|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2
Learnsmart 1.1 2.1 3.1 4.1 5.1 6.1 7.1 8.1 9.1 10.1 11.1 12.1 13.1 13.2 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | Final Exam 1 2
Principals Of Financial Accounting Homework 8 Part 1
Milano Gallery purchases the copyright on an oil painting
for $330,000 on
January 1, 2017. The copyright legally protects its owner for 12 more years. The company plans to market and sell prints of the original for 19 years. Prepare entries to record the purchase of the copyright on January 1, 2017, and its annual amortization on December 31, 2017. 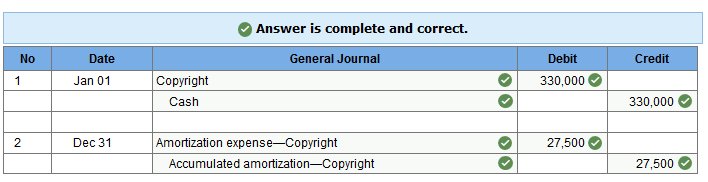
Gilly Construction trades in an old tractor for a new tractor, receiving a $26,000 trade-in allowance and paying the remaining $78,000 in cash. The old tractor had cost $91,000, and straight-line accumulated depreciation of $49,375 had been recorded to date under the assumption that it would last eight years and have a $12,000 salvage value. Answer the following questions assuming the exchange has commercial substance. 1. What is the book value of the old tractor at the time of exchange? 2. What is the loss on this asset exchange? 3. What amount should be recorded (debited) in the asset account for the new tractor? 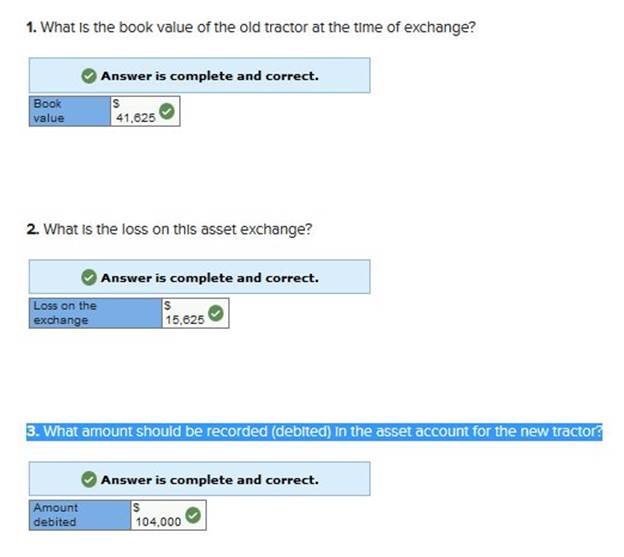
$650,000 cost less $487,500 accumulated depreciation. The building is depreciated on a straight-line basis assuming a 20-year life and no salvage value. During the first week in January of the current calendar year, major structural repairs are completed on the building at a $65,000 cost. The repairs extend its useful life for 5 years beyond the 20 years originally estimated. 1. Determine the building’s age (plant asset age) as of the prior year-end balance sheet date. 2. Prepare the entry to record the cost of the structural repairs that are paid in cash. 
3. Determine the book value of the building immediately after the repairs are recorded. 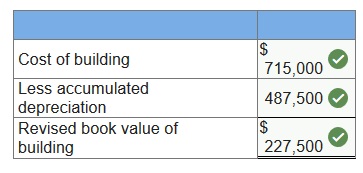
4. Prepare the entry to record the current calendar year’s depreciation. 
Quick Co. acquired the following assets from a liquidating competitor for a $200,000 lump-sum purchase price: Competitor's carrying amount Fair value Inventory $ 70,000 50,000 Land 40,000 50,000 Building 110,000 150,000 $220,000 $250,000 What amount should Quick report as the cost of the building? $120,000 $100,000 $200,000 $150,000 150,000 / 250,000 = .60 200,000 x .60 = 120,000 On April 2, 2017, Montana Mining Co. pays $4,248,270 for an ore deposit containing 1,598,000 tons. The company installs machinery in the mine costing $238,000, with an estimated seven-year life and no salvage value. The machinery will be abandoned when the ore is completely mined. Montana begins mining on May 1, 2017, and mines and sells 142,700 tons of ore during the remaining eight months of 2017. Prepare the December 31, 2017, entries to record both the ore deposit depletion and the mining machinery depreciation. Mining machinery depreciation should be in proportion to the mine’s depletion. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answers to the nearest whole number.) 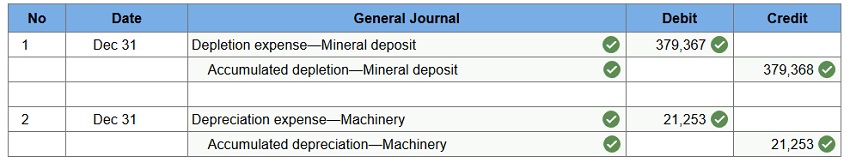
On January 1, 2017, Robinson Company purchased Franklin Company at a price of $3,900,000. The fair market value of the net assets purchased equals $2,750,000. What is the amount of goodwill that Robinson records at the purchase date? estimated useful life of eight years and a salvage value of $60,000. Hall chose to depreciate the machine using the double-declining balance method. What was the carrying amount of the machine in Hall's balance sheet at the end of its second year of operations? $60,000 $61,250 $80,000 $78,750 8 / 2 = .25 140,000 x .25 = 35,000 140,000 – 35,000 = 105,000 105,000 x .25 = 26,250 105,000 – 26,250 = 78,750 During the current year, property owned by Arp Co. was acquired by the city in connection with a condemnation proceeding, resulting in a payment of $100,000 to Arp. The property's carrying amount was $70,000. Arp paid $45,000 in the current year for replacement property. In Arp's income statement for the current year ended December 31, what amount of gain should be reported on this involuntary conversion, disregarding income tax considerations? $15,000 $0 $25,000 $30,000 100,000 - 70,000 = 30,000 In January Year 1, Huff Mining Corporation purchased a mineral mine for $3.6 million with removable ore estimated by geological surveys at 2,160,000 tons. The property has an estimated fair value of $360,000 after the ore has been extracted. Huff incurred $1,080,000 of development costs preparing the property for the extraction of ore. During Year 3, 270,000 tons were removed and 240,000 tons were sold. For the year ended December 31, Year 3, Huff should include what amount of depletion in its cost of goods sold? $360,000 $405,000 $540,000 $480,000 3,600,000 - 360,000 + 1,080,000 = 4,320,000 4,320,000 / 2,160,000 = 2.0 240,000 × 2 = 480,000 Cantor Co. purchased a coal mine for $2,000,000. It cost $500,000 to prepare the coal mine for extraction of the coal. It was estimated that 750,000 tons of coal would be extracted from the mine during its useful life. Cantor planned to sell the property for $100,000 at the end of its useful life. During the current year, 15,000 tons of coal were extracted and sold. What would be Cantor's depletion amount per ton for the current year? $3.20 $2.50 $2.66 $3.30 $3.20 2,000,000 - 100,000 + 500,000 = 2,400,000 2,400,000 / 750,000 = 3.20 Four years ago on January 2, Randall Co. purchased a long-lived asset. The purchase price of the asset was $250,000, with no salvage value. The estimated useful life of the asset was 10 years. Randall used the straight-line method to calculate depreciation expense. An impairment loss on the asset of $30,000 was recognized on December 31 of the current year. The estimated useful life of the asset at December 31 of the current year did not change. What amount should Randall report as depreciation expense in its income statement for the next year? $20,000 $30,000 $25,000 $22,000 250,000 / 10 x 4 = 100,000 250,000 – 100,000 – 30,000 = 120,000 120,000 / 6 = 20,000 Equipment bought by Wilson Steam Generating Company 3 years ago was charged to equipment expense in error. The cost of the equipment was $100,000, with no expected salvage value and a 10-year estimated life. Wilson uses the straight-line depreciation method on similar equipment. The error was discovered at the end of Year 3 prior to the issuance of Wilson's financial statements. After correction of the error, the correct carrying value of the equipment will be $30,000 $80,000 $70,000 $100,000 100,000 x 3 / 10 = 30,000 100,000 – 30,000 = 70,000 On January 2, Dix Co. replaced its boiler with a more efficient one. The following information was available on that date: Purchase price of new boiler $ 60,000 Carrying amount of old boiler 5,000 Fair value of old boiler 2,000 Installation cost of new boiler 8,000 The old boiler was sold for $2,000. What amount should Dix capitalize as the cost of the new boiler? $60,000 $66,000 $68,000 $63,000 60,000 + 8,000 = 68,000 Turtle Co. purchased equipment on January 2, Year 1, for $50,000. The equipment had an estimated 5-year service life. Turtle's policy for 5-year assets is to use the 200% double-declining-balance depreciation method for the first 2 years of the asset's life, and then switch to the straight-line depreciation method. In its December 31, Year 3, balance sheet, what amount should Turtle report as accumulated depreciation for equipment? $38,000 $42,000 $39,200 $30,000 $38,000 50,000 × .4 = 20,000 50,000 - 20,000 × .4 = 12,000 50,000 - 20,000 - 12,000 / 3 = 6,000 20,000 + 12,000 + 6,000 = 38,000 On July 1, one of Rudd Co.'s delivery vans was destroyed in an accident. On that date, the van's carrying value was $2,500. On July 15, Rudd received and recorded a $700 invoice for a new engine installed in the van in May and another $500 invoice for various repairs. In August, Rudd received $3,500 under its insurance policy on the van, which it plans to use to replace the van. What amount should Rudd report as gain (loss) on disposal of the van in its income statement for the year? $300 $(200) $0 $1,000 $300 3,500 - 2,500 - 700 = 300 Talton Co. installed new assembly line production equipment at a cost of $185,000. Talton had to rearrange the assembly line and remove a wall to install the equipment. The rearrangement cost $12,000, and the wall removal cost $3,000. The rearrangement did not increase the life of the assembly line, but it did make it more efficient. What amount of these costs should be capitalized by Talton? $200,000 $185,000 $188,000 $197,000 185,000 + 12,000 + 3,000 = 200,000 On January 1, Year 1, Bay Co. acquired a land lease for a 21-year period with no option to renew. The lease required Bay to construct a building in lieu of rent. The building, completed on January 1, Year 2, at a cost of $840,000, will be depreciated using the straight-line method. At the end of the lease, the building's estimated fair value will be $420,000. What is the building's carrying amount in Bay's December 31, Year 2, balance sheet? $798,000 $820,000 $800,000 $819,000 840,000 / 20 = 42,000 840,000 – 42,000 = 798,000 On January 1, Nick Co. purchased a delivery truck for $60,000. The truck's salvage value is $2,000, and its estimated useful life is 10 years. The productive life of the truck is estimated to be 100,000 miles. During the first year, the truck was driven 19,000 miles. Nick uses the double-declining balance method of depreciation. What amount of depreciation expense should Nick record for the first year? $11,600 $11,020 $5,800 $12,000 60,000 × 2 × .10 = 12,000 Amble, Inc., exchanged a truck with a carrying amount of $12,000 and a fair value of $20,000 for another truck and $5,000 cash. The fair value of the truck received was $15,000. The exchange was not considered to have commercial substance. At what amount should Amble record the truck received in the exchange? $9,000 $12,000 $15,000 $7,000 20,000 – 5,000 = 15,000 Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2
Learnsmart 1.1 2.1 3.1 4.1 5.1 6.1 7.1 8.1 9.1 10.1 11.1 12.1 13.1 13.2 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | Final Exam 1 2
|
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |