|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
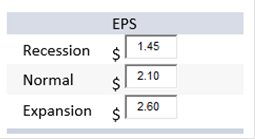
Principles Of Fianance: Homework Chapter 13 Homework 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | Final Exam 1 2 Kaelea, Inc., has no debt outstanding and a total market value of $100,000. Earnings before interest and taxes, EBIT, are projected to be $8,400 if economic conditions are normal. If there is strong expansion in the economy, then EBIT will be 24 percent higher. If there is a recession, then EBIT will be 31 percent lower. The company is considering a $35,000 debt issue with an interest rate of 6 percent. The proceeds will be used to repurchase shares of stock. There are currently 4,000 shares outstanding. Ignore taxes for this problem. a. Calculate earnings per share, EPS, under each of the three economic scenarios before any debt is issued. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answers to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.)
b. Calculate the percentage changes in EPS when the economy expands or enters a recession. (A negative answer should be indicated by a minus sign. Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answers as a percent rounded to the nearest whole number, e.g., 32.) Recession -31.00% Expansion 24.00% Assume the company goes through with recapitalization. c. Calculate earnings per share, EPS, under each of the three economic scenarios after the recapitalization. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answers to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) Recession $1.42 Normal $2.42 Expansion $3.20 d. Calculate the percentage changes in EPS when the economy expands or enters a recession. (A negative answer should be indicated by a minus sign. Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.)
Explanation: a and b. A table outlining the income statement for the three possible states of the economy is shown below. The EPS is the net income divided by the 4,000 shares outstanding. The last row shows the percentage change in EPS the company will experience in a recession or an expansion economy.
c and d. If the company undergoes the proposed recapitalization, it will repurchase: Share price = Equity / Shares outstanding Share price = $100,000 / 4,000 Share price = $25 Shares repurchased = Debt issued / Share price Shares repurchased = $35,000 / $25 Shares repurchased = 1,400 The interest payment each year under all three scenarios will be: Interest payment = $35,000(.06) Interest payment = $2,100 The last row shows the percentage change in EPS the company will experience in a recession or an expansion economy under the proposed recapitalization.
Uptown Construction is comparing two different capital structures. Plan I would result in 16,000 shares of stock and $160,000 in debt. Plan II would result in 18,000 shares of stock and $110,000 in debt. The interest rate on the debt is 9 percent. Ignoring taxes, EPS will be identical for Plans I and II when EBIT equals which one of the following? $60,750 $50,400 $48,550 $53,700 $69,600 
Earnings before interest and taxes, EBIT, are projected to be $8,500 if economic conditions are normal. If there is strong expansion in the economy, then EBIT will be 20 percent higher. If there is a recession, then EBIT will be 25 percent lower. The company is considering a $28,200 debt issue with an interest rate of 7 percent. The proceeds will be used to repurchase shares of stock. There are currently 4,100 shares outstanding. Assume the company has a market-to-book ratio of 1.0. a. Calculate return on equity, ROE, under each of the three economic scenarios before any debt is issued, assuming no taxes. (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) Recession 7.7% Normal 10.37% Expansion 12.44% b. Calculate the percentage changes in ROE when the economy expands or enters a recession, assuming no taxes. (A negative answer should be indicated by a minus sign. Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answers as a percent rounded to the nearest whole number, e.g., 32.) Recession -25% Expansion 20% Assume the firm goes through with the proposed recapitalization and no taxes. c. Calculate return on equity, ROE, under each of the three economic scenarios after the recapitalization. (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) Recession 8.18% Normal 12.13% Expansion 15.29% d. Calculate the percentage changes in ROE for economic expansion and recession. (A negative answer should be indicated by a minus sign. Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) Recession -32.56% Expansion 26.05% Assume the firm has a tax rate of 40 percent. e. Calculate return on equity, ROE, under each of the three economic scenarios before any debt is issued. Also, calculate the percentage changes in ROE for economic expansion and recession. (A negative answer should be indicated by a minus sign. Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) ROE Recession 4.66% Normal 6.22% Expansion 7.46% %AROE Recession -25% Expansion 20% f. Calculate return on equity, ROE, under each of the three economic scenarios after the recapitalization. Also, calculate the percentage changes in ROE for economic expansion and recession, assuming the firm goes through with the proposed recapitalization. (A negative answer should be indicated by a minus sign. Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places.) Recession 4.91% Normal 7.28% Expansion 9.17% %ROE Recession -32.55% Expansion 25.96% Explanation: a and b. A table outlining the income statement for the three possible states of the economy is shown below. The EPS is the net income divided by the 4,100 shares outstanding. The last row shows the percentage change in EPS the company will experience in a recession or an expansion economy.
to the market value of equity. Using the equation for ROE: ROE = NI / $82,000 The ROE for each state of the economy under the current capital structure and no taxes is:
If the company undergoes the proposed recapitalization, it will repurchase: Share price = Equity / Shares outstanding Share price = $82,000 / 4,100 Share price = $20 Shares repurchased = Debt issued / Share price Shares repurchased = $28,200 / $20 Shares repurchased = 1,410 The interest payment each year under all three scenarios will be: Interest payment = $28,200(.07) Interest payment = $1,974 The last row shows the percentage change in EPS the company will experience in a recession or an expansion economy under the proposed recapitalization.
Equity = $82,000 – 28,200 Equity = $53,800 So, the ROE for each state of the economy is: ROE = NI / $53,800
A table outlining the income statement with taxes for the three possible states of the economy is shown below. The share price is $20, and there are 4,100 shares outstanding. The last row shows the percentage change in EPS the company will experience in a recession or an expansion economy.
If there are corporate taxes and the company maintains its current capital structure, the ROE is:
If the company undergoes the proposed recapitalization, it will repurchase: Share price = Equity / Shares outstanding Share price = $82,000 / 4,100 Share price = $20 Shares repurchased = Debt issued / Share price Shares repurchased = $28,200 / $20 Shares repurchased = 1,410 The interest payment each year under all three scenarios will be: Interest payment = $28,200(.07) Interest payment = $1,974 A table outlining the income statement with taxes for the three possible states of the economy and assuming the company undertakes the proposed capitalization is shown below.
the ROE for each state of the economy is:
Bird Houses is an all-equity firm with a total market value of $388,980 and18,000 shares of stock outstanding. Management is considering issuing $68,000 of debt at an interest rate of 6.5 percent and using the proceeds on a stock repurchase. Ignore taxes. How many shares will the firm repurchase if it issues the debt securities? (Round the number of shares repurchased down to the nearest whole share.) 3,116 shares 3,167 shares 3,021 shares 3,207 shares 3,146 shares 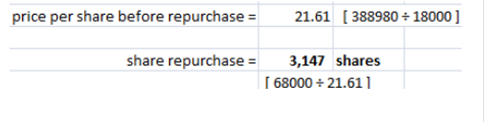
Kyle Corporation is comparing two different capital structures, an all-equity plan (Plan I) and a levered plan (Plan II). Under Plan I, the company would have 790,000 shares of stock outstanding. Under Plan II, there would be 540,000 shares of stock outstanding and $10.5 million in debt outstanding. The interest rate on the debt is 8 percent, and there are no taxes. a. Assume that EBIT is $3.1 million. Compute the EPS for both Plan I and Plan II. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answers to 2 decimal places, 32.16.) EPS Plan I $3.92 Plan II $4.18 b. Assume that EBIT is $3.6 million. Compute the EPS for both Plan I and Plan II. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answers to 2 decimal places, 32.16.) EPS Plan I $4.55 Plan II $5.11 c. What is the break-even EBIT? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer in dollars, not millions of dollars, e.g., 1,234,567. Round your answer to the nearest whole number, e.g., 32.) Break-even EBIT 2,654,400 Explanation: a. Under Plan I, the unlevered company, net income is the same as EBIT with no corporate tax. The EPS under this capitalization will be: EPS = $3,100,000 / 790,000 shares EPS = $3.92 Under Plan II, the levered company, net income will be reduced by the interest payment. The interest payment is the amount of debt times the interest rate, so: Net income = $3,100,000 – .08($10,500,000) Net income = $2,260,000 And the EPS will be: EPS = $2,260,000 / 540,000 shares EPS = $4.19 Plan II has the higher EPS when EBIT is $3,100,000. b. Under Plan I, the net income is $3,600,000 and the EPS is: EPS = $3,600,000 / 790,000 shares EPS = $4.56 Under Plan II, the net income is: Net income = $3,600,000 – .08($10,500,000) Net income = $2,760,000 And the EPS is: EPS = $2,760,000 / 540,000 shares EPS = $5.11 Plan II has the higher EPS when EBIT is $3,600,000. c. To find the breakeven EBIT for two different capital structures, we set the equations for EPS equal to each other and solve for EBIT. The breakeven EBIT is: EBIT / 790,000 = [EBIT – .08($10,500,000)] / 540,000 EBIT = $2,654,400 Northwestern Lumber Products currently has 12,400 shares of stock outstanding and no debt. Patricia, the financial manager, is considering issuing $160,000 of debt at an interest rate of 6.95 percent and using the proceeds to repurchase shares. Given this, how many shares of stock will be outstanding once the debt is issued if the break-even level of EBIT between these two capital structure options is $48,000? Ignore taxes. 2,667 shares 2,873 shares 3,051 shares 2,558 shares 3,025 shares 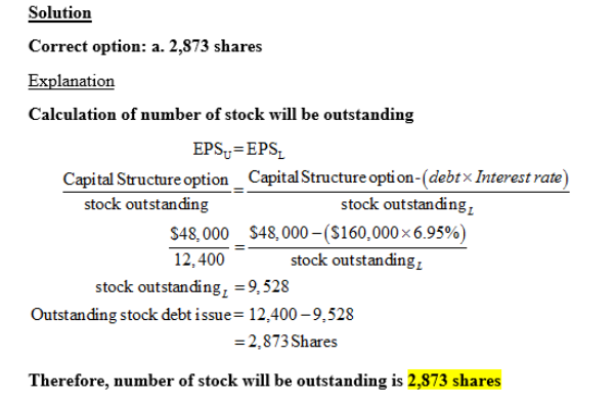
Crosby Industries has a debt–equity ratio of 1.6. Its WACC is 9 percent, and its cost of debt is 4 percent. There is no corporate tax. a. What is the company’s cost of equity capital? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) Cost of equity 17% b. What would the cost of equity be if the debt–equity ratio were 2? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to the nearest whole number, e.g., 32.) Cost of equity 19% What would the cost of equity be if the debt–equity ratio were .5? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) Cost of equity 11.5% What would the cost of equity be if the debt–equity ratio were zero? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to the nearest whole number, e.g., 32.) Cost of equity 9% Explanation: a. With the information provided, we can use the equation for calculating WACC to find the cost of equity. The equation for WACC (assuming no taxes) is: WACC = (E / V)RE + (D / V)RD The company has a debt–equity ratio of 1.6, which implies the weight of debt is 1.6/2.6, and the weight of equity is 1/2.6, so WACC = .09 = (1 / 2.6)RE + (1.6 / 2.6)(.04) RE = .1700, or 17.00% b. To find the cost of equity under different capital structures, we can again use the WACC equation. With a debt–equity ratio of 2, the cost of equity is: .09 = (1 / 3)RE + (2 / 3)(.04) RE = .1900, or 19.00% With a debt–equity ratio of .5, the cost of equity is: .09 = (1 / 1.5)RE + (.5 / 1.5)(.04) RE = .1150, or 11.50% And with a debt–equity ratio of 0, the cost of equity is: .09 = (1)RE + (0)(.04) RE = WACC = .0900, or 9.00% Calvert Corporation expects an EBIT of $19,750 every year forever. The company currently has no debt, and its cost of equity is 14.0 percent. The company can borrow at 8.5 percent and the corporate tax rate is 40. a. What is the current value of the company? (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) Value of the firm $ 84,642.86 b. What will the value of the firm be if the company takes on debt equal to 50 percent of its unlevered value? (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) Value of the firm $ 101,571.43 What will the value of the firm be if the company takes on debt equal to 100 percent of its unlevered value? (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) Value of the firm $ 118,500 c. What will the value of the firm be if the company takes on debt equal to 50 percent of its levered value? (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) Value of the firm $ 105,803.58 What will the value of the firm be if the company takes on debt equal to 100 percent of its levered value? (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) Value of the firm $ 141,071.43 Explanation: a. With no debt, we are finding the value of an unlevered firm, so: VU = EBIT(1 – TC) / RA VU = $19,750(1 − .40) / .140 VU = $84,642.86 b. The general expression for the value of a leveraged firm is: VL = VU + TCD If debt is 50 percent of VU, then D = (.50)VU, and we have: VL = VU + TC[(.50)VU] VL = $84,642.86 + .40(.50)($84,642.86) VL = $101,571.43 If debt is 100 percent of VU, then D = (1)VU, and we have: VL = VU + TC[(1)VU] VL = $84,642.86 + .40(1)($84,642.86) VL = $118,500.00 c. According to M&M Proposition I with taxes: VL = VU + TCD With debt being 50 percent of the value of the levered firm, D must equal (.50)VL, so: VL = VU + TC[(.50)VL] VL = $84,642.86 + .40(.50)(VL) VL = $105,803.57 If the debt is 100 percent of the levered value, D must equal VL, so: VL = VU + TC[(1)VL] VL = $84,642.86 + .40(1)(VL) VL = $141,071.43 Debbie's Cookies has a return on assets of 12.6 percent and a cost of equity of 14.8 percent. What is the pretax cost of debt if the debt-equity ratio is .38? Ignore taxes. A. 5.87 percent B. 95.29 percent C. 9.04 percent D. 7.31 percent E. 6.81 percent .148 = .126 + [(.126 -RD) ×.38] RD = .0681, or 6.81 percent The Park Place has a return on assets of 12.9 percent, a cost of equity of 16.2 percent, and a pretax cost of debt of 7.7 percent. What is the debt-equity ratio? Ignore taxes. A. .44 B. .47 C. .67 D. .91 E. .63 .162 = .129 + [(.129 -.077) × D/E] D/E = .63 An all-equity firm has a return on assets of 13.3 percent. The firm is considering converting to a debt-equity ratio of .48. The pretax cost of debt is 8.6 percent. Ignoring taxes, what will the cost of equity be if the firm switches to the levered capital structure? A. 16.01 percent B. 15.28 percent C. 16.60 percent D. 17.03 percent E. 15.56 percent RE = .133 + [(.133 -.086) × .48] RE=.1556, or 15.56 percent Brick House Markets has a tax rate of 34 percent and taxable income of $308,211. What is the value of the interest tax shield if the interest expense is $39,700? A. $14,887 B. $15,010 C. $15,595 D. $13,498 E. $16,023 Interest tax shield = .34 ×$39,700 = $13,498 Green Tea House has a tax rate of 35 percent and an interest tax shield valued at $8,046 for the year. How much did the firm pay in annual interest? A. $2,816.10 B. $2,304.11 C. $23,468.09 D. $21,107.99 E. $22,988.57 Interest = $8,046/.35 = $22,988.57 Newborn Nursery has 12,000 bonds outstanding with a face value of $1,000 each. The coupon rate is 6.9 percent and the tax rate is 34 percent. What is the present value of the interest tax shield? A. $4.14 million B. $4.86 million C. $3.87 million D. $3.92 million E. $4.08 million PV of tax shield = .34 ×12,000 ×$1,000 = $4.08 million Southern Foods has a $13 million bond issue outstanding with a coupon rate of 7.15 percent and a yield to maturity of 7.39 percent. What is the present value of the tax shield if the tax rate is 34 percent? A. $283,140 B. $316,030 C. $4,053,400 D. $3,960,000 E. $4,420,000 PV of tax shield = .34×$13,000,000= $4,420,000 Granny's Home Remedy has a $27 million bond issue outstanding with a coupon rate of 8.75 percent and a current yield of 8.13 percent. What is the present value of the tax shield if the tax rate is 35 percent? A. $768,285 B. $826,875 C. $839,002 D. $8,160,000 E. $9,450,000 PV of tax shield = .35×$27,000,000 = $9,450,000 Forbidden Fruit Extracts expects its earnings before interest and taxes to be $287,600 a year forever. Currently, the firm has no debt. The cost of equity is 15.4 percent and the tax rate is 34 percent. The company is in the process of issuing $3 million of bonds at par that carry an annual coupon rate of 7.6 percent. What is the unlevered value of the firm? A. $1,371,429 B. $1,331,971 C. $1,107,405 D. $969,325 E. $1,232,571 VU = [287,600 × (1 -.34)] / 0.154 = 1,232,571 Kline Construction is an all-equity firm that has projected perpetual earnings before interest and taxes of $628,000. The current cost of equity is 17.6 percent and the tax rate is 35percent. The company is in the process of issuing $4.3 million of 8.3 percent annual coupon bonds at par. What is the levered value of the firm? A. $3,824,318 B. $3,541,085 C. $3,422,225 D. $2,713,185 E. $3,385,695 VU = [628,000 ×(1 -.35)] / 0.176 = $2,319,318 VL = 2,319,318 + (0.35 × 4,300,000) = 3,824,318 Stevenson's Bakery is an all-equity company that has projected perpetual earnings before interest and taxes of $43,700 a year. The cost of equity is 15.2 percent and the tax rate is 34 percent. The company can borrow money at 7.15 percent. If the company borrows $50,000, what will be its levered value? A. $187,613 B. $189,919 C. $206,750 D. $229,507 E. $203,682 VU = [$43,700 ×(1 -.34)]/.152 = $189,750 VL = $189,750 + (.34 ×$50,000) = $206,750 Ready To Go is an all-equity firm specializing in hot ready-to-eat meals. Management has estimated the firm's earnings before interest and taxes will be $68,000 annually forever. The present cost of equity is 14.1 percent. Currently, the firm has no debt but is considering borrowing $450,000 at 8 percent interest. The tax rate is 34 percent. What is the value of the unlevered firm? A. $323,017 B. $346,511 C. $314,141 D. $318,298 E. $305,200 VU = [$68,000 ×(1 -.34)]/.141 = $318,298 Great Lakes Shipping is an all-equity firm with anticipated earnings before interest and taxes of $386,000 annually forever. The present cost of equity is 17.1 percent. Currently, the firm has no debt but is considering borrowing $1.48 million at 8.5 percent interest. The tax rate is 35 percent. What is the value of the levered firm? A. $1,985,251 B. $2,006,519 C. $1,888,47 D. $1,666,667 E. $2,018,181 VU = [$386,000 ×(1 -.35)]/.171 = $1,467,251.46 VL = $1,467,251.46 + (.35 ×$1,480,000) = $1,985,251 Jericho Snacks is an all-equity firm with estimated earnings before interest and taxes of $624,000 annually forever. Currently, the firm has no debt but is considering borrowing $725,000 at 6.75 percent interest. The tax rate is 35 percent and the current cost of equity is 15.2 percent. What is the value of the levered firm? A. $3,187,271 B. $2,769,535 C. $3,307,271 D. $2,922,171 E. $3,506,418 VU = [$624,000 ×(1 -.35)]/.152 = $2,668,421.05 VL = $2,668,421.05 + (.35 ×$725,000) = $2,922,171 The Fruit Mart is an all-equity firm with a current cost of equity of 17.4 percent. The estimated earnings before interest and taxes are $169,500 annually forever. Currently, the firm has no debt but is in the process of borrowing $400,000 at 9.5 percent interest. The tax rate is 35 percent. What is the value of the unlevered firm? A. $649,207 B. $753,571 C. $656,411 D. $719,307 E. $633,190 VU = [$169,500 ×(1 -.35)]/.174 = $633,190 Roller Coaster's has a WACC of 11.6 percent, ignoring taxes. It has a target capital structure of 60 percent equity and 40 percent debt and a cost of equity of 14.27 percent. What is the cost of debt? A. 5.5 percent B. 7.6 percent C. 9.3 percent D. 9.4 percent E. 18.7 percent .1427 = .116 + (.116 - RD) × (.40 / .60) RD = .076 A firm has a cost of debt of 7.8 percent and a cost of equity of 15.6 percent. The debt-equity ratio is .52. There are no taxes. What is the firm's weighted average cost of capital? A. 11.76 percent B. 11.29 percent C. 12.93 percent D. 12.47 percent E. 10.20 percent 12.93 percent WACC = [(1/1.52) ×.156] + [(.52 /1.52) ×.078] = .1293, or 12.93 percent A firm has a weighted average cost of capital of 11.28 percent and a cost of equity of 14.7 percent. The debt-equity ratio is .72. There are no taxes. What is the firm's cost of debt? A. 6.53 percent B. 6.27 percent C. 6.44 percent D. 7.23 percent E. 7.08 percent 1128 = [(1/1.72 × .147] + [(.72 /1.72) ×RD] RD = 6.53 percent Jasper Industrial has no debt outstanding and a total market value of $216,000. Earnings before interest and taxes, EBIT are projected to be $15,000 if economic conditions are normal. If there is strong expansion in the economy, then EBIT will be 12 percent higher. If there is a recession, then EBIT will be 15 percent lower. There are currently 8,600 shares outstanding. Ignore taxes. What is the percentage change in EPS when a normal economy slips into recession? A. -15.5 percent B. -15.2 percent C. -15.0 percent D. -16.1 percent E. -14.8 percent EPSNormal = $15,000/8,600 = $1.744 EPSRecession = $15,000(1 - .15)/ 8,600 = $1.483 Percentage change ($1.483 -1.744)/$1.744 = -15 percent Gabe's Market is comparing two different capital structures. Plan I would result in 15,000 shares of stock and $210,000 in debt. Plan II would result in 13,000 shares of stock and $252,000 in debt. The interest rate on the debt is 8 percent. Ignoring taxes, compare both of these plans to an all-equity plan assuming that EBIT will be $52,000. The all-equity plan would result in 25,000 shares of stock outstanding. Of the three plans, the firm will have the highest EPS with _____ and the lowest EPS with ____. A. Plan I; Plan II B. Plan II; the all-equity plan C. Plan II; Plan I D. Plan I; the all-equity plan E. the all-equity plan; Plan I EPSAll-equity = $52,000/25,000 = $2.08 EPSPlan I = [$52,000 - ($210,000 × .08)]/15,000 = $2.35 EPSPlan II = [$52,000 - ($252,000 × .08)]/13,000 = $2.45 Uptown Construction is comparing two different capital structures. Plan I would result in 16,000 shares of stock and $160,000 in debt. Plan II would result in 18,000 shares of stock and $110,000 in debt. The interest rate on the debt is 9 percent. Ignoring taxes, EPS will be identical for Plans I and II when EBIT equals which one of the following? A. $48,550 B. $50,400 C. $69,600 D. $53,700 E. $60,750 [EBIT - ($160,000 ×.09)]/16,000 = [EBIT -($110,000 ×.09)]/18,000 EBIT = $50,400 Bruno's is considering changing from its current all-equity capital structure to 30 percent debt. There are currently 7,500 shares outstanding at a price per share of $39. EBIT is expected to remain constant at $23,000. The interest rate on new debt is 7.5 percent and there are no taxes. Tracie owns $12,675 worth of stock in the company. The firm has a 100 percent payout. What would Tracie's cash flow be under the new capital structure assuming that she keeps all of her shares? A. $998 B. $1,109 C. $1,115 D. $1,037 E. $1,016 All-equity value = 7,500 ×$39 = $292,500 Shares repurchased = 7,500 ×.30= 2,250 shares EPS = [$23,000 - ($292,500)(.30)(.075)]/(7,500 -2,250) = $3.1274 Cash flow = ($3.1274) ($12,675/$39) = $1,016 Delta Mowers has a debt-equity ratio of .6. Its WACC is 11.8 percent, and its cost of debt is 7.7 percent. There is no corporate tax. What is the firm's cost of equity capital? A. 12.60 percent B. 14.26 percent C. 13.83 percent D. 14.29 percent E. 14.80 percent WACC = .118 = (1/1.6) RE + (.6/1.6)(.077) = .1426, or 14.26 percent Triangle Enterprises has no debt but can borrow at 8 percent. The firm's WACC is currently 13.2 percent, and there is no corporate tax. If the firm converts to 30 percent debt, what will its cost of equity be? A. 16.67 percent B. 12.95 percent C. 14.47 percent D. 16.39 percent E. 15.43 percent 15.43 percent WACC = .132 = .70RE + .30(.08) RE = .1543, or 15.43 percent The Piano Movers can borrow at 7.8 percent. The firm currently has no debt, and the cost of equity is 15 percent. The current value of the firm is $680,000. What will the value be if the firm borrows $140,000 and uses the proceeds to repurchase shares? The corporate tax rate is 35 percent. A. $820,000 B. $540,000 C. $750,000 D. $571,000 E. $729,000 VL = $680,000 + (.35)($140,000) = $729,000 Sand Mountain Resort has a tax rate of 32 percent. Its total interest payment for the year just ended was $41,000. What is the interest tax shield for the year? A. $27,590 B. $13,120 C. $13,410 D. 427,880 E. $41,000 $13,120 Interest tax shield = $41,000 ×.32 = 13,120 Marcos & Sons has no debt. Its current total value is $13 million. What will the company's value be if it sells $5 million in debt and has a tax rate of 35 percent? Assume all debt proceeds are used to repurchase equity. A. $16.25 million B. $18.00 million C. $11.25 million D. $13.00 million E. $14.75 million VL = $13 million + ($5 million× .35) = $14.75 million Glass Growers has a cost of capital of 11.1 percent. The company is considering converting to a debt-equity ratio of .46. The interest rate on debt is7.3 percent. What would be the companys new cost of equity? Ignore taxes. A. 12.85 percent B. 11.13 percent C. 12.36 percent D. 12.44 percent E. 11.61 percent WACC = .111 = (1/1.46)(RE) + (.46 /1.46)(.073) RE= .1285, or 12.85 percent Homework 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | Final Exam 1 2
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |