|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Principals Of Managerial Accounting: Homework Chapter 10 Part 1 Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2 14.1 14.2 15.1 15.2
Learnsmart 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Final Exam 1 2 Homework Help? Order Up, Inc., provides order fulfillment services for dot.com merchants. The company maintains warehouses that stock items carried by its dot.com clients. When a client receives an order from a customer, the order is forwarded to Order Up, which pulls the item from storage, packs it, and ships it to the customer. The company uses a predetermined variable overhead rate based on direct labor-hours. In the most recent month, 140,000 items were shipped to customers using 5,800 direct labor-hours. The company incurred a total of $15,950 in variable overhead costs. According to the company's standards, 0.04 direct labor-hours are required to fulfill an order for one item and the variableoverhead rate is $2.80 per direct labor-hour. Required : 1 a. According to the standards, what variable overhead cost should have been incurred to fill the orders for the 140 ,0 00 items? {Omit the"$" sign in your response.) Total standard variable overhead cost: 15,680 1b. How much does this differ from the actual variable overhead cost? {Input the amount as a positive value. Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter " 0" wherever required. Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect {i.e ., zero variance). Omit the"$" sign in your response.) Spending variance: $ 270 2. Break down the difference computed in (1) above into a variable overhead rate variance and a variable overhead efficiency variance. {Do not round intermediate calculations. Input all amounts as positive values. Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter "0" wherever required. Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect {i.e., zero variance). Omit the "$"sign in your response.) Variable overhead rate variance: $ 290 Variable overhead efficiency: $ 560 One of the company's products is stuffed cannelloni with roasted pepper sauce, fresh baby corn, and spring salad. During the most recent week, the company prepared 6,000 of these meals using 1,150 direct labor-hours. The company paid these direct labor workers a total of $11 ,500 for this work, or $1 0 per hour. According to the standard cost card for this meal, it should require 0.20 direct labor-hours at a cost of $9.50 per hour. Required : 1a. According to the standards, what direct labor cost should have been incurred to prepare 6,000 meals? (Omit the "$" sign in your response.) Total standard direct labor cost $ 11,400 1b. How much does this differ from the actual direct labor cost? (Input the amount as a positive value. Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter "0" wherever required. Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Omit the"$" sign in your response.) Spending variance; $ 100 2. Break down the difference computed in (1) above into a labor rate variance and a labor efficiency variance. (Input all amounts as positive values. Do not round intermediate calculations. Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter " 0" wherever required. Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Omit the"$" sign in your response.) Labor rate variance $ 575 Labor efficiency variance $ 475 The Worldwide Credit Card, Inc., uses standards to control the labor time involved in opening mail from card holders and recording the enclosed remittances. Incoming mail is gathered into batches, and a standard time is set for opening and recording each batch. The labor standards relating to one batch are as follows: 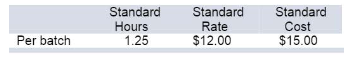
The record showing the time spent last week in opening batches of mail has been misplaced. However, the batch supervisor recalls that 168 batches were received and opened during the week, and the controller recalls the following variance data relating to these batches: 
1. Determine the number of actual labor-hours spent opening batches during the week. Actual labor hours: 250 2. Determine the actual hourly rate paid to employees for opening batches last week. (Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Omit the "$" sign in your response.) Actual hourly rate $ 11.4 studied the prior month's reports. "Every month the lab teeters between a profit and a loss. Are we going to have to increase our lab fees again?" "We can't," replied Lois Ankers, the controller. "We' re getting lots of complaints about the last increase, particularly from the insurance companies and governmental health units. They're now paying only about 80 % of what we bill. I'm beginning to think the problem is on the cost side." To determine if lab costs are in li ne with other hospitals, Mr. Warr en has asked you to evaluate the costs for the past month. Ms. Ankers has provided you with the fo ll ow in g information: a. Two basic types of tests are performed in the lab- smears and blood tests. Dur in g the past month, 2, 700 smears and 900 blood tests were performed in the lab. b. Small glass plates are used in both types of tests. During the past month, the hospital purchased 16,000 plates at a cost of $38,400. This cost is net of a 4% purchase discount. A total of 2,000 of these plates were unused at the end of the month; no plates were on hand at the beginning of the month. c. Du ring the past month, 1,800 hours of labor time were us ed in performing smears and blood tests. The cost of this labor time was $ 18 ,450. d. The lab's variable overhead cost last month totaled $11,700. Cottonwood Hospital has never used standard costs. By searching industry literature, however, you have determined the following nationwide averages for hospital labs: Plates: Three plates are required per lab test. These plates cost $2.50 each and are disposed of after the test is completed. Labor: Each smear should require 0.3 hours to complete, and each blood test should require 0.6 hours to complete. The average cost of this lab time is $ 12 per hour. Overhead: Overhead cost is based on direct labor-hours. The average rate of variable overhead is $6 per hour. Required: 1. Compute the materials price variance for the plates purchased last month and compute a materials quantity variance for the plates used last month. (Input all amounts as positive values. Leave no cells blank • be certain to enter "0" wherever required. Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Omit the "$" sign in your response.) Materials price variance: $ 1,600 Materials quantity variance: $ 8,000 2. For labor cost in the lab: a. Compute a labor rate variance and a labor efficiency variance. (Input all amounts as positive values. Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter "0" wherever required. Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Omit the "$" sign in your response.) Labor rate variance: $ 3,150 Labor efficiency variance: $ 5,400 b. In most hospitals, three-fourths of the workers in the lab are certified technicians and one-fourth are assistants. In an effort to reduce costs, Cottonwood Hospital employs only one-half certified technicians and one-half assistants. Would you recommend that this policy be continued? Yes 3a. Compute the variable overhead rate and efficiency variances. (Input all amounts as positive values. Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter " 0" wherever required. Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Omit the"$" sign in your response.) Variable overhead rate variance: $ 900 Variable overhead efficiency variance: $ 2,700 3b. ls there any relation between the variable overhead efficiency variance and the labor efficiency variance? Yes Sonne Company produces a perfume called Whim. The direct materials and direct labor standards for one bottle of Whim are given below: 
During the most recent month, the following activity was recorded: a. Twenty thousand ounces of material were purchased at a cost of $2.40 per ounce. b. All of the material was used to produce 2,500 bottles of Whim. c. Nine hundred hours of direct labor time were recorded at a total labor cost of $10,800. Required: 1. Compute the direct materials price and quantity variances for the month. (Input all amounts as positive values. Do not round your per unit rates. Leave no cells blank be certain to enter "0 " wherever required. Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Omit the"$" sign in your response.) Direct materials price variance: $ 2,000 Direct materials quantity variances: $ 5,000 2. Compute the direct labor rate and efficiency variances for the month. (Input all amounts as positive values. Do not round your per unit rates. Leave no cells blank • be certain to enter " 0" wherever required. Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Omit the"$" sign in your response.) Direct labor rate variance: $ 1,800 Direct labor efficiency variances: $ 1,000 On June 30, 2024, Clooney Printers purchased a printer for $58,000. It expects the printer to last for four years and have a residual value of $2,000. Compute the depreciation expense on the printer for the year ended December 31, 2024, using the straight−line method. A. $7,000 B. $14,000 C. $8,167 D. $14,500 Which of the following is true when the estimate of an asset's useful life is changed? A. The asset's remaining depreciable book value will be spread over the asset's new useful life. B. The depreciation expense in the prior years is restated. C. Prior years' financial statements must be restated. D. The new estimate is ignored until the last year of the asset's life. A company's accountant capitalized a payment that should have been recorded as a revenue expenditure. How will this error affect the company's financial statements? A. Net income will be overstated. B. Assets will be understated. C. Revenues will be understated. D. Liabilities will be understated. An asset was purchased for $25,000 on January 1, 2025. The asset's estimated useful life was five years, and its residual value was $5,000. The straight−line method of depreciation was used. Calculate the gain or loss if the asset is sold for $18,000 on December 31, 2025, the last day of the accounting period. A. $3,000 gain B. $1,500 gain C. $3,000 loss D. no gain or no loss The type of intangible asset related to the exclusive right to reproduce and sell a book or intellectual property is a ________. A. Franchise B. Patent C. Copyright D. Trademark 16,000 tons are extracted and sold. Calculate depletion expense for the first year. (Round any intermediate calculations to the nearest cent.) A. $100,200 B. $150,300 C. $291,520 D. $200,400 Carpenters Company a manufacturing company, acquired equipment on January 1, 2023 for $590,000. Estimated useful life of the equipment was seven years and the estimated residual value was $20,000. On January 1, 2026, after using the equipment for three years, the total estimated useful life has been revised to nine total years. Residual value remains unchanged. The company uses the straight−line method of depreciation. Calculate depreciation expense for 2026. (Round any intermediate calculations to two decimal places, and your final answer to the nearest dollar.) A. $65,556 B. $54,286 C. $63,333 D. $56,190 Millburn Company has acquired a property that included both land and a building for $520,000. The company hired an appraiser who has determined that the market value of the land is $360,000 and that of the building is $400,000. At what amount should the company record the cost of land? (Round any intermediate calculations to two decimal places, and your final answer to the nearest dollar.) A. $353,600 B. $260,000 C. $244,400 D. $169,200 Businesses record goodwill ________. A. if they acquire another company at an amount higher than the market value of its net assets B. when they continue the business of an acquired company C. when they enjoy an outstanding reputation and loyalty with customers D. if their market value has increased significantly in the recent years Masonry Construction Group paid $5,000 for a plant asset that had a market value of $16,500. At which of the following amounts should the plant asset be recorded? A. $16,500 B. $5,000 C. $2,500 D. $10,000 On January 1, 2024, Sanderson Company acquired a machine for $1,050,000. The estimated useful life of the asset is five years. Residual value at the end of five years is estimated to be $116,000. What is the book value of the machine at the end of 2025 if the company uses the straight−line method of depreciation? A. $676,400 B. $560,400 C. $630,000 D. $629,996 Which of the following is true of goodwill? A. Goodwill is not amortized. B. Both created and acquired goodwill must be recorded in the books. C. Goodwill must be capitalized when acquired and amortized over seven years or less. D. Goodwill must be expensed when acquired. Which of the following is a characteristic of a plant asset, such as a building? A. It will have a negligible value at the end of its useful life. B. It is available for sale to customers in the ordinary course of business. C. It is used in the operations of a business. D. It has a short useful life. On January 1, 2024, Jordan Company acquired a machine for $1,010,000. The estimated useful life of the asset is five years. Residual value at the end of five years is estimated to be $57,000. Calculate the depreciation expense per year using the straight−line method. A. $247,600 B. $202,000 C. $190,600 D. $252,500 Regarding impairment of intangible assets, which of the following statements is incorrect? A. Intangible assets are impaired when there has been a permanent decline in the value of the asset. B. Impairment occurs when the fair value of an intangible asset is less than the book value. C. Intangible assets with an indefinite life are tested for impairment annually. D. If any impairment occurs, the company records a loss in the period in which the intangible asset was acquired. Freeman Company owns a delivery truck. Which of the following costs, associated with the truck, will be capitalized and depreciated? A. normal engine repair B. replacement of tires C. modification for new use D. oil change and lubrication Which of the following is an expense that results from the usage of a natural resource? A. amortization B. depreciation C. depletion D. obsolescence A fully depreciated plant asset ________. A. is no longer reported on the balance sheet B. can no longer be used in the business C. is removed from the accounting records D. can be discarded, sold, or exchanged for another plant asset Which of the following requires businesses to record depreciation? A. going concern principle B. matching principle C. revenue recognition principle D. cost principle Danube Company purchased a used machine for $16,000. The machine required installation costs of $6,000 and insurance while in transit of $1,300. At which of the following amounts would the machine be recorded? A. $16,000 B. $23,300 C. $22,000 D. $17,300 Bachman Company plans to develop a shopping center. In the first quarter, the following amounts were incurred: Acquisition of land $20,000 Surveys and legal fees 800 Land clearing 1,100 Fencing 2,000 Install lighting and signage 1,660 What amount should be recorded as the cost of the land in the company's books? A. $23,560 B. $23,100 C. $23,900 D. $21,900 In 2024, a company purchased a small business for $250,000. The market value of the small business's assets was $400,000, and the market value of the liabilities was $200,000. The company recorded goodwill of $50,000 at the time of acquisition. At the end of 2025, it measured goodwill and found it had a remaining fair value of only $20,000. At year−end 2025, the company will ________. A. record an impairment loss B. record a gain in goodwill C. record accumulated depletion D. record a loss on sale of assets On January 1, 2024, Tyson Manufacturing Company purchased a machine for $41,200,000. Tyson's management expects to use the machine for 28,000 hours over the next six years. The estimated residual value of the machine at the end of the sixth year is $47,000. The machine was used for 4,600 hours in 2024 and 5,800 hours in 2025. What is the depreciation expense for 2024 if the company uses the units−of−production method of depreciation? (Round any intermediate calculations to two decimal places, and your final answer to the nearest dollar.) A. $8,524,550 B. $6,760,850 C. $13,733,333 D. $6,768,578 Which of the following should be included in the cost of land? A. cost of installing signage B. cost of installing fences C. cost to clear the land of old buildings D. cost to build sidewalks on the land Which of the following items should be amortized? A. natural resources B. tangible property, plant, and equipment, other than land C. goodwill D. patents, copyrights, trademarks Which of the following depreciation methods allocates a varying amount of depreciation to expense each year based on an asset's usage? A. the annuity method B. the straight−line method C. the units−of−production method D. the double−declining−balance method The expected value of an asset at the end of its useful life is known as ________. A. residual value B. market value C. book value D. carrying value Equipment was originally acquired for $208,000 and has accumulated depreciation of $90,000. The business exchanges this equipment for new equipment. The new equipment has a market value of $303,000 and the business pays $51,000 cash. Assume the exchange has commercial substance. The exchange results in a ________. A. gain of $134,000 B. loss of $185,000 C. gain of $185,000 D. loss of $134,000 Which of the following depreciation methods always allocates a higher amount of depreciation in earlier years than in later years? A. the double−declining−balance method B. the straight−line method C. the units−of−production method D. the first−in, first−out method The cost of an asset is $1,020,000, and its residual value is $140,000. Estimated useful life of the asset is five years. Calculate depreciation for the second year using the double−declining−balance method of depreciation. A. $176,000 B. $204,000 C. $244,800 D. $352,000 A photocopier has an original cost of $100,000 and accumulated depreciation of $92,000. If the business discards this plant asset, the result is ________. A. a loss of $8,000 B. a gain of $8,000 C. a loss of $92,000 D. no gain or no loss Westin Delivery Service owns a delivery truck. Which of the following costs, associated with the truck, will be treated as a revenue expenditure? A. oil change and lubrication B. modification for new use C. addition to storage capacity D. major engine overhaul Which of the following is the correct accounting treatment for a patent? A. A patent must be capitalized and amortized over 20 years or less. B. A patent must be depreciated or impaired, but not amortized. C. A patent must be shown as a current asset on the balance sheet. D. A patent must be expensed, not capitalized, in the period in which it is purchased. The cost of an asset is $1,150,000, and its residual value is $160,000. Estimated useful life of the asset is four years. Calculate depreciation for the first year using the double−declining−balance method of depreciation. A. $287,500 B. $575,000 C. $247,500 D. $495,000 Motor Sales sold its old office furniture for $5,000. The original cost was $15,000, and at the time of sale, accumulated depreciation was $14,000. What is the effect of this transaction? A. gain of $5,000 B. loss of $4,000 C. loss of $5,000 D. gain of $4,000 Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2 14.1 14.2 15.1 15.2
Learnsmart 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | Final Exam 1 2 Homework Help? |
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |