|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2
Learnsmart 1.1 2.1 3.1 4.1 5.1 6.1 7.1 8.1 9.1 10.1 11.1 12.1 13.1 13.2 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | Final Exam 1 2
Principals Of Financial Accounting Homework 7 Part 1
At December 31, 2017, Hawke Company reports the following
results for its calendar year.
In addition, its unadjusted trial balance includes the following items.
1. Prepare the adjusting entry for this company to recognize bad debts under each of the following independent assumptions. Bad debts are estimated to be 3% of credit sales. Bad debts are estimated to be 2% of total sales. An aging analysis estimates that 6% of year-end accounts receivable are uncollectible. Adjusting entries (all dated December 31, 2017). 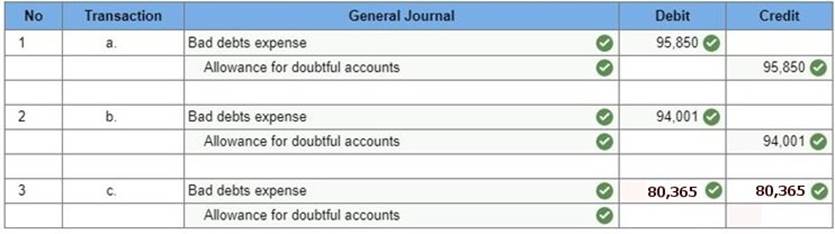
At December 31, 2017, Hawke Company reports the following results for its calendar year.
In addition, its unadjusted trial balance includes the following items.
2. Show how Accounts Receivable and the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts appear on its December 31, 2017, balance sheet given the facts in part 1a. 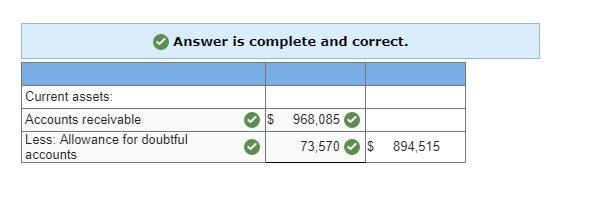 At December 31, 2017, Hawke Company reports the following results for its calendar year.
In addition, its unadjusted trial balance includes the following items.
3. Show how Accounts Receivable and the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts appear on its December 31, 2017, balance sheet given the facts in part 1c. 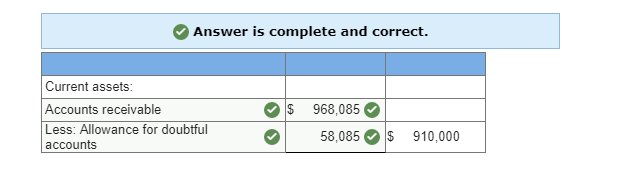
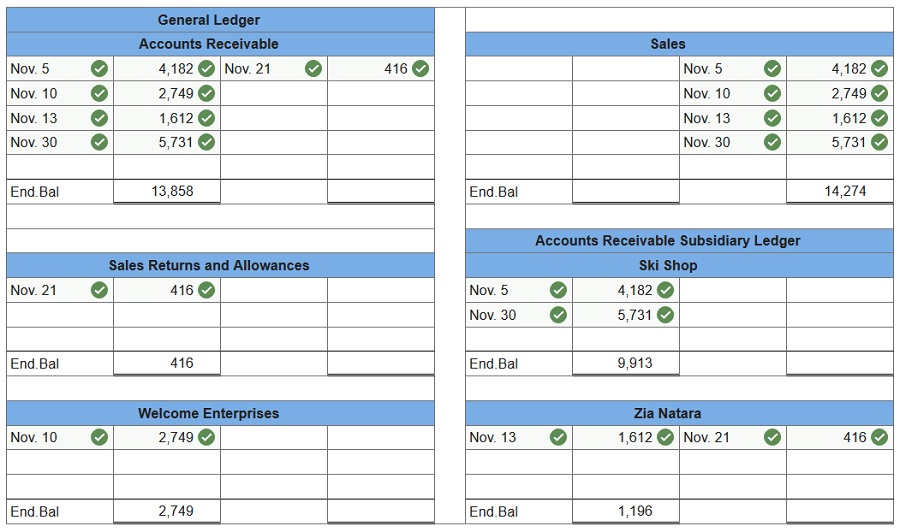
2. Prepare a schedule of accounts receivable. 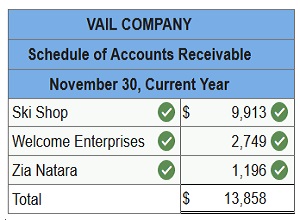
Levine Company uses the perpetual inventory system and allows customers to use two credit cards in charging purchases. With the Suntrust Bank Card, a 4% service charge for credit card sales is assessed. The second credit card that Levine accepts is the Continental Card. Continental assesses a 2.5% charge on sales for using its card. Apr 8 – Sold merchandise for $4,600 (that had cost $3,399) and accepted the customer’s Suntrust Bank Card. Apr 12 – Sold merchandise for $3,200 (that had cost $2,074) and accepted the customer’s Continental Card. Prepare journal entries to record the above selected credit card transactions of Levine Company. (Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) 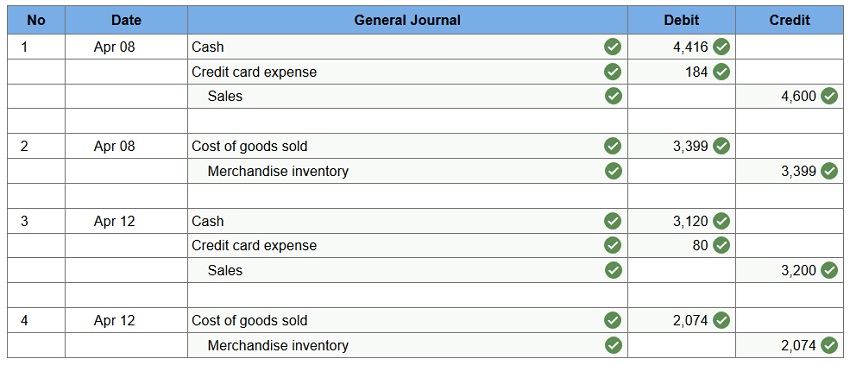
Z-Mart uses the perpetual inventory system and allows customers to use the Z-Mart store credit card in charging purchases. Z-Mart assesses a per-month interest fee for any unpaid balance on its store credit card at each month-end. Apr 30 – Z-Mart sold merchandise for $1,900 (that had cost $1,100) and accepted the customer’s Z-Mart store credit card. May 31 – Z-Mart recorded $7 of interest earned from its store credit card as of this month-end. Prepare journal entries to record the above selected credit card transactions of Z-Mart. 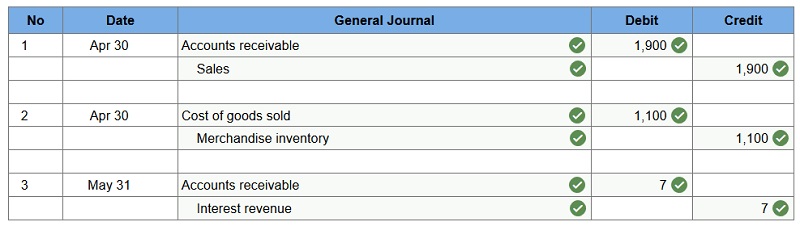
Dexter Company applies the direct write-off method in accounting for uncollectible accounts. March 11 – Dexter determines that it cannot collect $8,400 of its accounts receivable from its customer Leer Company. March 29 – Leer Company unexpectedly pays its account in full to Dexter Company. Dexter records its recovery of this bad debt. Prepare journal entries to record the above selected transactions of Dexter. 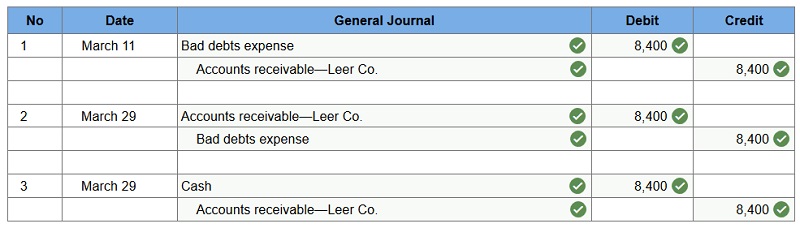
At year-end (December 31), Chan Company estimates its bad debts as 0.50% of its annual credit sales of $837,000. Chan records its Bad Debts Expense for that estimate. On the following February 1, Chan decides that the $419 account of P. Park is uncollectible and writes it off as a bad debt. On June 5, Park unexpectedly pays the amount previously written off. Prepare the journal entries for these transactions. 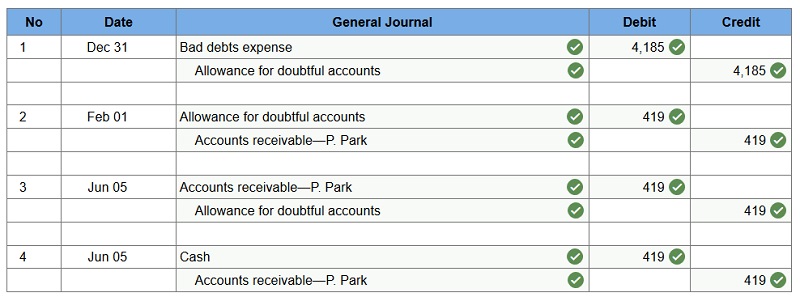
The following accounts were abstracted from Roxy Co.'s unadjusted trial balance at December 31: Debit Credit (Cr) Accounts receivable 1,000,000 Allowance for uncollectible accounts 8,000 Net credit sales 3,000,000 Roxy estimates that 3% of the gross accounts receivable will become uncollectible. After adjustment at December 31, the allowance for uncollectible accounts should have a credit balance of: A. $90,000 B. $82,000 C. $38,000 D. $30,000 1,000,000 x .03 = 30,000 If the liabilities of a business increased $75,000 during a period of time and the equity in the business decreased $30,000 during the same period, the assets of the business must have: A. Decreased $105,000 B. Decreased $45,000 C. Increased $30,000 D. Increased $45,000 E. Increased $105,000 Change in Assets = Change in Liabilities + Change in Equity Change in Assets = $75,000 + (-$30,000) = + $45,000 For the year ended December 31, Beal Co. estimated its allowance for uncollectible accounts using the year-end aging of accounts receivable. The following data are available: Allowance for uncollectible accounts, 1/1 42,000 Provision for uncollectible accounts (2% on credit sales of $2,000,000) 40,000 Uncollectible accounts written off, 11/30 46,000 Estimated uncollectible accounts per aging, 12/31 52,000 After year-end adjustment, the uncollectible accounts expense should be: A. $46,000 B. $48,000 C. $52,000 D. $56,000 42,000 + 40,000 = 82,000 82,000 – 46,000 = 36,000 52,000 – 36,000 = 16,000 40,000 + 16,000 = 56,000 Fast-Forward has net income of $18,955 and assets at the beginning of the year of $200,000. Its assets at the end of the year total $246,000. Compute its return on assets. A. 7.7% B. 8.5% C. 9.5% D. 11.8% E. 13.0% 18,955 / [(200,000 + 246,000) / 2] = 18,955 / 223,000 = 0.85 or 8.5% A company has net credit sales of $900,000 for the year and it estimates that uncollectible accounts will be 2% of sales. If Allowance for Doubtful Accounts has a credit balance of $1,000 prior to adjustment, its balance after adjustment will be a credit of a. $18,000 b. $19,000 c. $17,980 d. $17,000 (900,000 x .02) + 1000 = 19,000 Roth Inc. received from a customer a one-year, $500,000 note bearing annual interest of 8 percent. After holding the note for six months, Roth discounted the note at Regional Bank at an effective interest rate of 10 percent. What amount of cash did Roth receive from the bank? A. $540,000 B. $523,810 C. $513,000 D. $495,238 500,000 x .08 = 40,000 500,000 + 40,000 = 540,000 540,000 x .5 x .10 = 27,000 540,000 – 27,000 = 513,000 On July 9, Mifflin Company receives an $8,500, 90-day, 8% note from customer Payton Summers as payment on account. Compute the amount due at maturity for the note. (Use 360 days a year.) $8,628 $8,192 $8,613 $8,500 $8,670 An analysis and aging of the accounts receivable of Yates Company at December 31 reveal these data: Accounts receivable $ 1,600,000 Allowance for doubtful accounts per books before adjustment (credit) 100,000 Amounts expected to become uncollectible 130,000 What is the cash realizable value of the accounts receivable at December 31 after adjustment? a. $1,370,000 b. $1,500,000 c. $1,600,000 d. $1,470,000 d. $1,470,000 1,600,000 - 130,000 On the December 31 balance sheet of Mann Co., the current receivables consisted of the following: Trade accounts receivable $93,000 Allowance for uncollectible accounts (2,000) Claim against shipper for goods lost in transit (November) 3,000 Selling price of unsold goods sent by Mann on consignment at 130% of cost (not included in Mann's ending inventory) 26,000 Security deposit on lease of warehouse used for storing some inventories 30,000 Total $150,000 At December 31, the correct total of Mann's current net receivables was: A. $94,000 B. $120,000 C. $124,000 D. $150,000 93,000 – 2,000 – 91,000 91,000 + 3,000 = 94,000 A company has net sales of $1,200,000 and average accounts receivable of $400,000. What is its accounts receivable turnover for the period? 0.33 5.00 20.0 73.0 3.0 Under IFRS, the term provision: Refers to expense Usually refers to a liability whose amount or timing is uncertain. Means establishing a provision for bad debts. Means establishing a contra-asset account. Means establishing an asset account. Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2
Learnsmart 1.1 2.1 3.1 4.1 5.1 6.1 7.1 8.1 9.1 10.1 11.1 12.1 13.1 13.2 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | Final Exam 1 2
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |