|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Homework Chapter 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 Test 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 Final Exam 01 02 Project Office Accounting: Homework Chapter 13 General Questions & Answers Exercise 13.1 Classifying income statement items. LO 13-1 The accounts listed below appear on the worksheet of Heritage Crafts. Indicate the section of the classified income statement in which each account will be reported. 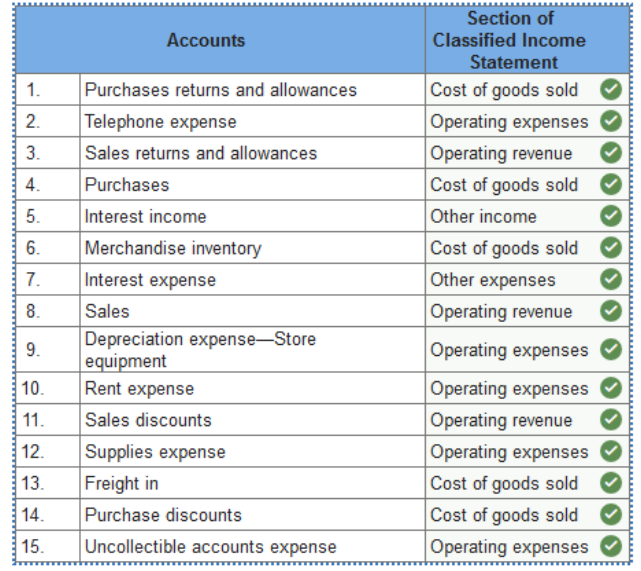
Exercise 13.2 Classifying balance sheet items. LO 13-3 The following accounts appear on the worksheet of Heritage Crafts at December 31, 2019. Indicate the section of the classified balance sheet in which each account will be reported. 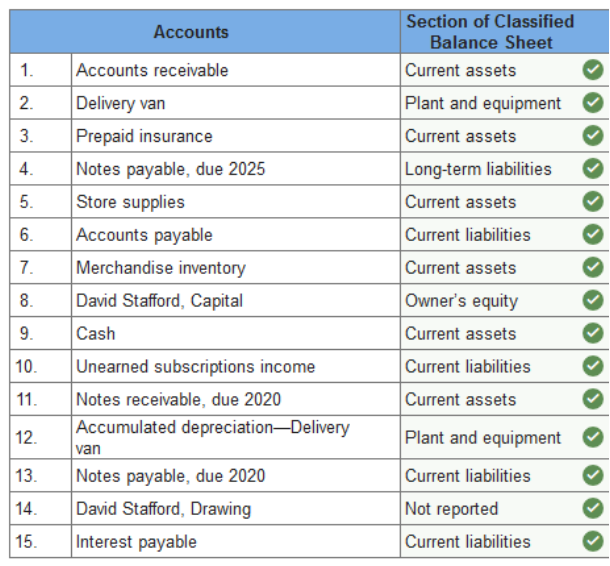
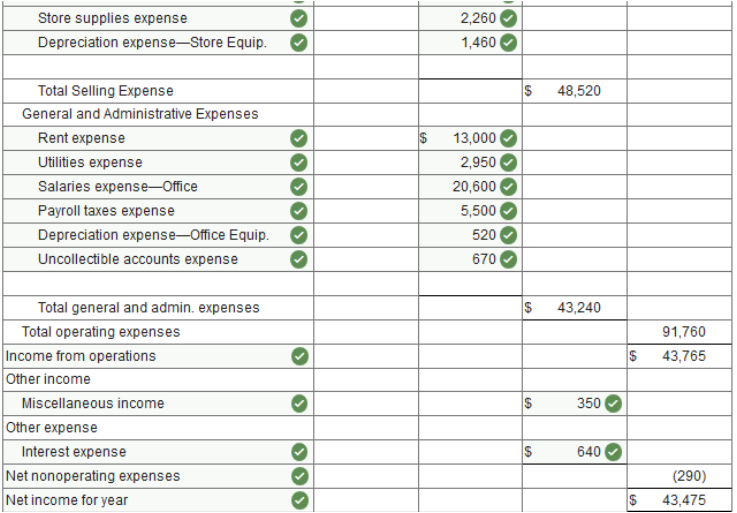
Exercise 13.3 Preparing a classified income statement. LO 13-1 The worksheet of Bridget's Office Supplies contains the following revenue, cost, and expense accounts. The merchandise inventory amounted to $59,275 on January 1, 2019, and $52,225 on December 31, 2019. The expense accounts numbered 611 through 617 represent selling expenses, and those numbered 631 through 646 represent general and administrative expenses.
Prepare a classified income statement for this firm for the year ended December 31, 2019. 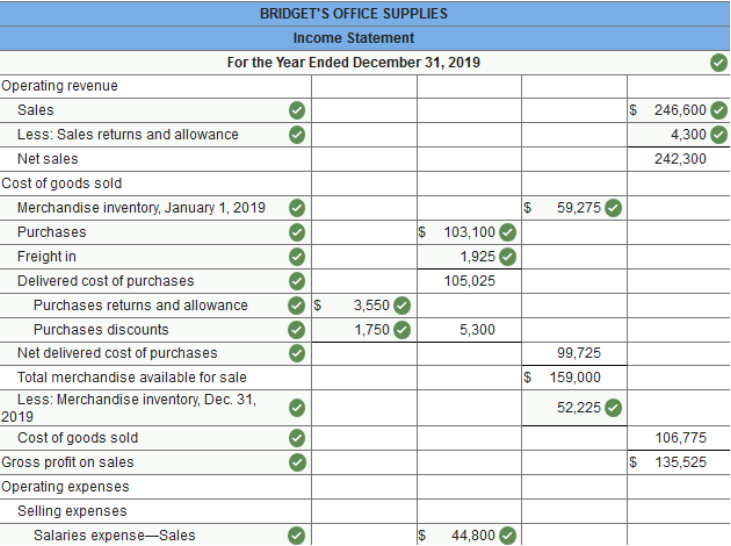
Exercise 13.4 Preparing a statement of owner's equity. LO 13-2 The worksheet of Bridget's Office Supplies contains the following revenue, cost, and expense accounts. The merchandise inventory amounted to $59,175 on January 1, 2019, and $52,125 on December 31, 2019. The expense accounts numbered 611 through 617 represent selling expenses, and those numbered 631 through 646 represent general and administrative expenses.
The worksheet of Bridget's Office Supplies contains the following owner’s equity accounts. No additional investments were made during the period.
Net income for the year $43,835. Prepare a statement of owner's equity for the year ended December 31, 2019. 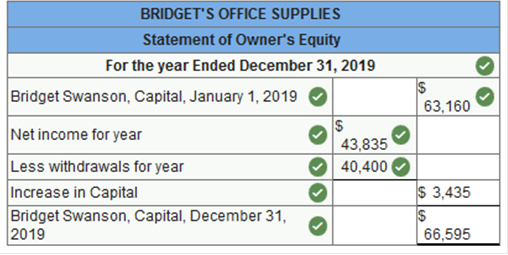
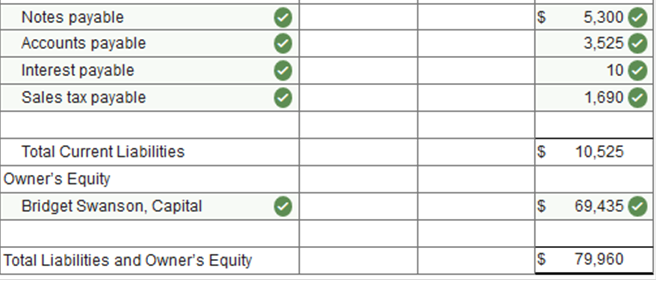
Exercise 13.5 Preparing a classified balance sheet. LO 13-3 The worksheet of Bridget's Office Supplies contains the following revenue, cost, and expense accounts. The merchandise inventory amounted to $57,775 on January 1, 2019, and $50,725 on December 31, 2019. The expense accounts numbered 611 through 617 represent selling expenses, and those numbered 631 through 646 represent general and administrative expenses.
The worksheet of Bridget's Office Supplies contains the following owner’s equity accounts.
Net income for the year $48,875. The worksheet of Bridget's Office Supplies contains the following asset and liability accounts. The balance of the Notes Payable account consists of notes that are due within a year.
Prepare a balance sheet dated December 31, 2019. 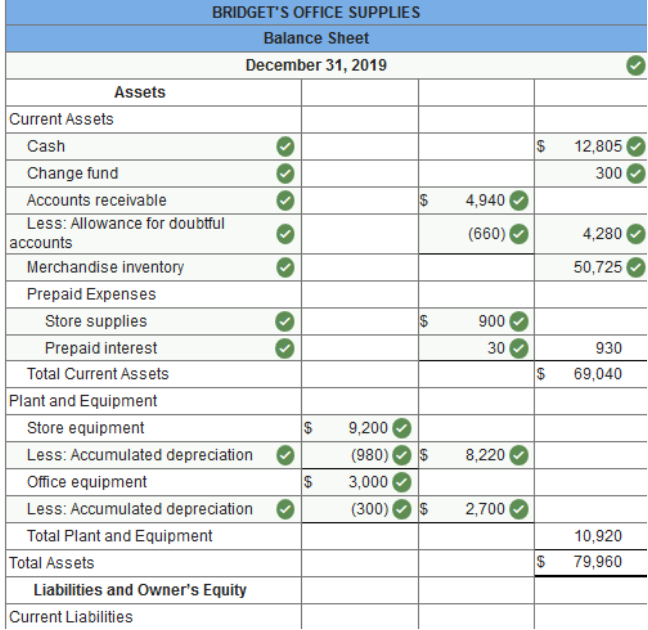
Exercise 13.6 Recording closing entries. LO 13-5 On December 31, 2019, the Income Statement section of the worksheet for Capeletti Distributors contained the following information.
Assume further that the owner of the firm is John Capeletti and that the John Capeletti, Drawing account had a balance of $26,000 on December 31, 2019. Prepare the entries that should be made in the general journal to close the revenue, cost of goods sold, expense, and other temporary accounts. 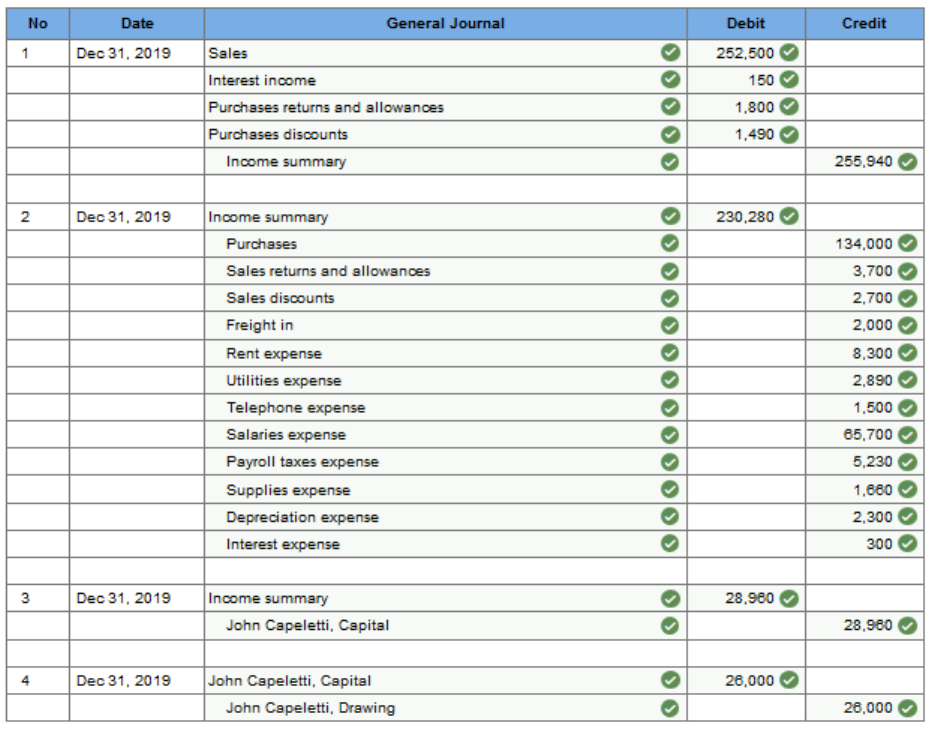
Exercise 13.7 Journalizing reversing entries. LO 13-7
Examine the above adjusting entries and determine which ones should be reversed. Show the reversing entries that should be recorded in the general journal as of January 1, 2020. (Record the entries in the order given. Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) 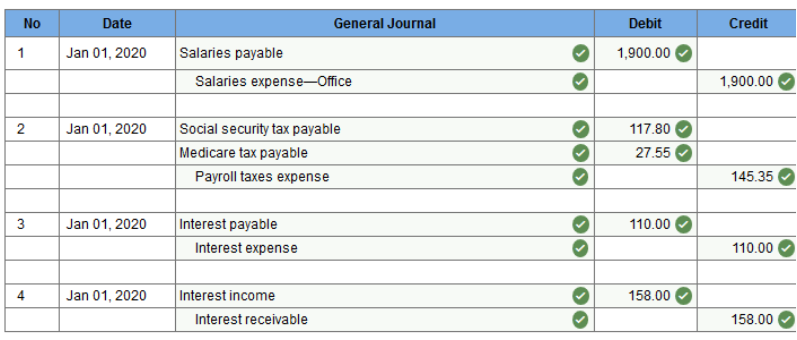
Exercise 13.8 Preparing a postclosing trial balance. LO 13-6 The Adjusted Trial Balance section of the worksheet for Van Zant Janitorial Supplies follows. The owner made no additional investments during the year.
Prepare a postclosing trial balance for the firm on December 31, 2019. 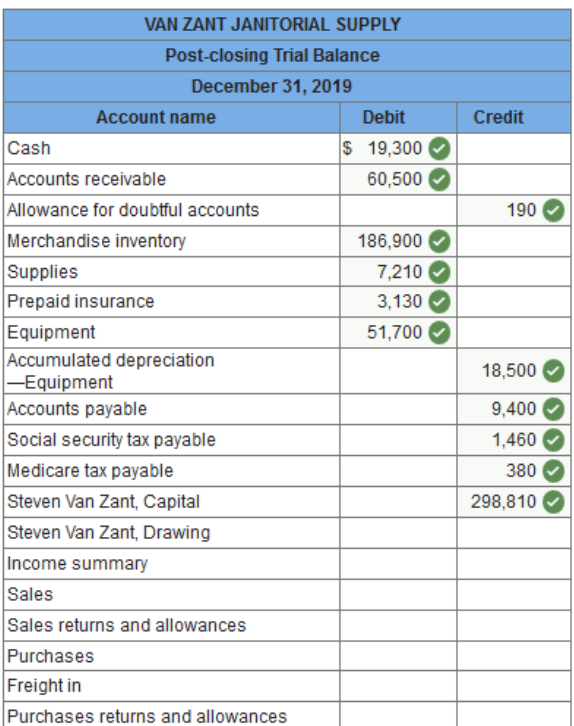
Exercise 13.9 Calculating ratios. LO 13-6 The following selected accounts were taken from the financial records of Los Olivos Distributors at December 31, 2019. All accounts have normal balances.
Accounts Receivable at December 31, 2018, was $57,300. Merchandise inventory at December 31, 2018, was $56,700. Based on the account balances above, calculate the following: The gross profit percentage. Working capital. The current ratio. The inventory turnover. The accounts receivable turnover. All sales were on credit. The gross profit percentage. 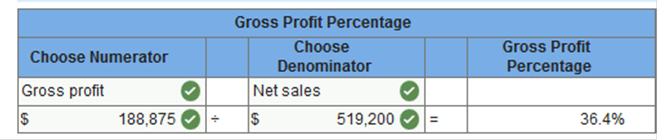
Working capital. 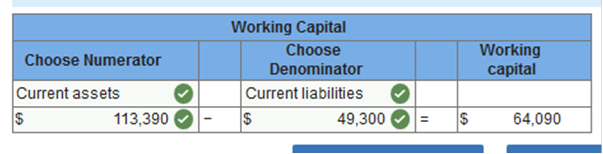
The current ratio. 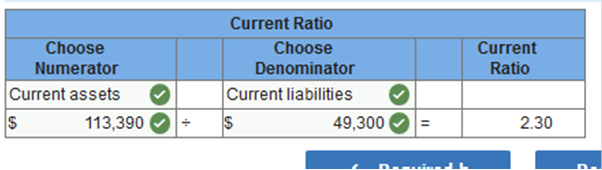
The inventory turnover. 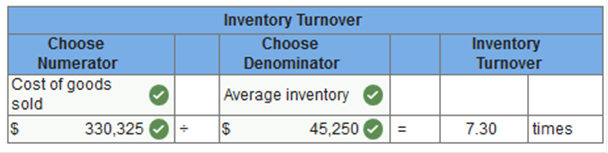
The accounts receivable turnover. All sales were on credit. 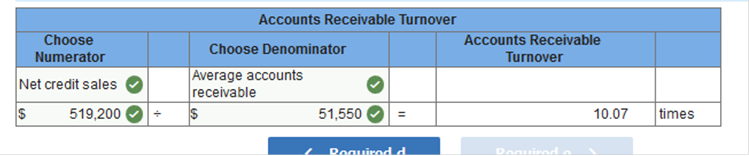
Exercise 13.10 Calculating the accounts receivable turnover and the inventory turnover. LO 13-6 Solomon Company reports the following in its most recent year of operations: Sales, $1,081,600 (all on account) Cost of goods sold, $633,600 Gross profit, $448,000 Accounts receivable, beginning of year, $94,000 Accounts receivable, end of year, $114,000 Merchandise inventory, beginning of year, $59,000 Merchandise inventory, end of year, $69,000. Based on these balances, compute: The accounts receivable turnover. The inventory turnover. The accounts receivable turnover. 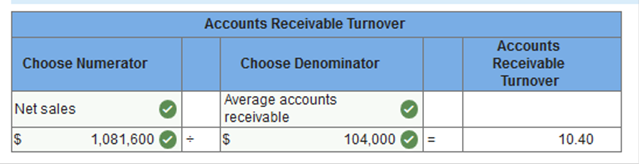
The inventory turnover. 
Roberto company has sales of $1,000,000, sales returns and allowances of $10,000, sales discounts of $2,000, and salary expense-sales of $120,000. what is the amount of net sales? a) $1,012,000 b) $988,000 c) $1,132,000 d) $868,000 1,000,000 - 12,000 = 988,000 kelley company has beginning inventory of $125,000, purchases of $950,000, purchases returns and allowances of $25,000, freight-in of $10,000, and ending inventory of $118,000. what is the amount of the cost of goods sold? a) $922,000 b) $928,000 c) $992,000 d) $942,000 950,000 - 25,000 + 10,000 + 7,000 = 942,000 Chen company has net sales of $500,000, cost of gods sold of $300,000, and interest expense of $10,000. What is the amount of gross profit on sales? a) $200,000 b) $198,000 c) $202,000 d) none of these 500,000 - 300,000 = 200,000 The balance of James Wilson, Capital at the beginning of the period was 50,000. During the period, his company had net income of 40,000, and he withdrew 35,000 from the business for personal use. What is the amount of the James Wilson, Capital account at the end of the accounting period? a) $125,000 b) $5,000 c) $45,000 d) $55,000 40,000 - 35,000 = 5,000 5,000 + 50,000 = 55,000 How should purchases returns and allowances be shown on the income statement? a) as other income b) as an addition to the delivered cost of purchases c) as a deduction from the delivered cost of purchases d) as other expenses c) as a deduction from the delivered cost of purchases Which of the following would not be classified as a Plant and Equipment on a balance sheet? a) prepaid insurance b) autos c) store equipment d) office equipment Which of the following is not a current asset? a) a merchandise inventory b) a note receivable due in 11 months c) prepaid insurance covering the next eight months d) a note receivable due in 13 months Arrange the accounting cycle: 1. analyze transactions 2. journalize the data about transactions 3. post the data about transactions 4. prepare a worksheet 5. prepare financial statements 6. journalize and post adjusting entries 7. journalize the post-closing entries 8. prepare a post-closing trial balance 9. interpret the financial info A type of income statement on which several subtotals are computed before the net income is calculated, such as gross profit, is called a _______ income statement. multiple-step single-total multi-total single-step Which of the following is not a general and administrative expense? a) rent expense b) salaries expense-office c) advertising expense d) uncollectible accounts expense On October 1, 2011, Paige Turner Publishing received $5,400 in cash for monthly subscriptions covering one year, recording the entry as a debit to Cash and a credit to Unearned Subscriptions. The correct adjusting entry at December 31, 2011, is Debit Unearned Subscriptions $1,350 Credit Subscriptions Income $1,350 Palmer Company determines its allowances for doubtful accounts by applying an expected loss percentage of 1.8 percent to the total of accounts receivable $1,500,000. Prior to the adjusting entry the allowance account has a debit balance of $1,180. How much will be charged to expense in the adjusting entry? $28,180 On December 1, 20X1, a firm accepted a 6-month, 12 percent note for $10,000 from a customer. The adjusting entry on December 31 to record the interest earned on the note is: a debit to Interest Receivable for $100 a credit to Interest Income for $100. Thompson Industries determines its provision for uncollectible accounts by applying an estimated loss percentage of 1 percent to net credit sales. In 2011, net credit sales were $5,800,000. Prior to the adjusting entry, Allowances for Doubtful Accounts contained a credit balance of $5,000. How much will be charged to Uncollectible Accounts Expense in 2011? $58,000 Vanessa Company reported net sales of $1,000,000, cost of goods sold of $600,000, and gross profit of $400,000. Merchandise Inventory was $50,000 and $70,000 at the beginning and end of the period, respectively. What is the inventory turnover, rounded to two decimal places? 6.67 times Marco Company reported net sales of $1,500,000, cost of goods sold of $800,000, and gross profit of $700,000. Accounts Receivable were $175,000 and $225,000 at the beginning and end of the period, respectively. What is the accounts receivable turnover, rounded to two decimal places? 7.50 times Chen Company has net sales of $500,000, cost of goods sold of $300,000, and interest expense of $10,000. What is the amount of gross profit on sales? $200,000 On October 1, 2011, Paige Turner Publishing received $58,800 in cash for monthly subscriptions covering one year, recording the entry as a debit to Cash and a credit to Unearned Subscriptions. The correct adjusting entry at December 31, 20X1, is Debit Unearned Subscriptions $14,700 Credit Subscriptions Income $14,700. Robin Banks, incorporated owns an armored truck which was purchased for $88,000. The Accumulated Depreciation on the truck is $60,000. The book value of the armored truck is $28,000 On September 1, 20X1, a firm accepted a 6-month, 6% note for $50,000 from a customer with an overdue account balance. The accrued interest recorded for this note on December 31, 20X1, is $1,000.00 If an account has a credit balance of $8,400 in the Trial Balance section of a worksheet and there is a credit of $700 in the Adjustments section, the account balance in the Adjusted Trial Balance section of the worksheet is $9,100 credit. On January 1, 2011, a firm purchased machinery for $28,000. Depreciation expense for the year ending December 31, 2011, given the straight-line method, a 10-year useful life, and a salvage value of $3,000, is $2,500. Rose Bush Nursery purchased a delivery truck for $40,000. The truck is expected to have a useful life of 5 years and a residual value of $2,800. The company uses the straight-line method of depreciation. If the truck was purchased on June 1, 2011, what is the amount of depreciation expense for the truck for one full year? $7,440 The balance of James Wilson, Capital at the beginning of the period was $50,000. During the period, his company had net income of $40,000, and he withdrew $35,000 from the business for personal use. What is the amount of the James Wilson, Capital account at the end of the accounting period? $55,000 Homework Chapter 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 Test 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 Final Exam 01 02 Project
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |