|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2
Learnsmart 1.1 2.1 3.1 4.1 5.1 6.1 7.1 8.1 9.1 10.1 11.1 12.1 13.1 13.2 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | Final Exam 1 2
Principals Of Financial Accounting Homework 4 Part 1
Exercise 4-21C Recording estimates of future returns LO
P6
Lopez Company reports unadjusted first-year merchandise sales of $136,000 and cost of merchandise sales of $47,600. a. Compute gross profit using the unadjusted numbers. 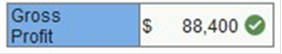
The company expects future returns and allowances equal to 4% of sales and 4% of cost of sales. b-1&2. Prepare the year-end adjusting entry to record the sales expected to be refunded and cost side of sales returns and allowances. 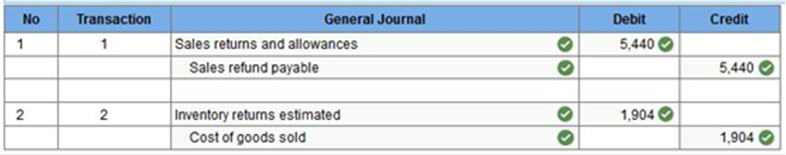
b-3. Compute gross profit using the adjusted numbers. .04 x 136,000 = 5,440 .04 x 47,600 = 1,904 136,000 – 47,600 – 5,440 + 1,904 Exercise 4-8 Inventory and cost of sales transactions in T-accounts LO P1, P2 The following supplementary records summarize Tesla Company’s merchandising activities for year 2017 (it uses a perpetual inventory system).
Record the summarized activities in the T-accounts below. 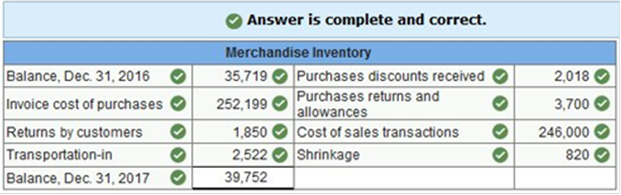
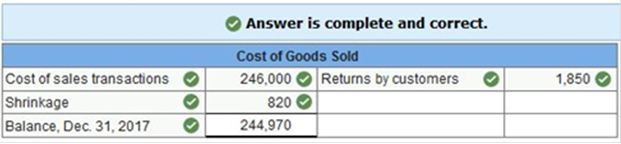

Exercise 4-6 Recording sales, purchases, and cash discounts-buyer and seller LO P1, P2 Santa Fe Retailing purchased merchandise “as is” (with no returns) from Mesa Wholesalers with credit terms of 2/10, n/60 and an invoice price of $28,000. The merchandise had cost Mesa $19,096. Assume that both buyer and seller use a perpetual inventory system and the gross method. 1. Prepare entries that the buyer records for the (a) purchase, (b) cash payment within the discount period, and (c) cash payment after the discount period. 2. Prepare entries that the seller records for the (a) sale, (b) cash collection within the discount period, and (c) cash collection after the discount period. 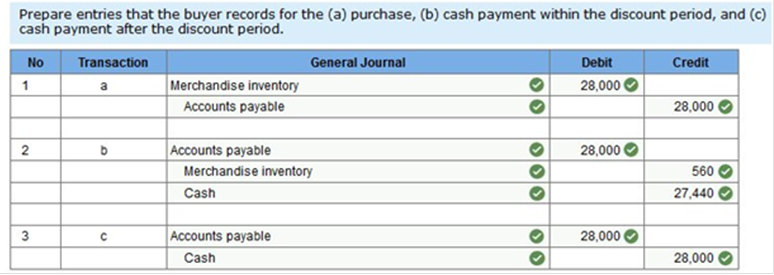
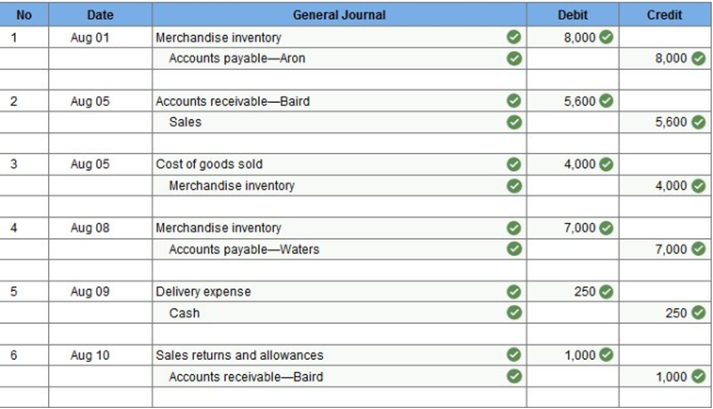
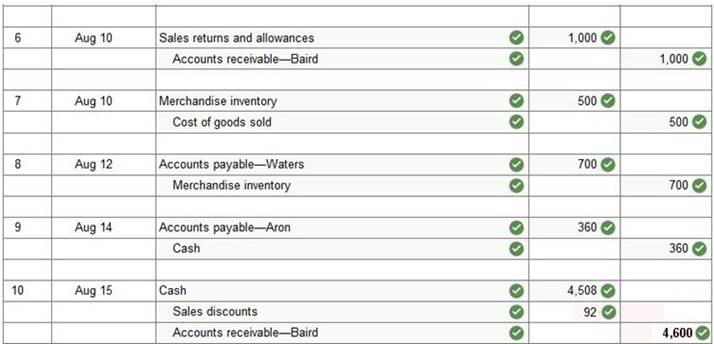
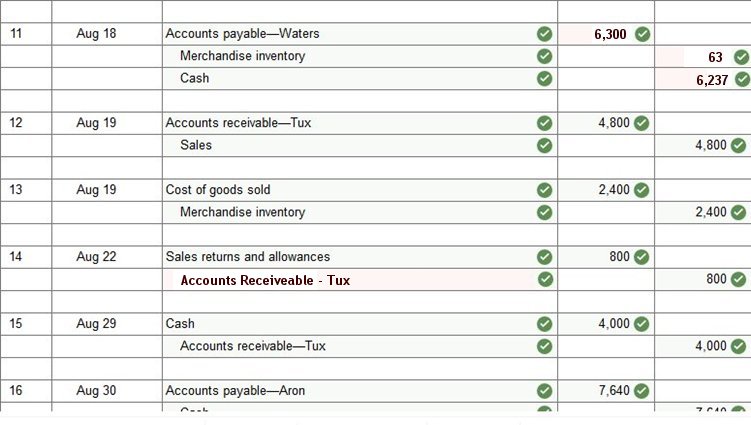
Problem 4-2A Preparing journal entries for merchandising activities-perpetual system LO P1, P2 Prepare journal entries to record the following merchandising transactions of Lowe’s, which uses the perpetual inventory system and the gross method. (Hint: It will help to identify each receivable and payable; for example, record the purchase on August 1 in Accounts Payable—Aron.)
Benson Company uses the periodic inventory system. Sales for 2013 were $470,000 while operating expenses were $175,000. Beginning and ending inventories for 2013 were $70,000 and $60,000, respectively. Net purchases were $180,000 while freight in was $15,000. The net income or loss for 2013 was: A) $90,000 net income B) $30,000 net income C) $10,000 net income D) $30,000 net loss E) None of the above 70,000 $180,000 + $15,000 - $60,000 - $175,000 = $90,000 Smith Company purchases $60,000 of inventory during the period and sells $18,000 of it for $30,000. Beginning of the period inventory was $3,000. What is the company's inventory balance to be reported on its balance sheet at year end? A) $18,000 B) $ 2,000 C) $45,000 D) $ 3,000 $3,000 + 60,000 - $18,000 = $45,000 On August 1, Thomas & Sons bought goods with a list price of $4,800, terms 2/10, n/30. The firm records purchases at invoice price, using the periodic inventory system. On August 5, Thomas returned goods with a list price of $600 for credit. If Thomas paid the supplier the amount due on August 9, the appropriate entry would be: A/c Payable is debited 4,200 Cash is credited $4,116 Purchase Disc credited $84. Sysco Company purchased $4,000 worth of merchandise, FOB shipping point, under the periodic method. Transportation costs were an additional $350. The company later returned $750 worth of merchandise and paid the invoice within the 2% cash discount period. The total amount paid for this merchandise is: A) $3,535 B) $3,520 C) $4,263 D) $3,528 Discount = (4,000 - 750) x 2% = 65 Amt paid = 4,000 - 750 - 65 + 350 (shipping) = 3,535 A company's current assets are $29,240, its quick assets are $16,290 and its current liabilities are $12,820. Its acid-test ratio equals 1.27 16,290 / 12,820 = 1.27 Prince Company had cash sales of $94,275, credit sales of $83,450, sales returns and allowances of $1,700, and sales discounts of $3,475. Prince's net sales for this period equal: $172,550 Net Sales = $94,275 + $83,450 − $1,700 − $3,475 = $172,550 A company purchased $1,800 of merchandise on July 5 with terms 2/10, n/30. On July 7, it returned $200 worth of merchandise. On July 28, it paid the full amount due. Assuming the company used a perpetual inventory system, and records purchases using the gross methods, the correct journal entry to record the merchandise return on July 7 is: Accounts Payable $200 Merchandise Inventory $200 Which of the following accounts would be closed at the end of the accounting period with a debit? Sales Which of the following statements regarding merchandise inventory is false? Merchandise inventory appears on the balance sheet of a service company. Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2
Learnsmart 1.1 2.1 3.1 4.1 5.1 6.1 7.1 8.1 9.1 10.1 11.1 12.1 13.1 13.2 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | Final Exam 1 2
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |