|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2
Learnsmart 1.1 2.1 3.1 4.1 5.1 6.1 7.1 8.1 9.1 10.1 11.1 12.1 13.1 13.2 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | Final Exam 1 2
Principals Of Financial Accounting Homework 1 Part 1
Identify how each of the
following separate transactions 1 through 10 affects financial
statements.
ü For increases, place a “+” and the dollar amount in the column or columns. ü For decreases, place a “−” and the dollar amount in the column or columns. ü Some cells may contain both an increase (+) and a decrease (−) along with dollar amounts. ü The first transaction is completed as an example. ü For the balance sheet, identify how each transaction affects total assets, total liabilities, and total equity. ü For the income statement, identify how each transaction affects net income. ü For the statement of cash flows, identify how each transaction affects cash flows from operating activities, ü cash flows from investing activities, and cash flows from financing activities. 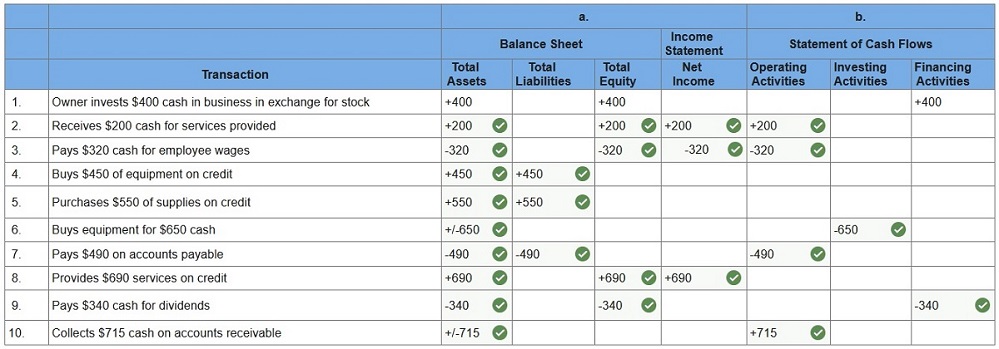
Gabi Gram started The Gram Co., a new business that began operations on May 1. The Gram Co. completed the following transactions during its first month of operations.
Enter the amount of each transaction on individual items of the accounting equation. Do not determine new account balances after each transaction. (Enter the transactions in the given order. Enter reductions to account balances with a minus sign. Select “NA” if the transaction does not include an expense.) 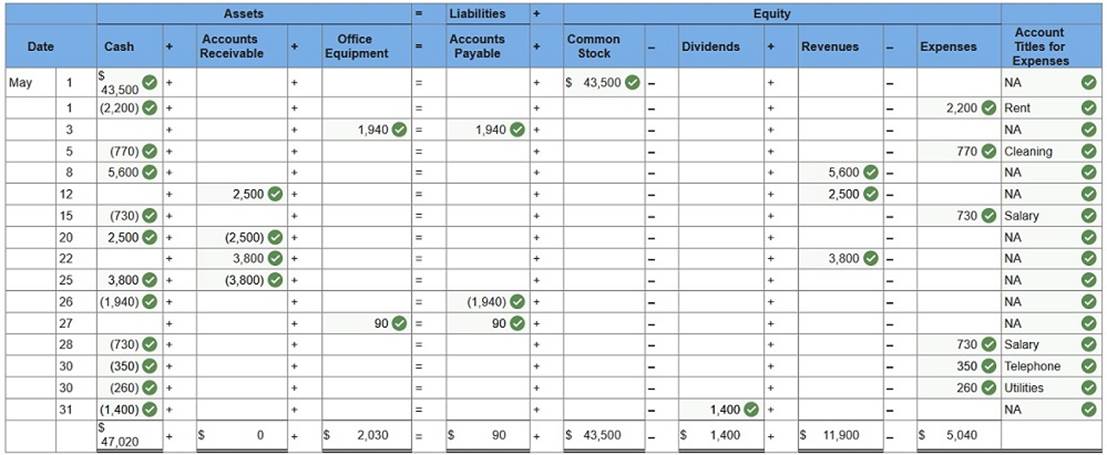
Gabi Gram started The Gram Co., a new business that began operations on May 1. The Gram Co. completed the following transactions during its first month of operations.
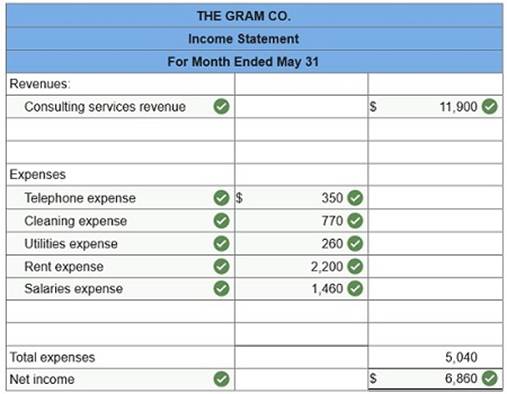
Prepare statement of retained earnings for May. 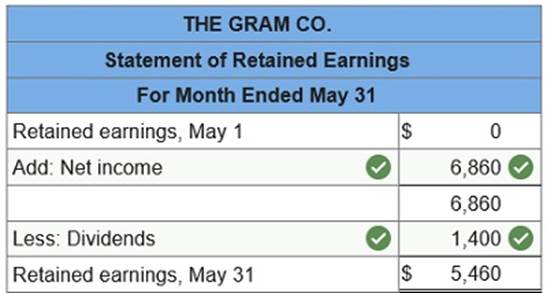
Prepare balance sheet for May 31. 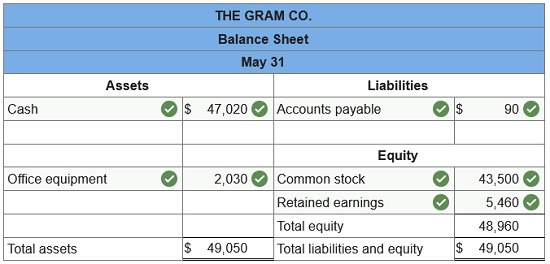
Prepare statement of cash flows for May. 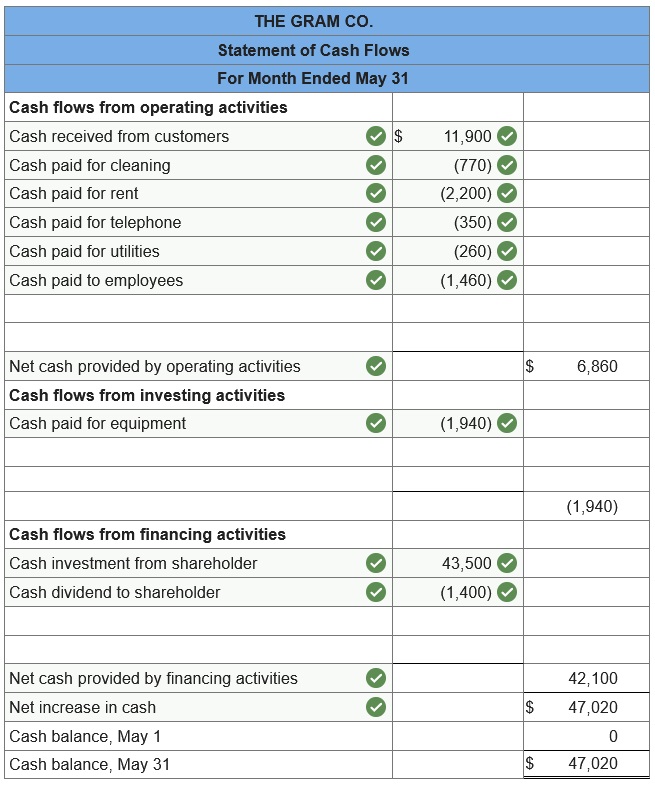
Enter the amount of each transaction on individual items of the accounting equation. (Enter reductions to account balances with a minus sign.) 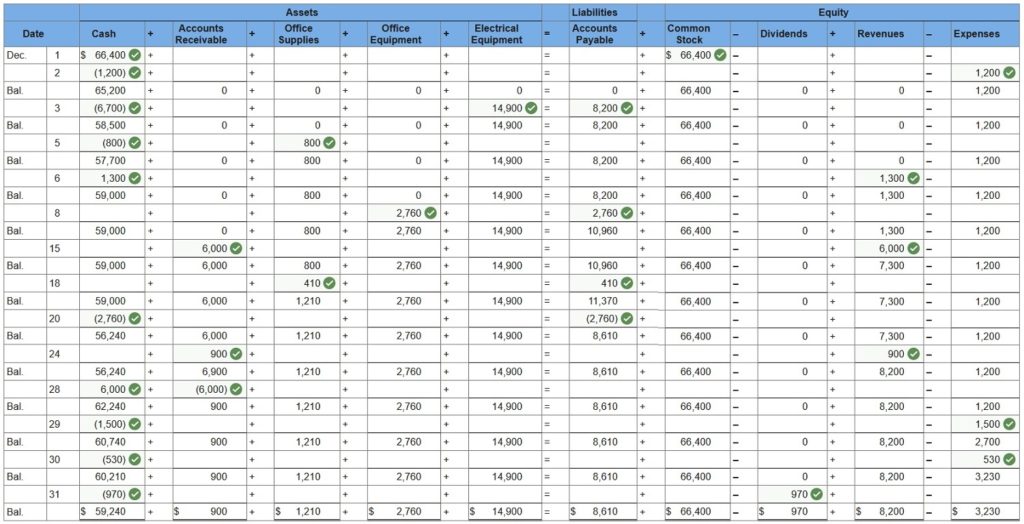
Sanyu Sony started a new business and completed these transactions during December.
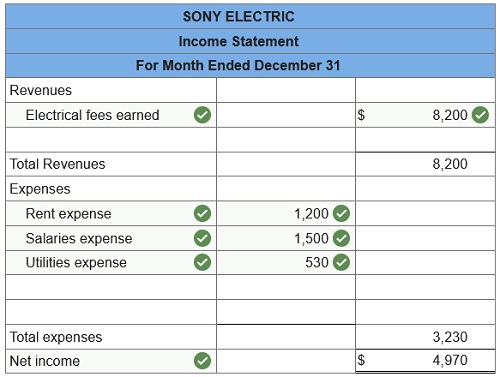
Prepare a statement of retained earnings for the current month. 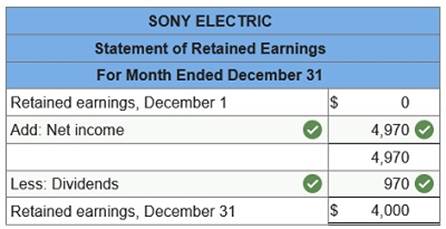
reports the following income statement accounts for the year ended December 31, 2015 (euros in millions).
Using the above information prepare BMW’s income statement for the year ended December 31, 2015. (Enter your answers in millions.) 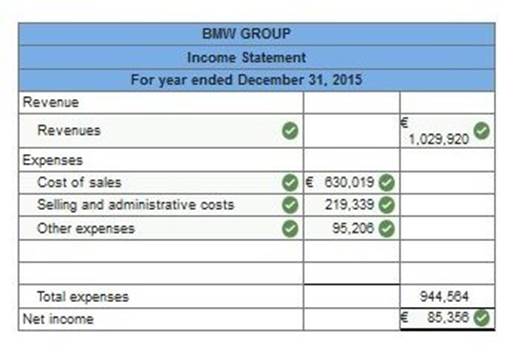
Exercise 1-20 Preparing an income statement for a global company LO P2 Ford Motor Company, one of the world’s largest automakers, reports the following income statement accounts for the year ended December 31, 2015 ($ in millions).
Using the above information prepare Ford’s income statement for the year ended December 31, 2015. (Enter your answers in millions.) 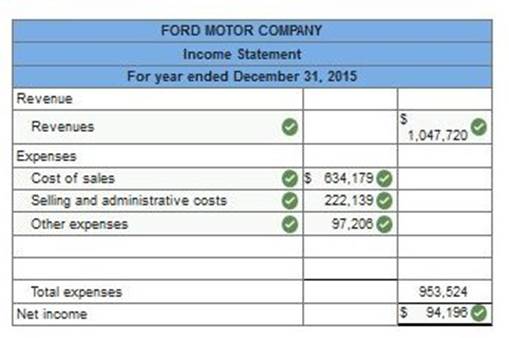
Determine the missing amount from each of the separate situations given below 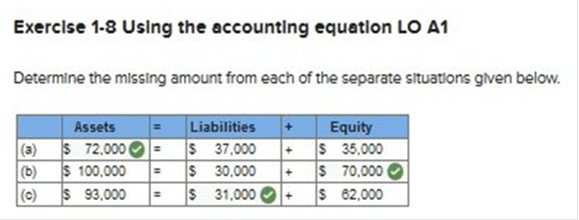
reports the following income statement accounts for the year ended December 31, 2015 (euros in millions).
Using the above information prepare BMW’s income statement for the year ended December 31, 2015. (Enter your answers in millions.) 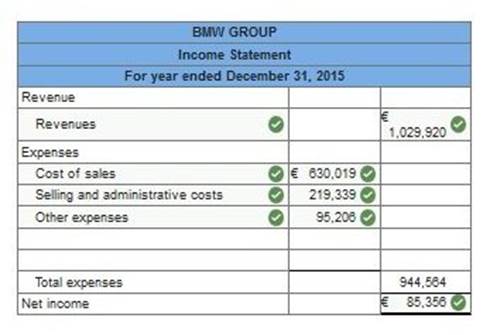
Exercise 1-20 Preparing an income statement for a global company LO P2 Ford Motor Company, one of the world’s largest automakers, reports the following income statement accounts for the year ended December 31, 2015 ($ in millions).
Using the above information prepare Ford’s income statement for the year ended December 31, 2015. (Enter your answers in millions.) 
Determine the missing amount from each of the separate situations given below 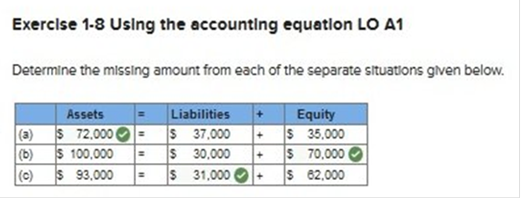
On October 1, 2021, Santana Rey launched a computer services company, Business Solutions, that is organized as a corporation and provides consulting services, computer system installations, and custom program development. Rey adopts the calendar year for reporting purposes and expects to prepare the company’s first set of financial statements on December 31, 2021. 
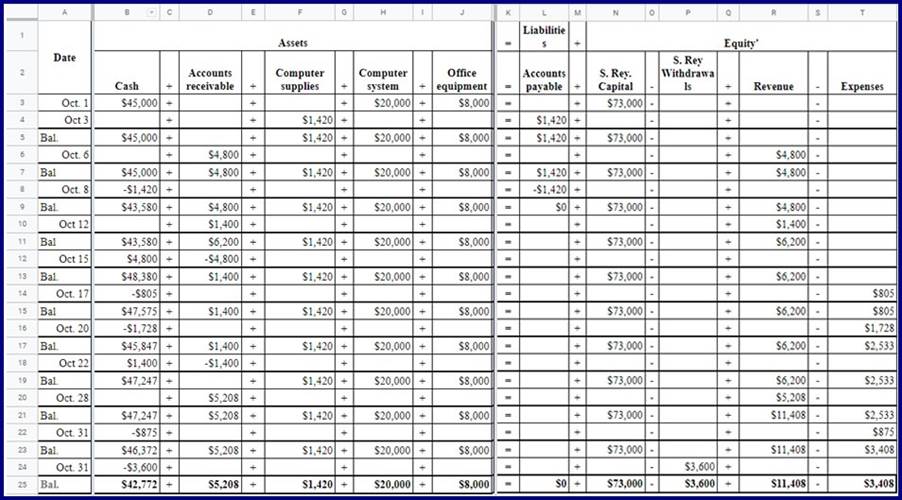
Explanation 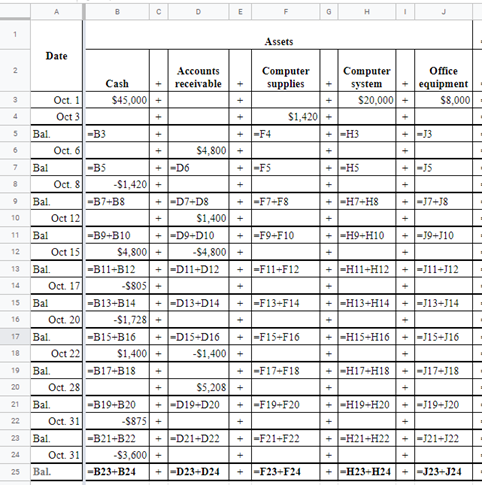 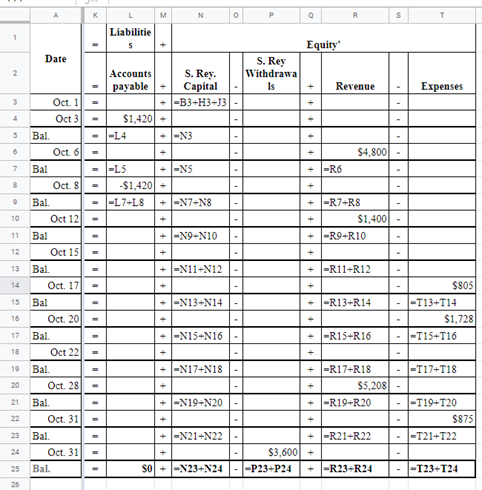
On October 31, the company's records show the following items and amounts. 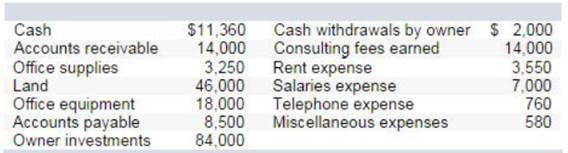
Using the above information prepare an October income statement for the business. 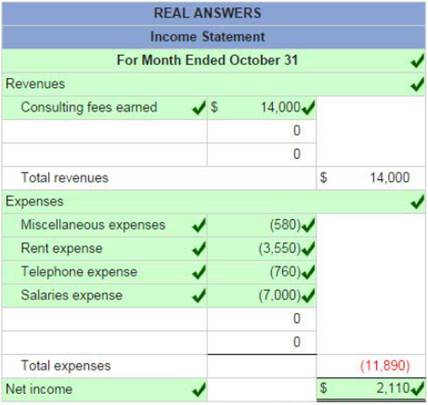
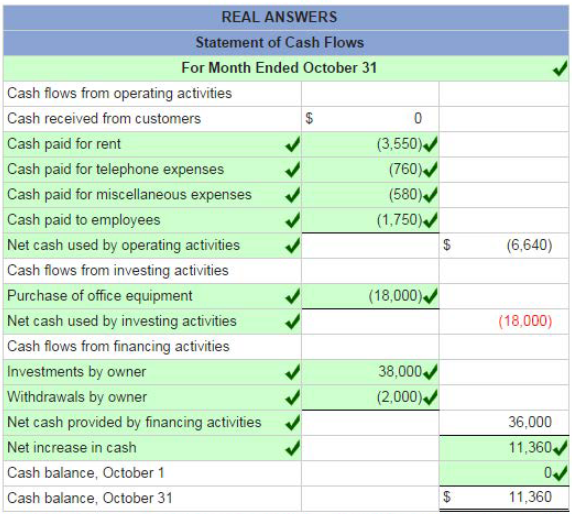
Red text indicates no response was expected. No points were deducted. On October 1, Keisha King organized Real Answers, a new consulting firm; on October 3, the owner contributed $84,000 cash. On October 3 1, the company's records show the following items and amounts. 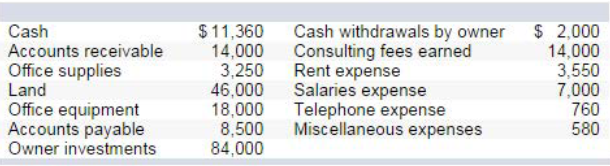
Using the above information prepare an October statement of owner's equity for Real Answers. 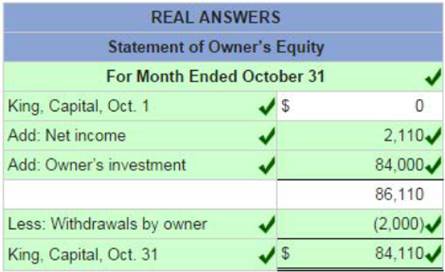
On October 1, Keisha King organized Real Answers, a new consult in g firm; on October 3, the owner contributed $84 ,000 cash. On October 31, the company's records show the following items and amounts. 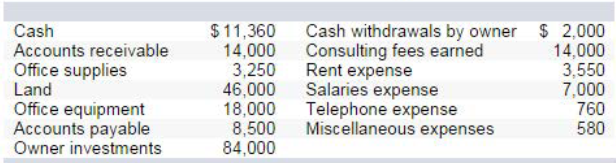
Using the above information prepare an October 31 balance sheet for Real Answers. 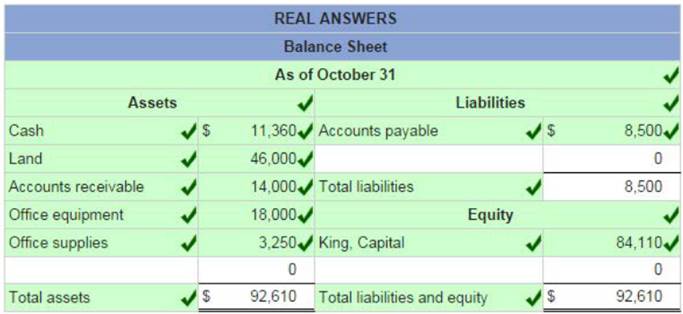
On October 1, Keisha King organized Real Answers, a new consulting firm; on October 3, the owner invested $84,000 of assets. On October 31, the company's records show the following items and amounts. 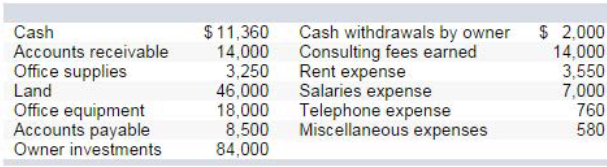

Red text indicates no response was expected. No points were deducted. Swiss Group reports net income of $40,000 for 2013. At the beginning of 2013, Swiss Group had $200,000 in assets. By the end of 20 13, assets had grown to $300,000. 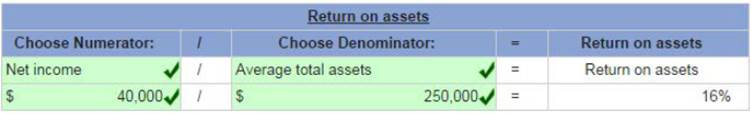
Match each description with its section from statement of cash flows. 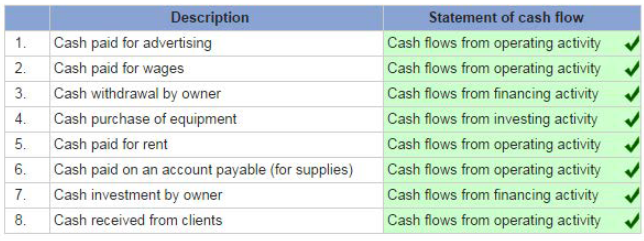
$11,000 $19,000 $49,000 $30,000 During its first year of operations, Mario Lupo formed Lupo Company as a corporation and personally invested $15,000 in the business in exchange for common stock. Lupo Company also paid dividends of $2,000. The company earned $35,000 of revenues and incurred $23,000 of expenses. At the end of the year, the company’s equity totaled: $13,000 $15,000 $25,000 $75,000 Return on assets measures a company’s ability to generate an adequate return on its investment in: common stock profitability revenues assets The return on assets for your small business was 11.2% last year and 12.6% this year. Your return on assets: Improved Worsened Stayed about the same Rosalind Company reported revenues of $111,500, expenses of $92,545, and net income of $18,955 for the year. Assets totaled $200,000 at the beginning of the year and $246,000 at the end of the year. The company’s return on assets for the year (round the percent to one decimal) is: 8.5% 5.0% 9.5% 11.8% Classify the following business activities using the drop-down list. Happenings that affect the accounting equation – Events Exchanges of value between two entities – External Transactions Exchanges within an entity – Internal Transactions The business pays $2,000 in cash to the landlord for office space rent Expenses reduce by $2,000 Equity remains unchanged Equity reduces by $2,000 Assets increase by $2,000 Liabilities reduce by $2,000 On January 31, Jean Consulting Company receives a bill for that month’s utilities in the amount of $500. Jean sets it aside because she does not plan to pay the bill until its due date of February 15. What effect, if any, does this event have on the company’s accounting equation as of January 31? The business must record this event, which would decrease cash and decrease equity on January 31. The business must record this event, which would decrease cash and increase equity on January 31. The business must record this event, which would increase liabilities and decrease equity on January 31. Because the bill is set aside for payment in February, there would be no effect on the accounting equation as of January 31. The four basic financial statements are: Income Statement, Sheet of retained earnings, Balance statement, and Statement of cash flows. Income Statement, Statement of earnings, Balance statement, and Statement of cash flows. Income sheet, Statement of retained earnings, Balance sheet, and Statement of cash flows. Income Statement, Statement of retained earnings, Balance sheet, and Statement of cash flows. Identify which items belong on the income statement. Accounts receivable, net income, and dividends Revenue, expenses and net income Cash, accounts receivable, and common stock Dividends, beginning retained earnings, ending retained earnings Identify which items belong on the statement of retained earnings. Accounts receivable, net income, and dividends Revenue, expenses and net income Cash, accounts receivable, and common stock Dividends, beginning retained earnings, ending retained earnings Identify which items belong on the balance sheet. Accounts receivable, net income, and dividends Revenue, expenses and net income Cash, accounts receivable, and common stock Dividends, beginning retained earnings, ending retained earnings Identify which items belong on the statement of cash flows. Accounts receivable, net income, and dividends Cash flows from investing, operating and financing activities Cash, accounts receivable, and common stock Dividends, beginning retained earnings, ending retained earnings Homework 1.1 1.2 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.2 5.1 5.2 6.1 6.2 7.1 7.2 8.1 8.2 9.1 9.2 10.1 10.2 11.1 11.2 12.1 12.2 13.1 13.2
Learnsmart 1.1 2.1 3.1 4.1 5.1 6.1 7.1 8.1 9.1 10.1 11.1 12.1 13.1 13.2 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | Final Exam 1 2
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |