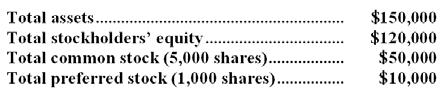|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Principals Of Managerial Accounting: Homework Chapter 1 Part 2 Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2 14.1 14.2 15.1 15.2
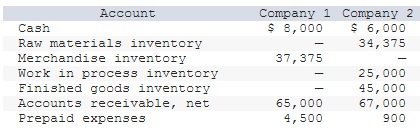
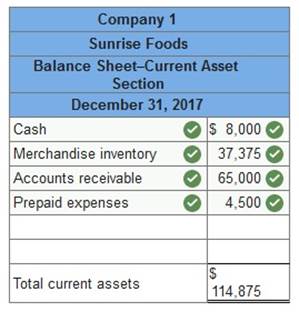
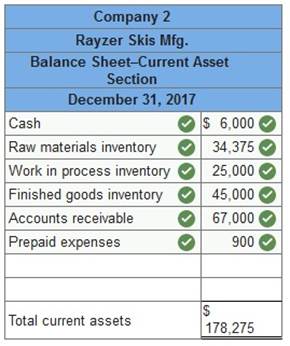
Learnsmart 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Final Exam 1 2 Homework Help? Current assets for two different companies at fiscal year-end 2017 are listed here. One is a manufacturer, Rayzer Skis Mfg., and the other, Sunrise Foods, is a grocery distribution company.
Required: Identify which set of numbers relates to the manufacturer and which to the merchandiser. Which of these company is manufacturer: Company 2 Which of these company is merchandiser: Company 1 Prepare the current asset section for each company from this information.
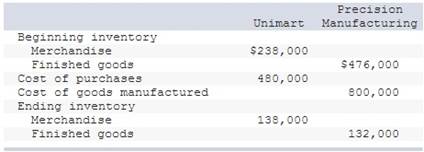
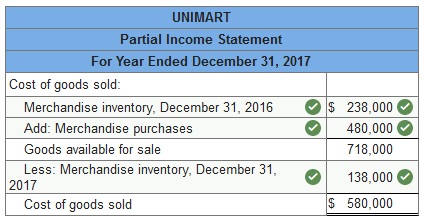
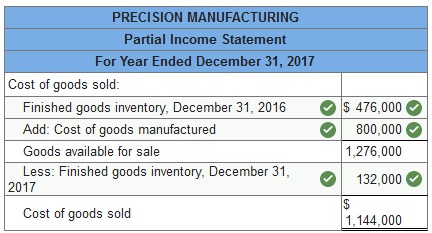
Compute cost of goods sold for each of these two companies for the year ended December 31, 2017..
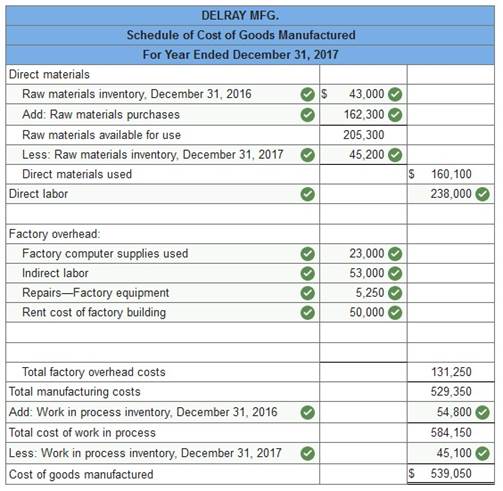
Prepare its schedule of cost of goods manufactured for the year ended December 31, 2017.
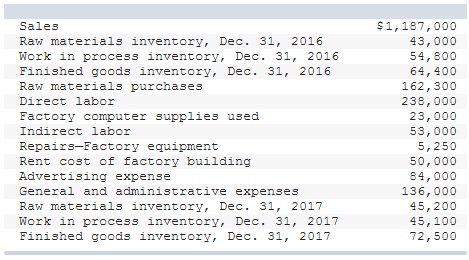
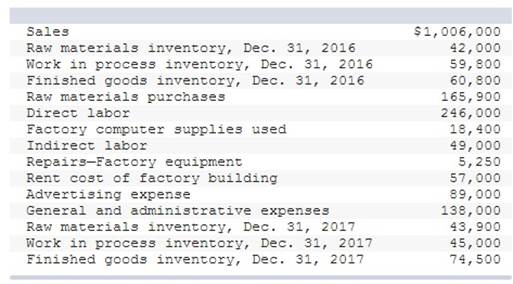
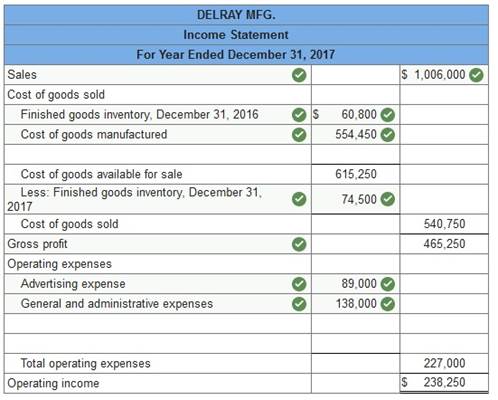
The following selected account balances are provided for Delray Mfg.
Prepare an income statement for Delray Mfg. (a manufacturer).
Which of the following accounts would appear on a schedule of cost of goods manufactured?
Raw materials, factory insurance expired, indirect labor. Raw materials, work in process, finished goods. Direct labor, delivery equipment, and depreciation on factory equipment. Direct materials, indirect labor, sales salaries. Direct labor, factory repairs and maintenance, wages payable.
The following information relates to the manufacturing operations of the Abbra Publishing Company for the year:
The raw materials used in manufacturing during the year totaled $1,018,000. Raw materials purchased during the year amount to:
$955,000 $892,000 $1,565,000 $408,000 $1,081,000
Beginning
Raw Materials + Purchases – Ending Raw Materials = Raw Materials Used
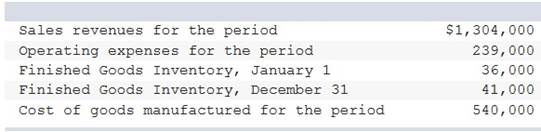
Using the information below, calculate cost of goods sold for the period:
$774,000 $769,000 $530,000 $535,000 $448,000
Beginning Finished Goods Inventory + Cost of goods manufactured – Ending Finished Goods Inventory = Cost of goods sold. $36,000 + 540,000 – 41,000 = $535,000.
Flexibility of practice when applied to managerial accounting means that:
The information must be presented in electronic format so that it is easily changed. Managers must be willing to accept the information as the accountants present it to them, rather than in the format they ask for. The managerial accountants need to be on call twenty-four hours a day. Managerial accounting system differ across companies depending on the nature of the business and the arrangement of its internal operations. Managers must be flexible with information provided in varying forms and using inconsistent measures.
The following information is available for the year ended December 31:
$87,500 $85,700 $86,900 $85,400 $86,600 Beginning Raw Materials + Purchases – Ending Raw Materials = Raw
Materials Used All of the following statements regarding manufacturing costs are true except:
Which of the following is not part of the sales activity in the flow of manufacturing activities?
Beginning Finished Goods Inventory + Cost of Goods Manufactured = Finished Goods Available for Sale. Finished Goods Available for Sale – Ending Finished Goods Inventory = Cost of Goods Sold. A direct cost is a cost that is:
Total manufacturing costs incurred during the year do not include:
Managerial accounting is different from financial accounting in that:
Cameroon Corp. manufactures and sells electric staplers for $15.40 each. If 10,000 units were sold in December, and management forecasts 3% growth in sales each month, the dollar amount of electric stapler sales budgeted for February should be:
$163,379
December
sales $15.40 * 10,000 = $154,000
Bengal Co. provides the
following sales forecast for the next three months:
The company wants to end each month with ending finished goods inventory equal to 25% of the next month's sales. Finished goods inventory on June 30 is 1,325 units. The budgeted production units for July are:
5,475 units
July
units + 25% of August units - June ending inventory = July production
Bengal Co. provides the
following sales forecast for the next three months:
The company wants to end each month with ending finished goods inventory equal to 30% of the next month's sales. Finished goods inventory on June 30 is 1,800 units. The budgeted production units for August are:
6,625 units.
August
units + 30% of September units - July ending inventory = August production
Flack Corporation, a
merchandiser, provides the following information for its December budgeting
process:
6,110 units.
Budgeted
sales units + desired ending inventory - beginning inventory = purchases
A sporting equipment store expects to purchase $7,400 of ski boots in October. The store had $3,400 of ski boots in merchandise inventory at the beginning of October and expects to have $2,400 of ski boots in merchandise inventory at the end of October to cover part of anticipated November sales. What is the budgeted cost of goods sold for October?
$8,400.
Cost of
Goods Sold = Beginning inventory + purchases - ending inventory
Alliance Company’s budgets production of 24,000 units in January and 28,000 units in the February. Each finished unit requires 3 pounds of raw material K that costs $3.00 per pound. Each month’s ending raw materials inventory should equal 35% of the following month’s budgeted materials. The January 1 inventory for this material is 25,200 pounds. What is the budgeted materials cost for January?
$228,600.
Budgeted
production units * materials requirement per unit = materials needed
Boulware Company’s budgeted production calls for 6,000 units in October and 9,000 units in November. Each unit requires 7 pounds (lbs.) of raw material A. Each month’s ending inventory of raw materials should equal 25% of the following month’s budgeted materials requirements. The October 1 inventory for this material is 10,500 pounds. What is the budgeted materials purchases for this key material in pounds for October?
47,250 lbs.
Materials
needed + ending inventory requirements - beginning inventory available =
materials to be purchased
Southland Company is preparing a cash budget for August. The company has $16,400 cash at the beginning of August and anticipates $124,000 in cash receipts and $133,900 in cash disbursements during August. Southland Company wants to maintain a minimum cash balance of $10,000. The preliminary cash balance at the end of August before any loan activity is:
$6,500.
Frankie's Chocolate Co. reports the following information from its sales budget:
Cash sales are normally 30% of total sales and all credit sales are expected to be collected in the month following the date of sale. The total amount of cash expected to be received from customers in September is:
$107,000.
Justin Company's budget includes the following credit sales for the current year:
September, $30,000 October, $41,000 November, $35,000 December, $37,000
Experience has shown that payment for the credit sales is received as follows: 10% in the month of sale, 65% in the first month after sale, 23% in the second month after sale, and 2% is uncollectible. How much cash can Justin Company expect to collect in November as a result of current and past credit sales?
$37,050.
A company's history indicates that 30% of its sales are for cash and the rest are on credit. Collections on credit sales are 20% in the month of the sale, 50% in the next month, 25% the following month, and 5% is uncollectible. Projected sales for December, January, and February are $65,000, $90,000 and $100,000, respectively. The February expected cash receipts from all current and prior credit sales is:
$56,875
Amount collected in February:
Memphis Company anticipates total sales for April, May, and June of $820,000, $920,000, and $970,000 respectively. Cash sales are normally 25% of total sales. Of the credit sales, 40% are collected in the same month as the sale, 55% are collected during the first month after the sale, and the remaining 5% are not collected. Compute the amount of cash received from total sales during the month of June.
$913,000.
Bakker Corporation has provided the following production and average cost data for two levels of monthly production volume. The company produces a single product.
Production volume 4,000 units 5,000 Direct materials $89.70 per unit $89.70 per unit Direct labor $22.60 per unit $22.60 per unit Manufacturing overhead $70.50 per unit $60.30 per unit
The best estimate of the total variable manufacturing cost per unit is:
$89.70 $131.80 $19.50 $112.30
Jumpst Corporation uses the cost formula Y = $3,600 + $0.30X for the maintenance cost in Department B, where X is machine-hours. The August budget is based on 20,000 hours of planned machine time. Maintenance cost expected to be incurred during August is:
A. $3,600 B. $6,000 C. $6,300 D. $9,600
Given the cost formula, Y = $9,000 + $2.50X, total cost for an activity level of 3,000 units would be:
A. $9,750 B. $12,000 C. $16,500 D. $7,500
Sandler Corporation bases its predetermined overhead rate on the estimated machine-hours for the upcoming year. Data for the upcoming year appear below:
Compute the company’s predetermined overhead rate.
POHR = $14.98 per machine-hour The average stockholders' equity for Horn Co. last year was $2,000,000. Included in this figure was $200,000 of preferred stock. Preferred dividends were $16,000. If the return on common stockholders' equity was 12.5% for the year, net income was: A. $225,000 B. $250,000 C. $241,000
D. $234,000
Artist Company's net income last year was $500,000. The company has 150,000 shares of common stock and 40,000 shares of preferred stock outstanding. There was no change in the number of common or preferred shares outstanding during the year. The company declared and paid dividends last year of $1.70 per share on the common stock and $0.70 per share on the preferred stock. The earnings per share of common stock is closest to:
$3.15 $3.52 $1.63 $3.33
Archer Company had net income of $40,000 last year. The company has 5,000 shares of common stock and 2,500 shares of preferred stock outstanding. There was no change in the number of common or preferred shares outstanding during the year. Preferred dividends were $2 per share. The earnings per share of common stock was:
$7.00 $8.00 $5.33 $7.50
The following account balances have been provided for the end of the most recent year:
The book value per share of common stock is:
$22 $25 $20 $28 Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2 14.1 14.2 15.1 15.2
Learnsmart 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Final Exam 1 2 Homework Help? |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |