|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Homework Chapter 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 Test 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 Final Exam 01 02 Project Office Accounting: Homework Chapter 10 General Questions & Answers Exercise 10.1 Computing gross earnings. LO 10-2 The hourly rates of four employees of Ernesto’s Enterprises follow, along with the hours that these employees worked during one week. Determine the gross earnings of each employee. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) 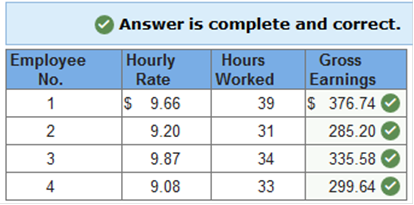
Exercise 10.2 Computing regular earnings, overtime earnings, and gross pay. LO 10-2 During one week, four production employees of Morgan Manufacturing Company worked the hours shown below. All these employees receive overtime pay at one and one-half times their regular hourly rate for any hours worked beyond 40 in a week. Determine the regular earnings, overtime earnings, and gross earnings for each employee. (Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.) 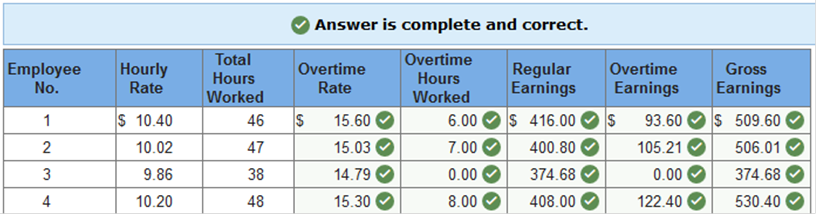
Exercise 10.3 Determining social security withholding. LO 10-3 The monthly salaries for December and the year-to-date earnings of the employees of Bush Consulting Company as of November 30 follow. Determine the amount of social security tax to be withheld from each employee’s gross pay for December. Assume a 6.2 percent social security tax rate and an earnings base of $122,700 for the calendar year. (Round your final answers to 2 decimal places.) 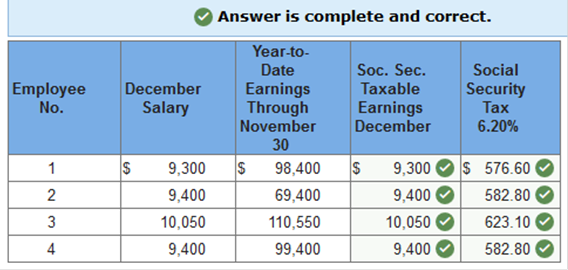
Exercise 10.4 Determining deduction for Medicare tax. LO 10-4 The monthly salaries for December and the year-to-date earnings of the employees of Bush Consulting Company as of November 30 follow. Determine the amount of Medicare tax to be withheld from each employee’s gross pay for December. Assume a 1.45 percent Medicare tax rate and that all salaries and wages are subject to the tax. (Round your final answers to 2 decimal places.) 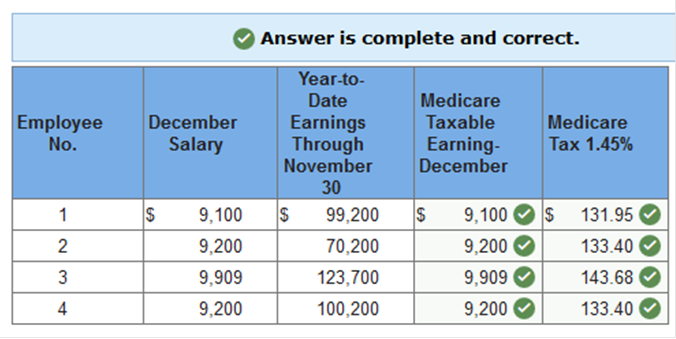
Exercise 10.5 Determining federal income tax withholding. LO 10-5 Data about the marital status, withholding allowances, and weekly salaries of the four office workers at Peter Office Supply Company follow. Find the amount of federal income tax to be deducted from each employee’s gross pay. 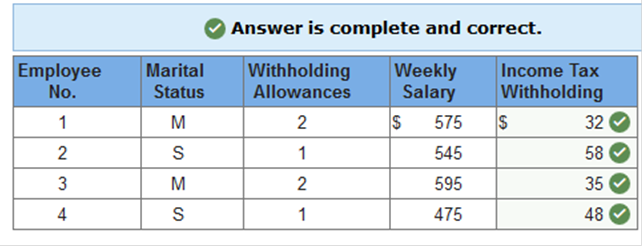
Exercise 10.6 Recording payroll transactions in the general journal. LO 10-7 Private Publishing has two office employees. A summary of their earnings and the related taxes withheld from their pay for the week ending August 7, 2019, follows.
1 & 2. Prepare the general journal entry to record the company’s payroll and to summarize the checks to pay the weekly payroll. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) 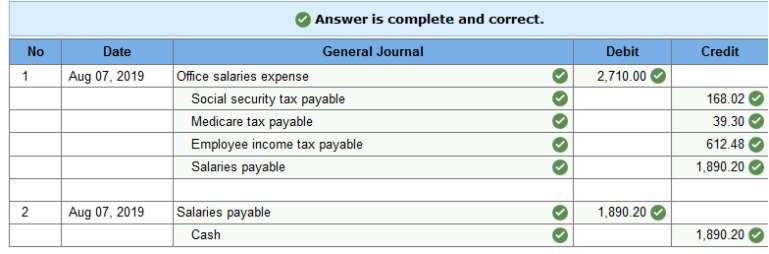
Exercise 10.7 Journalizing payroll transactions. LO 10-7 On July 31, 2019, the payroll register for White Sales Company showed the following totals for the month: gross earnings, $37,600; social security tax, $2,331.20; Medicare tax, $545.20; income tax, $2,976.79; and net amount due, $31,746.81. Of the total earnings, $29,858.46 was for sales salaries and $7,741.54 was for office salaries. Prepare a general journal entry to record the monthly payroll of the firm on July 31, 2019. (Round your final answers to 2 decimal places.) 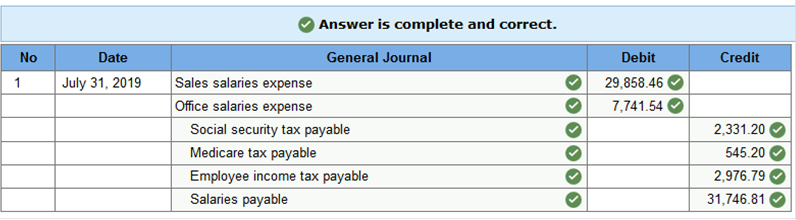
Problem 10.1A Computing gross earnings, determining deductions, journalizing payroll transactions. LO 10-2, 10-3, 10-4, 10-5, 10-7 Kathy Burnett works for Triumph Industries. Her pay rate is $12.24 per hour and she receives overtime pay at one and one-half times her regular hourly rate for any hours worked beyond 40 in a week. During the pay period that ended December 31, 2019, Kathy worked 43 hours. Kathy is married and claims three withholding allowances on her W-4 form. Kathy’s cumulative earnings prior to this pay period total $27,000. Kathy’s wages are subject to the following deductions: Social Security tax at 6.2 percent Medicare tax at 1.45 percent Federal income tax (use the withholding table shown in - Figure 10.2b Health and disability insurance premiums, $141 Charitable contribution, $18 U.S. Savings Bond, $100 Required: Compute Kathy’s regular, overtime, gross, and net pay. Assuming the weekly payroll has been recorded, journalize the payment of her wages for the week ended December 31, 2019. Analyze: Based on Kathy’s cumulative earnings through December 31, how much overtime pay did she earn this year? Compute Kathy’s regular, overtime, gross, and net pay. (Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.) 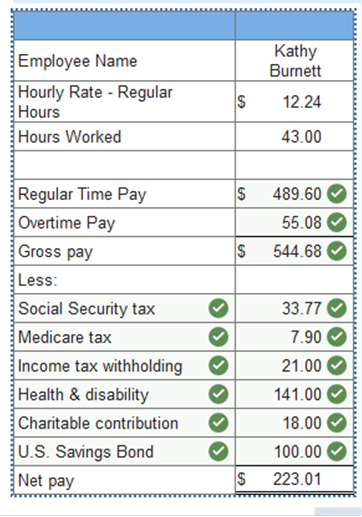
Assuming the weekly payroll has been recorded, journalize the payment of her wages for the week ended December 31, 2019. (Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.) 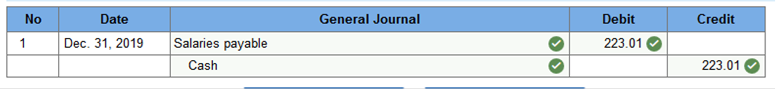
Based on Kathy’s cumulative earnings through December 31, how much overtime pay did she earn this year? (Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.) 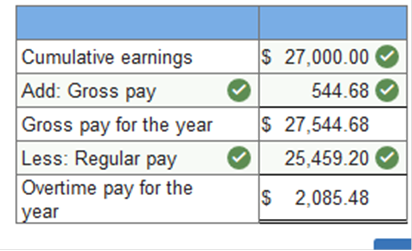
Problem 10.2A Computing gross earnings, determining deductions, preparing payroll register, journalizing payroll transactions. LO 10-2, 10-3, 10-4, 10-5 City Place Movie Theaters has four employees and pays them on an hourly basis. During the week beginning June 24 and ending June 30, 2019, these employees worked the hours shown below. Information about hourly rates, marital status, withholding allowances, and cumulative earnings prior to the current pay period also appears below. Consider any hours worked beyond 40 in the week as overtime hours and overtime pay at one and one-half times their regular hourly rate.
Required: Compute the regular, overtime, and gross earnings for each employee. Enter the figures in the payroll register. Compute the amount of social security tax to be withheld from each employee’s earnings. Assume a 6.2 percent social security rate on the first $122,700 earned by the employee during the year. Enter the figures in the payroll register. Compute the amount of Medicare tax to be withheld from each employee’s earnings. Assume a 1.45 percent Medicare tax rate on all salaries and wages earned by the employee during the year. Enter the figures in the payroll register. Determine the amount of federal income tax to be withheld from each employee’s total earnings. Use the tax tables in Figure 10.2a & Figure 10.2b. Enter the figures in the payroll register. Compute the net pay of each employee and enter the figures in the payroll register. Total and prove the payroll register. Prepare a general journal entry to record the payroll for the week ended June 30, 2019. Record the general journal entry to summarize payment of the payroll on July 3, 2019. Analyze: What are Andy Anderson’s cumulative earnings on June 30, 2019? Compute the regular, overtime, gross earnings, social security tax and Medicare tax to be withheld from each employee’s earnings. Assume a 6.2 percent social security rate on the first $122,700 earned by the employee during the year. Assume a 1.45 percent Medicare tax rate on all salaries and wages earned by the employee during the year. Determine the amount of federal income tax to be withheld from each employee’s total earnings. (Use the table shown in Figure 10.2A & Figure 10.2B whichever is applicable). Finally compute the net pay of each employee. (Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.) 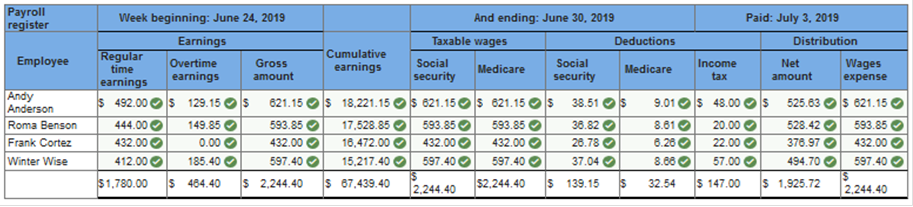
Prepare a general journal entry to record the payroll expenses and also summarize payment of the payroll for the week ended June 30, and July 3, 2019. (Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.) 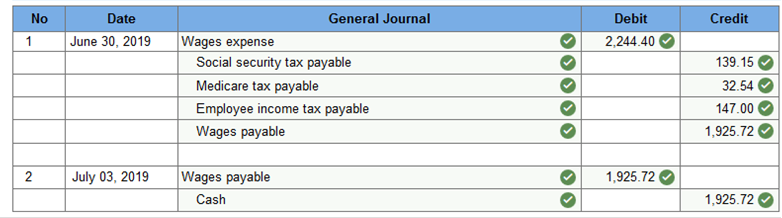
What are Andy Anderson’s cumulative earnings on June 30, 2019? (Round your intermediate calculations and final answer to 2 decimal places.) 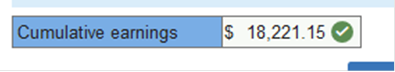
Problem 10.3A Computing gross earnings, determining deductions, preparing payroll register, journalizing payroll transactions. LO 10-2, 10-3, 10-4, 10-5 Alexander Wilson operates Metroplex Courier and Delivery Service. He has four employees who are paid on an hourly basis. During the workweek beginning December 15 and ending December 21, 2019, his employees worked the number of hours shown below. Information about their hourly rates, marital status, and withholding allowances also appears below, along with their cumulative earnings for the year prior to the December 15–21 payroll period. Consider any hours worked beyond 40 in the week as overtime hours and overtime pay at one and one-half times their regular hourly rate.
Required: Compute the regular, overtime, and gross earnings for each employee. Enter the figures in the payroll register. Compute the amount of social security tax to be withheld from each employee’s gross earnings. Assume a 6.2 percent social security rate on the first $122,700 earned by the employee during the year. Enter the figures in the payroll register. Compute the amount of Medicare tax to be withheld from each employee’s gross earnings. Assume a 1.45 percent Medicare tax rate on all salaries and wages earned by the employee during the year. Enter the figures in the payroll register. Determine the amount of federal income tax to be withheld from each employee’s total earnings. Use the tax tables in Figure 10.2a & Figure 10.2b to determine the withholding for Russell. Withholdings are $91.00 for Bahamon, $279.00 for Garcia, and $226.00 for Price. Enter the figures in the payroll register. Compute the net amount due each employee and enter the figures in the payroll register. Total and prove the payroll register. Bahamon and Russell are office workers. Garcia and Price are delivery workers. Prepare a general journal entry to record the payroll for the week ended December 21, 2019. Prepare a general journal entry on December 23 to summarize payment of wages for the week. Analyze: What percentage of total taxable wages was delivery wages? Compute the regular, overtime, gross earnings; social security tax and Medicare tax to be withheld from each employee's earnings. Assume a 6.2 percent social security rate on the first $122,700 earned by the employee during the year. Assume a 1.45 percent Medicare tax rate on all salaries and wages earned by the employee during the year. Determine the amount of federal income tax to be withheld from each employee's total earnings. (Use the table shown in Figure 10.2A & Figure 10.2B whichever is applicable) to determine the withholding for Russell. Withholdings for Bahamon is $91.00, $279.00 for Garcia, and $226.00 for Price. Finally compute the net amount due of each employee. (Bahamon and Russell are office workers. Garcia and Price are delivery workers.) (Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.) 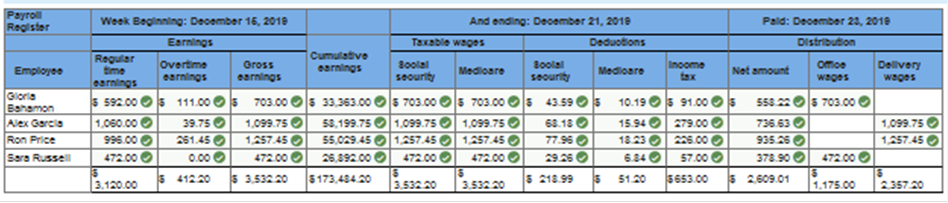
Prepare a general journal entry to record the payroll expenses and also summarize payment of wages for the week ended December 21 and December 23, 2019. (Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.) 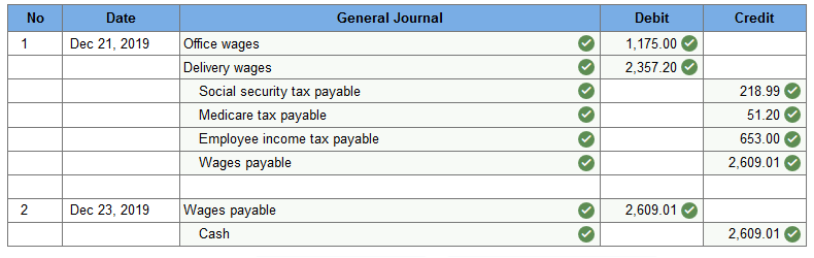
What percentage of total taxable wages was delivery wages? (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places and final answer to 1 decimal place.) 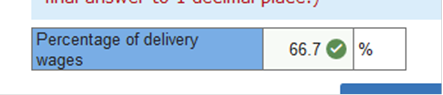
Problem 10.4A Computing gross earnings, determining deductions and net amount due, journalizing payroll transactions. Nashville Publishing Company pays its employees monthly. Payments made by the company on October 31, 2019, follow. Cumulative amounts paid to the persons named prior to October 31 are also given. Paul Parker, president, gross monthly salary of $18,700; gross earnings prior to October 31, $170,000. Carolyn Wells, vice president, gross monthly salary of $14,900; gross earnings paid prior to October 31, $151,000. Michelle Clark, independent accountant who audits the company's accounts and performs consulting services, $14,800; gross amounts paid prior to October 31, $43,200. James Wu, treasurer, gross monthly salary of $4,300; gross earnings prior to October 31, $51,100. Payment to Editorial Publishing Services for monthly services of Betty Jo Bradley, an editorial expert, $4,300; amount paid to Editorial Publishing Services prior to October 31, 2019, $32,400. Required: Use an earnings ceiling of $122,700 for social security taxes and a tax rate of 6.2 percent and a tax rate of 1.45 percent on all earnings for Medicare taxes. Prepare a schedule showing the following information: Each employee’s cumulative earnings prior to October 31. Each employee’s gross earnings for October. The amounts to be withheld for each payroll tax from each employee’s earnings; the employee’s income tax withholdings are Paul Parker, $4,904; Carolyn Wells, $4,191; James Wu, $987. The net amount due each employee. The total gross earnings, the total of each payroll tax deduction, and the total net amount payable to employees. Prepare the general journal entry to record the company’s payroll on October 31. Prepare the general journal entry to record payments to employees on October 31. Use an earnings ceiling of $122,700 for social security taxes and a tax rate of 6.2 percent and a tax rate of 1.45 percent on all earnings for Medicare taxes. Prepare a schedule showing the following information: (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.): 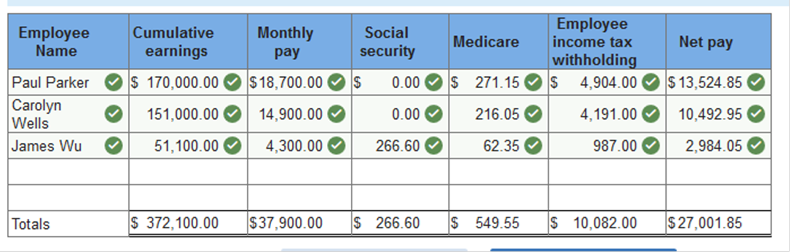
Prepare the general journal entry to record the company’s payroll expenses and also payments to employees on October 31, 2019. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) 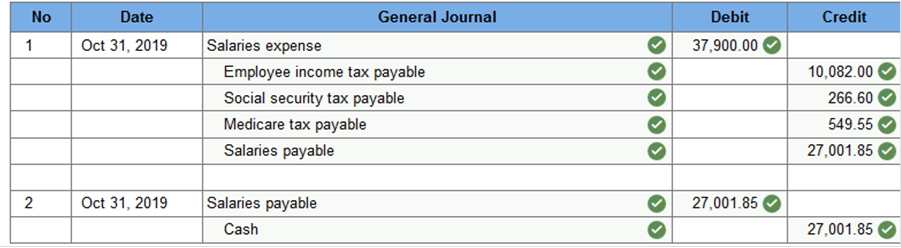
If retained earnings at the beginning of the period was $45 million and net income during the year was $9,907,500, how much was paid in dividends for the year? (Enter your answer in dollars not in millions. (5 should be entered as 5,000,000) Stockholders' equity: Preferred stock $50 par value: $0 Common stock $5 par value: 20,000 Additional paid-in capital: 100,000 Total paid-in capital: 120,000 Retained earnings: 53,000 Treasury stock: (3,700) Total stockholders' equity: $169,300 1,907,500 45,000,000 + 9,907,500 - 53,000,000 = 1,907,500 At the beginning of 20X1, a company issues 100,000 shares of 4%, $10 par value, cumulative preferred stock. All remaining shares outstanding are common stock. The company does not pay any dividends in 2011, but pays dividends of $100,000 at the end of 20X2. How much of the dividend will be paid to common stockholders in 2012? $20,000 Petite Fashions issued 500,000 of its 2 million shares of authorized common stock. At the end of the accounting period, 450,000 shares are outstanding. How many shares of treasury stock does Petite Fashions have? 50,000 shares 500,000 – 450,000 = 50,000 If the treasury stock was purchased for $20 per share, how many shares were purchased? (Enter your answer in total number of shares, not in thousands.) Stockholders' equity: Preferred stock $50 par value: $0 Common stock $5 par value: 20,000 Additional paid-in capital: 100,000 Total paid-in capital: 120,000 Retained earnings: 53,000 Treasury stock: (3,700) Total stockholders' equity: $169,300 185,000 3,700,000 / 20 = 185,000 A company issues 100,000 shares of $1 par value common stock for $17 per share. To record this transaction, the company would credit Additional Paid-in Capital for: $1,600,000. 17 – 1 (100,000) = 1,600,000 Assuming Net Income for the year is $98,000, what is the net operating cash flows given the following information: Depreciation Expense: $ 6,000 Increase in Prepaid Rent: $ 4,000 Decrease in Accounts Receivable: $ 3,000 Increase in Inventory: $ 5,000 Increase in Accounts Payable: $ 2,000 100,000 Suppose a company purchases 2,000 shares of its own $1 par value common stock for $16 per share. Which of the following is recorded at the time of the purchase? Debit Treasury Stock for $32,000. ABC Company's year end adjusted trial balance shows A/R of $100,000, Allowance for UA of $500 debit and sales of $750,000. Un-collectibles are estimated to be 0.4% of sales. The company uses the PERCENT OF A/R method of estimating bad debt. What is the amount of Un-collectible Account Expense that should be Booked? $3,500 A company issues 100,000 shares of $1 par value common stock for $17 per share. To record this transaction, the company would credit Common Stock for: $100,000. A company issues 10,000 shares of $0.05 par value common stock for $25 per share. Which of the following is recorded at issuance? Credit additional paid in capital for 500 Credit common stock for 500 Credit common stock for 250,000 Credit additional paid in capital for 250,000 Credit common stock for 500 ABC Company's year end adjusted trial balance shows A/R of $100,000, Allowance for UA of $500 debit and sales of $750,000. Un-collectibles are estimated to be 0.4% of sales. The company uses the PERCENT OF SALES method of estimating bad debt. What is the amount of Un-collectible Account Expense that should be Booked? $3,000 An auditor's professional skepticism would be heightened if the client does not perform a periodic reconciliation of cash. a. True b. False Which assertion relates cash balances including all cash transactions that have taken place during the period? a. Rights and obligations. b. Existence/occurrence. c. Presentation and disclosure. d. Completeness. e. Valuation or allocation. Which of these is not a common control for petty cash? a. Having internal audit conduct regular audits of the petty cash fund. b. Requiring receipts for all petty cash disbursements. c. Reconciling the petty cash fund before replenishing it. d. Limiting access to petty cash funds. The three major categories of marketable securities are: temporary investments in debt or equity securities, short-term cash management securities, and available-for-sale securities. a. True b. False Which type of account is used to process most cash transactions, including regular cash receipts and disbursements? a. savings account b. cash management account c. petty cash account d. general checking account Which of these is an audit document that lists all transfers between client bank accounts starting a short period before year end and continuing for a short period after year end? a. Bank deposit slip b. Cutoff bank statement. c. Bank confirmation. d. Interbank transfer statement. Which of the following is the description of an allocation assertion? a. The recorded balances reflect the true underlying economic value of those assets. b. Marketable securities exist at the balance sheet date. c. The company has title to marketable securities accounts as of the balance sheet date. d. The marketable securities balances include all securities transactions that have taken place during the period. e. Marketable securities are properly classified on the balance sheet and disclosed in the notes to the financial statements. Lapping occurs when an employee makes a sale but does not record it, and steals the cash. a. True b. False Complex financial instruments differ from more traditional financial instruments in that they have bundled many of the risks previously associated with one financial instrument and have marketed these bundled financial instruments separately. a. True b. False Which of these describes the audit procedure(s) to be performed to test the client's bank reconciliation at year-end for a customer note collected by the bank? a. Agree balance on reconciliation with the amount recorded on the client's general ledger b. Trace to cash disbursements journal; inquire of client as to the reason for the delay; trace items to a bank cutoff statement c. Confirm directly with the bank d. Trace cash receipts to cash journal; inquire of client as to the reason for the delay; trace items to a bank cutoff statement e. Inspect documentation related to the bank's credit memo . Homework Chapter 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 Test 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 Final Exam 01 02 Project
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |