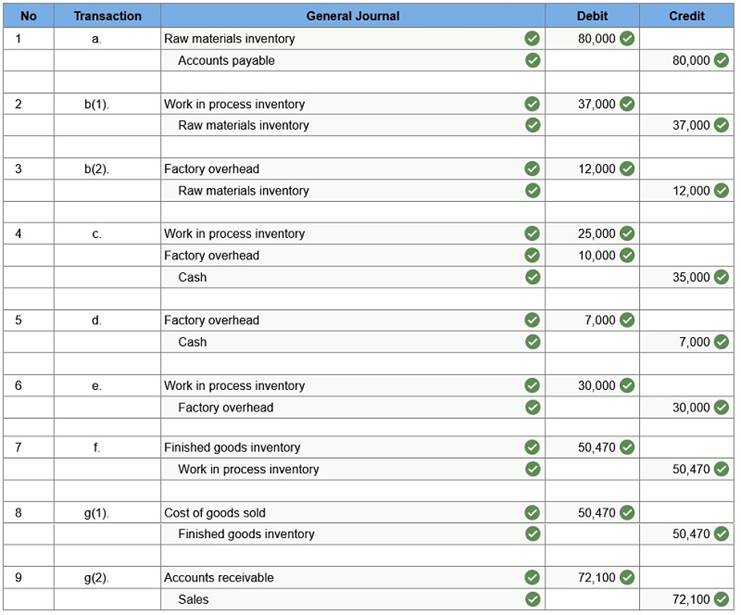
As of the end of June, the job cost sheets at Racing Wheels, Inc., show the following total costs accumulated on three custom jobs. 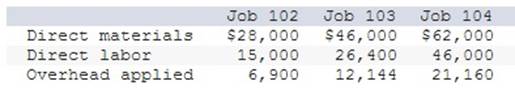
Job 102 was started in production in May and the following costs were assigned to it in May: direct materials, $14,000 direct labor, $3,800 overhead, $1,748 Jobs 103 and 104 were started in June. Overhead cost is applied with a predetermined rate based on direct labor cost. Jobs 102 and 103 were finished in June, and Job 104 is expected to be finished in July. No raw materials were used indirectly in June. Using this information, answer the following questions. (Assume this company’s predetermined overhead rate did not change across these months.) 1 & 2. Complete the table below to calculate the cost of the raw materials requisitioned and direct labor cost incurred during June for each of the three jobs? 3. Using the accumulated costs of the jobs, what predetermined overhead rate is used? 4. How much total cost is transferred to finished goods during June? 1 & 2. Complete the table below to calculate the cost of the raw materials requisitioned and direct labor cost incurred during June for each of the three jobs? 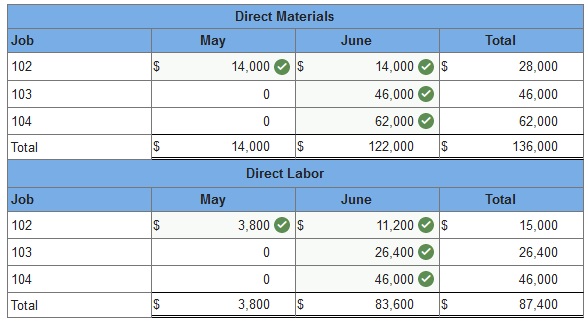
3. Using the accumulated costs of the jobs, what predetermined overhead rate is used? 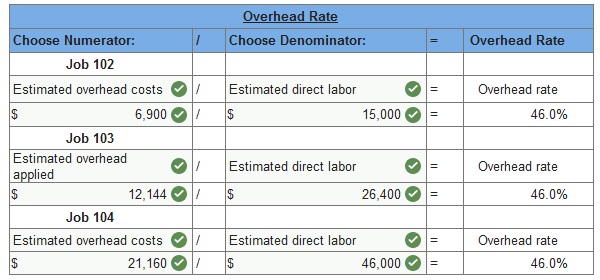
4. How much total cost is transferred to finished goods during June? 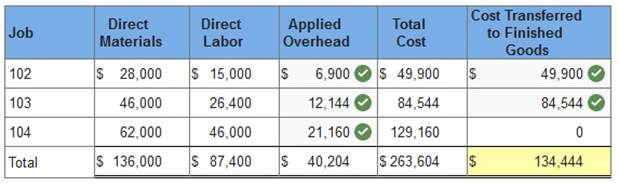
Starr Company reports the following information for August.
1. Raw materials purchased. 2. Direct materials used in production. 3. Direct labor used in production. 4. Applied overhead. 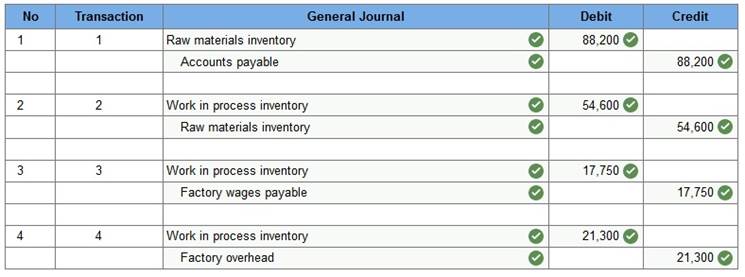
In December 2016, Custom Mfg. established its predetermined overhead rate for jobs produced during 2017 by using the following cost predictions: overhead costs, $700,000, and direct materials costs, $500,000. At year-end 2017, the company’s records show that actual overhead costs for the year are $785,900. Actual direct material cost had been assigned to jobs as follows.
1. Determine the predetermined overhead rate for 2017. 2 & 3. Enter the overhead costs incurred and the amounts applied during the year using the predetermined overhead rate and determine whether overhead is overapplied or underapplied. 4. Prepare the adjusting entry to allocate any over- or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold. 1. Determine the predetermined overhead rate for 2017. 
2 & 3. Enter the overhead costs incurred and the amounts applied during the year using the predetermined overhead rate and determine whether overhead is overapplied or underapplied. 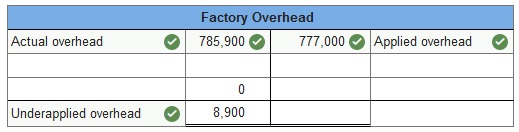
4. Prepare the adjusting entry to allocate any over- or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold. 
Kayak Company uses a job order costing system and allocates its overhead on the basis of direct labor costs. Kayak Company’s production costs for the year were: direct labor, $30,000; direct materials, $50,000; and factory overhead applied $6,000. The overhead application rate was:
Copy Center pays an average wage of $12 per hour to employees for printing and copying jobs, and allocates $18 of overhead for each employee hour worked. Materials are assigned to each job according to actual cost. Jobs are marked up 20% above cost to determine the selling price. If Job M-47 used $350 of materials and took 20 hours of labor to complete, what is the selling price of the job?
$950 * 120% = $1,140
Lowden Company has an overhead application rate of 160% and allocates overhead based on direct material cost. During the current period, direct labor cost is $50,000 and direct materials used cost $80,000. Determine the amount of overhead Lowden Company should record in the current period.
issued materials to production of $164,000 of which $24,000 were indirect. Portside incurred a factory payroll of $95,000, of which $25,000 was indirect labor. Portside uses a predetermined overhead rate of 170% of direct labor cost. The journal entry to record the issuance of materials to production is:
A company has an overhead application rate of 125% of direct labor costs. How much overhead would be allocated to a job if it required total labor costing $20,000?
At the current year-end, Simply Company found that its overhead was underapplied by $2,500, and this amount was not considered material. Based on this information, Simply should:
Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2 14.1 14.2 15.1 15.2
Learnsmart 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Final Exam 1 2 Homework Help? |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |