|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Principles Of Fianance: Homework Chapter 12 Homework 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | Final Exam 1 2 The Giuntoli Co. just issued a dividend of $2.70 per share on its common stock. The company is expected to maintain a constant 6 percent growth rate in its dividends indefinitely. If the stock sells for $44.50 a share, what is the company’s cost of equity? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) Cost of equity % Price of the stock = D1 / Ke - G 44.50 = 2.70(1+0.06) / X - 0.06 44.50(X - 0.06) = 2.862 44.50X - 2.67 = 2.862 44.50X = 2.862+2.67 44.50X = 5.532 X = 5.532/44.50 i.e 12.43% Explanation: With the information given, we can find the cost of equity using the dividend growth model. Using this model, the cost of equity is: RE = [$2.70(1.06) / $44.50] + .06 RE = .1243, or 12.43% Sixth Fourth Bank has an issue of preferred stock with a $6.00 stated dividend that just sold for $122 per share. What is the bank’s cost of preferred stock? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) Cost of preferred stock % 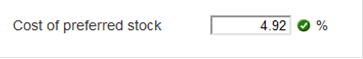
Cost of Preferred Stock = Stated Dividend/Selling Price * 100 = 6/122 * 100 = 4.92% Explanation: The cost of preferred stock is the dividend payment divided by the price, so: RP = $6.00 / $122 RP = .0492, or 4.92% Jiminy's Cricket Farm issued a 30-year, 10 percent semiannual bond 7 years ago. The bond currently sells for 86.5 percent of its face value. The company’s tax rate is 35 percent. a. What is the pretax cost of debt? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) Pretax cost of debt % b. What is the aftertax cost of debt? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) Aftertax cost of debt % c. Which is more relevant, the pretax or the after taxes cost of debt?  Expert Answer
Explanation: a. The pretax cost of debt is the YTM of the company’s bonds, so: P0 = $865 = $50(PVIFAR%,46) + $1,000(PVIFR%,46) R = 5.852% YTM = 2 × 5.852% YTM = 11.70% b. The aftertax cost of debt is: RD = .1170(1 – .35) RD = .0761, or 7.61% c. The aftertax rate is more relevant because that is the actual cost to the company. Bargeron Corporation has a target capital structure of 60 percent common stock, 5 percent preferred stock, and 35 percent debt. Its cost of equity is 13 percent, the cost of preferred stock is 6 percent, and the pretax cost of debt is 7.7 percent. The relevant tax rate is 35 percent. a. What is the company’s WACC? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) WACC % b. What is the aftertax cost of debt? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) Aftertax cost of debt % 
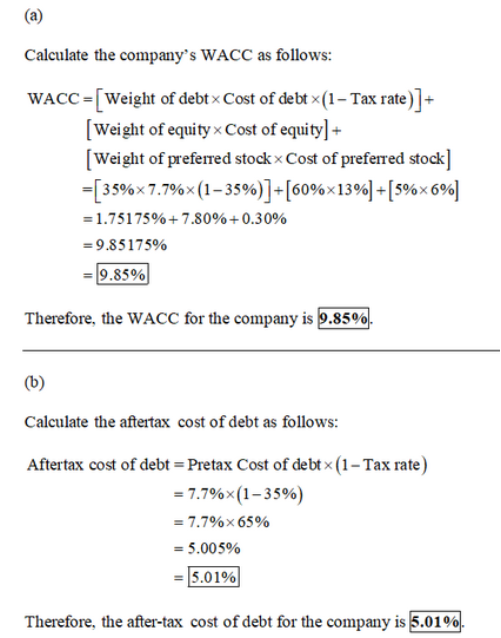
Explanation: a. Using the equation to calculate the WACC, we find: WACC = .60(.130) + .05(.060) + .35(.077)(1 – .35) WACC = .0985, or 9.85% b. Since interest is tax deductible, the aftertax cost of debt is: RD = .077(1 – .35) RD = .0501, or 5.01% Information on Gerken Power Co., is shown below. Assume the company’s tax rate is 38 percent. Debt: 8,800 8.1 percent coupon bonds outstanding, $1,000 par value, 22 years to maturity, selling for 103.5 percent of par; the bonds make semiannual payments. Common stock: 213,000 shares outstanding, selling for $83.30 per share; beta is 1.18. Preferred stock: 12,300 shares of 5.9 percent preferred stock outstanding, currently selling for $97.70 per share. Market: 7.15 percent market risk premium and 4.95 percent risk-free rate. Required: Calculate the company's WACC. (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) WACC % 
Expert Answer Step 1: 1) Cost of equity = risk-free rate + market risk premium*Beta Cost of equity =4.95 + 7.15*1.18 Cost of equity = 13.39% 2) Cost of Preferred Stock = 5.9/97.70 Cost of Preferred Stock = 6.04% 3) Before Tax Cost of Debt = rate(nper,pmt,pv,fv) *2 Nper (indicates the semi annual period) = 22*2 = 44 PV (indicates the price) = 1000*103.5% = 1035 PMT (indicate the semi annual payment) = 1000*8.1%*1/2 = $ 40.50 FV (indicates the face value) = 1000 Rate (indicates YTM) = ? Before Tax Cost of Debt = rate(44,40.50,-1035,1000) * 2 Before Tax Cost of Debt = 7.766 % After Tax Cost of Debt = 7.766*(1-38%) After Tax Cost of Debt = 4.81% Step 2: Market Value of Common Stock = 213000 · 83.30 = $ 17,742,900 Market value of Preferred Stock = 12300 · 97.70 = $ 1,201,710 Market Value of Bond = 8800 · 1035 = $ 9,108,000 Total Market Value = 17,742,900 + 1,201,710 + 9,108,000 = $ 28,052,610 Weight of Equity = 17,742,900/ 28,052,610 = 63.25% Weight of Preferred Stock = 1,201,710/ 28,052,610 = 4.28% Weight of Debt = 9,108,000/ 28,052,610 = 32.47% Step3: WACC = Weight of equity · Cost of equity + Weight of Preferred Stock · Cost of Preferred Stock + Weight of Debt · After Tax cost of Debt WACC = 63.25%*13.39 + 4.28%*6.04 + 32.47%*4.81 WACC = 10.29% Explanation: We will begin by finding the market value of each type of financing. We find: MVD = 8,800($1,000)(1.035) = $9,108,000 MVE = 213,000($83.30) = $17,742,900 MVP = 12,300($97.70) = $1,201,710 And the total market value of the firm is: V = $9,108,000 + 17,742,900 + 1,201,710 V = $28,052,610 Now, we can find the cost of equity using the CAPM. The cost of equity is: RE = .0495 + 1.18(.0715) RE = .1339, or 13.39% The cost of debt is the YTM of the bonds, so: P0 = $1,035 = $40.50(PVIFAR%,44) + $1,000(PVIFR%,44) R = 3.88% YTM = 3.88% × 2 YTM = 7.77% And the aftertax cost of debt is: RD = (1 – .38)(.0777) RD = .0481, or 4.81% The cost of preferred stock is: RP = $5.90 / $97.70 RP = .0604, or 6.04% Now we have all of the components to calculate the WACC. The WACC is: WACC = .0481($9,108,000 / $28,052,610) + .1339($17,742,900 / $28,052,610) + .0604($1,201,710 / $28,052,610) WACC = .1029, or 10.29% Notice that we didn’t include the (1 – TC) term in the WACC equation. We used the aftertax cost of debt in the equation, so the term is not needed here. The common stock just paid a $1.50 annual dividend and has a dividend growth rate of 2.5 percent. There are 7,500 shares of $9 preferred stock outstanding at a market price of $72 a share. The outstanding bonds mature in 11 years, have a total face value of $825,000, a face value per bond of $1,000, and a market price of $989 each, and a pretax yield to maturity of 8.3 percent. The tax rate is 35 percent. What is the firm's weighted average cost of capital? .0776, or 7.76 percent Common stock:44,000 $32 = $1,408,000 Preferred stock:7,500 $72 = $540,000 Debt: $989 / $1,000 $825,000 = $815,925 Value = $1,408,000 + 540,000 + 815,925 = $2,763,925 RE = [($1.50 1.025)/$32] + .025 = .073047 Rp = $9/$72= .125 WACC = ($1,408,000/ $2,763,925) (.073047) + ($540,000 / $2,763,925) (.125) + ($815,925 / $2,763,925) (.083)(1 -.35) = .0776, or 7.76 percent Beta Industries is considering a project with an initial cost of $6.9 million. The project will produce cash inflows of $1.52 million a year for seven years. The firm uses the subjective approach to assign discount rates to projects. For this project, the subjective adjustment is +2.2 percent. The firm has a pretax cost of debt of 9.1 percent and a cost of equity of 17.7 percent. The debt-equity ratio is .57 and the tax rate is 34 percent. What is the net present value of the project? (Round the answer to the nearest $100.) -$698,400 WACC = (1/1.57) (.177) + (.57 / 1.57) (.091) (1 -.34) = .134544 Project WACC = .134544 + .022 = .156544, or 15.6544 percent NPV = -$6.9m + ($1.52m) (PVIFA7, 15.6544%) = -$698,400 Pharrell, Inc., has sales of $603,000, costs of $255,000, depreciation expense of $62,000, interest expense of $29,000, and a tax rate of 30 percent. The firm paid out $45,000 in cash dividends and has 58,000 shares of common stock outstanding. What is the earnings per share (EPS) figure? Hint: EPS is equal to net income divided by number of shares of common stock outstanding. $3.10 Orchard Farms has a pretax cost of debt of 7.29 percent and a cost of equity of 16.3 percent. The firm uses the subjective approach to determine project discount rates. Currently, the firm is considering a project to which it has assigned an adjustment factor of 1.25 percent. The firm's tax rate is 35 percent and its debt-equity ratio is .48. The project has an initial cost of $3.9 million and produces cash inflows of $1.26 million a year for 5 years. What is the net present value of the project? $446,556 Project cost of capital = [(1/1.48)(.163) + (.48 /1.48)(.0729)(1 -.35)] + .0125 = .1380, or 13.80 percent NPV = -$3.9m + $1.26m(PVIFA5, 13.80%) = $446,556 Piedmont Hotels is an all-equity firm with 48,000 shares of stock outstanding. The stock has a beta of 1.19 and a standard deviation of 14.8 percent. The market risk premium is 7.8 percent and the risk-free rate of return is 4.1 percent. The company is considering a project that it considers riskier than its current operations so has assigned an adjustment of 1.35 percent to the project's discount rate. What should the firm set as the required rate of return for the project? .1473, or 14.73 percent Project cost of capital = .041 + 1.19(.078) + .0135 = .1473, or 14.73 percent Hailey, Inc., has sales of $19,640, costs of $9,390, depreciation expense of $2,060, and interest expense of $1,550. Assume the tax rate is 40 percent. What is the operating cash flow, or OCF? $7,594 Cromwell's Interiors is considering a project that is equally as risky as the firm's current operations. The firm has a cost of equity of 15.4 percent and a pretax cost of debt of 8.9 percent. The debt-equity ratio is .46 and the tax rate is 34 percent. What is the cost of capital for this project? .1240, or 12.40 percent Project cost of capital = (1 / 1.46) (.154) + (.46 / 1.46) (.089) (1 -.34) = .1240, or 12.40 percent Bruceton's is a specialty retailer with multiple brick-and-mortar stores and a cost of capital of 16.4 percent. Specialty Imports is a wholesaler of specialty items and has a cost of capital of 12.6 percent. Both firms are considering opening a new store in downtown Chicago at a cost of $1.1 million. Because this type of store would be trendy, it would have a life of only 8 years and no salvage value. The expected annual net cash flow is $229,000, regardless of which firm opens the store. Which company(ies), if either, should open the Chicago store? Neither company NPV = -$1.1m + $229,000(PVIFA8, 16.4%) = -$118,008.96 Both firms should use Bruceton's cost of capital of 16.4 percent as the project cost of capital since that rate is most applicable to the project's level of risk. At 16.4 percent, the NPV is negative, so neither company should open a Chicago store. Bear Tracks, Inc., has current assets of $2,250, net fixed assets of $10,100, current liabilities of $1,390, and long-term debt of $4,060. a. What is the value of the shareholders' equity account for this firm? b. How much is the company's net working capital? a. $6,900 b. $860 Lester's is a globally diverse company with multiple divisions and a cost of capital of 15.8 percent. Med, Inc., is a specialty firm in the medical equipment field with a cost of capital of 13.7 percent. With the aging of America, both firms recognize the opportunities that exist in the medical field and are considering expansion in this area. At present, there is an opportunity for multiple firms to be involved in a new medical devices project. Each project will require an initial investment of $8.4 million with annual returns of $2.2 million per year for seven years. Which company(ies), if either, should become involved in the new projects? Both Lester's and Med, Inc. Both firms should use Med, Inc.'s, cost of capital. Since the project has a positive NPV at 13.7 percent, both firms should accept the new project. NPV = -$8.4m + $2.2m(PVIFA7, 13.7%) = $1,121,389 Both firms should use Med, Inc.'s, cost of capital. Since the project has a positive NPV at 13.7 percent, both firms should accept the new project. There is 5 percent probability of recession, 20 percent probability of a poor economy, 48 percent probability of a normal economy, and 27 percent probability of a boom. A stock has returns of −20.7 percent, 4.3 percent, 12.1 percent and 27.8 percent in these states of the economy, respectively. What is the stock's expected return? 13.14% .05(−.207) + .20(.043) + .48(.121) + .27(.278) = .1314 or 13.14% Bob's is a retail chain of specialty hardware stores. The firm has 18,000 shares of stock outstanding that are currently valued at $82 a share and provide a rate of return of 13.2 percent. The firm also has 600 bonds outstanding that have a face value of $1,000, a market price of $1,032, and a coupon rate of 7 percent. These bonds mature in 7 years and pay interest semiannually. The tax rate is 35percent. The firm is considering expanding by building a new superstore. The superstore will require an initial investment of $9.3 million and is expected to produce cash inflows of $1.07 million annually over its 10-year life. The risks associated with the superstore are comparable to the risks of the firm's current operations. The initial investment will be depreciated on a straight line basis to a zero book value over the life of the project. At the end of the 10 years, the firm expects to sell the superstore for an aftertax value of $4.7 million. Should the firm accept or reject the superstore project and why? The project should be rejected because the NPV is negative at the firm's cost of capital. Reject; The NPV -$1.15 million. Stock: 18,000 $82 = $1,476,000 Bonds: 600 $1,032 = $619,200 Value = $1,476,000 + 619,200 = $2,095,200 $1,032 = [(.07 $1,000) / 2] ({1 / [1 + (r/ 2)]14} / (r / 2)) + $1,000 / [1 + (r / 2)]14 r = 6.43 percent WACC = ($1,476,000 / $2,095,200) (.132) + ($619,200 / $2,095,200) (.0643) (1 - .35) = .1053, or 10.53 percent NPV = -$9.3m + $1.07m (PVIFA10, 10.53%) + $4.7m/1.105310 = -$1.15 million The project should be rejected because the NPV is negative at the firm's cost of capital. Rockingham Motors issued a 30-year, 8 percent semiannual bond 3 years ago. The bond currently sells for 103.1 percent of its face value. The company's tax rate is 34 percent. What is the aftertax cost of debt? 0.0510, or 5.10 percent $1,031 = [(.08 $1,000) / 2] ({1 - 1 / [1 + (r/ 2)]54} / (r / 2)) + $1,000 / [1 + (r / 2)]54 r = 7.725 percent Aftertax cost of debt = .07725 (1 -.34) = .0510, or 5.10 percent If the economy booms, RTF, Inc., stock is expected to return 13 percent. If the economy goes into a recessionary period, then RTF is expected to only return 2 percent. The probability of a boom is 82 percent while the probability of a recession is 18 percent. What is the variance of the returns on RTF, Inc., stock? 0.001786 Healthy Snacks has a target capital structure of 60 percent common stock, 3 percent preferred stock, and 37 percent debt. Its cost of equity is 16.8 percent, the cost of preferred stock is 11.4 percent, and the pretax cost of debt is 8.3 percent. What is the company's WACC if the applicable tax rate is 34 percent? 0.1245, or 12.45 percent WACC = .60(.168) + .03(.114) + .37(.083)(1 -.34) = .1245, or 12.45 percent Precision Cuts has a target debt-equity ratio of .48. Its cost of equity is 16.4 percent, and its pretax cost of debt is 8.2 percent. If the tax rate is 34 percent, what is the company's WACC? 0.1284 or 12.84 percent WACC = (1/1.48) (.164) + (.48 / 1.48) (.082) (1 -.34) = .1284 or 12.84 percent Given the following information for Electric Transport, find the WACC. Assume the company's tax rate is 35 percent. Debt: 8,100, 6.9 percent coupon bonds outstanding. $1,000 par value, 17 years to maturity, selling for 101 percent of par, the bonds make semiannual payments. Common stock: 175,000 shares outstanding, selling for $77 per share, beta is 1.32. Preferred stock: 9,000 shares of $7.50 preferred stock outstanding, currently selling for $73 per share. Market: 7.9 percent market risk premium and 3.6 percent risk-free rate. 0.104, or 10.4 percent Common: 175,000 $77 = $13,475,000 Preferred: 9,000 $73 = $657,000 Debt: 8,100 1.01 $1,000 = $8,181,000 Value = $13,475,000 + 657,000 + 8,181,000 = $22,313,000 RE = .036 + 1.32(.079) = .1403 RP = $7.50 /$73= .1027 $1,010 = [(.069 $1,000) / 2] ({1- 1 / [1 + (r/ 2)]34} / (r / 2)) + $1,000 / [1 + (r / 2)]34 r = 6.80 percent WACC = ($13,475,000 / $22,313,000) (.1403) + (657,000 / 22,313,000)(.1027) + (8,181,000 / 22,313,000) (.0680) (1 -.35) = .104, or 10.4 percent The risk-free rate is 4.3 percent and the market expected return is 11 percent. What is the expected return of a stock that has a beta of 1.28? 12.88% .043 + 1.28(.110 − .043) = .1288 or 12.88% Lawler's is considering a new project. The company has a debt-equity ratio of .64. The company's cost of equity is 14.9 percent, and the after tax cost of debt is 5.3 percent. The firm feels that the project is riskier than the company as a whole and that it should use an adjustment factor of +1.8 percent. What is the project cost of capital if the tax rate is 34 percent? 0.1295, or 12.95 percent Project cost of capital = (1 / 1.64) (.149) + (.64 / 1.64) (.053) + .018 = 0.1295, or 12.95 percent You own a portfolio that has $2,300 invested in Stock A and $3,400 invested in Stock B. Assume the expected returns on these stocks are 9 percent and 15 percent, respectively. What is the expected return on the portfolio? 12.58% 2,300 + 3,400 = 5,700 (2,300 / 5,700)(.09) + (3,400 / 5,700)(.15) = .1258, or 12.58% Pharrell, Inc., has sales of $598,000, costs of $260,000, depreciation expense of $64,500, interest expense of $31,500, and a tax rate of 40 percent. What is the net income for this firm? $145,200 Pharrell, Inc., has sales of $590,000, costs of $268,000, depreciation expense of $68,500, interest expense of $35,500, and a tax rate of 40 percent. The firm paid out $38,500 in cash dividends. What is the addition to retained earnings? $92,300 A portfolio consists of 185 shares of Stock C that sells for $39 and 150 shares of Stock D that sells for $41. What is the portfolio weight of Stock C? 0.5398 185(39) / 185(39) + 150(41) = .5398 You own 410 shares of Stock X at a price of $39 per share, 280 shares of Stock Y at a price of $62 per share, and 345 shares of Stock Z at a price of $85 per share. What is the portfolio weight of Stock Y? 0.2770 280(62) / 410(39) + 280(62) + 345(85) = .2770 A portfolio consists of $13,400 in Stock M and $18,900 invested in Stock N. The expected return on these stocks is 8.50 percent and 11.60 percent, respectively. What is the expected return on the portfolio? 10.31% 13,400/(13,400 + 18,900) = .4149 .4149(.085 + (1 - .4149)(11.6%) = .1031 You recently purchased a stock that is expected to earn 18 percent in a booming economy, 13 percent in a normal economy and lose 4 percent in a recessionary economy. There is 21 percent probability of a boom, 68 percent chance of a normal economy, and 11 percent chance of a recession. What is your expected rate of return on this stock? 12.18% .21(.18) + .68(.13) + .11(-.04) = .1218 or 12.18% Weiland Co. shows the following information on its 2016 income statement: sales $157,500 costs $81,000 other expenses $4,300 depreciation expense $10,000 interest expense $7,500 taxes $19,145 dividends $7,650. In addition, you're told that the firm issued $3,500 in new equity during 2016 and redeemed $5,700 in outstanding long-term debt. What is the 2016 operating cash flow? What is the 2016 cash flow to creditors? What is the 2016 cash flow to stockholders? If net fixed assets increased by $20,700 during the year, what was the addition to NWC? $53,055 $13,200 $4,150 $5,005 Homework 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | Final Exam 1 2
|
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |