|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Intermediate Accounting (ACG 3101) Homework 9 Intermediate Accounting Homework 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | Exams Chapters 1-3 4-7 8-9 10-11 | Final Exam
Exercise 9-1 (Algo)
Lower of cost or net realizable value [LO9-1]
Herman Company has three products in its ending inventory. Specific per unit data at the end of the year for each of the products are as follows:
Required: What unit values should Herman use for each of its products when applying the lower of cost or net realizable value (LCNRV) rule to ending inventory? 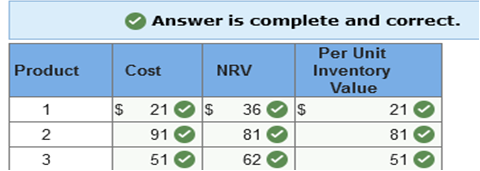 Explanation NRV = Selling price less costs to sell.
Exercise 9-2 (Algo) Lower of cost or net realizable value [LO9-1] The inventory of Royal Decking consisted of five products. Information about the December 31, 2021, inventory is as follows:
Costs to sell consist of a sales commission equal to 10% of selling price and shipping costs equal to 5% of cost. Required: What unit value should Royal Decking use for each of its products when applying the lower of cost or net realizable value (LCNRV) rule to units of ending inventory? 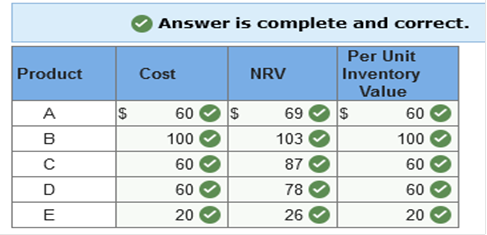 Explanation NRV = Selling price less costs to sell. Costs to sell = 10% of selling price and 5% of cost.
Exercise 9-10 (Algo) Gross profit method [LO9-2] A fire destroyed a warehouse of the Goren Group, Inc., on May 4, 2021. Accounting records on that date indicated the following:
The gross profit ratio has averaged 25% of sales for the past four years. Required: Use the gross profit method to estimate the cost of the inventory destroyed in the fire. 1,320,000 Explanation
Exercise 9-11 (Algo) Gross profit method [LO9-2] Royal Gorge Company uses the gross profit method to estimate ending inventory and cost of goods sold when preparing monthly financial statements required by its bank. Inventory on hand at the end of October was $59,900. The following information for the month of November was available from company records:
In addition, the controller is aware of $6,500 of inventory that was stolen during November from one of the company's warehouses. Required: 1. Calculate the estimated inventory at the end of November, assuming a gross profit ratio of 40%. 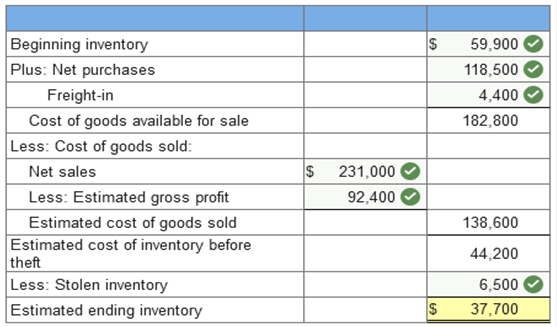 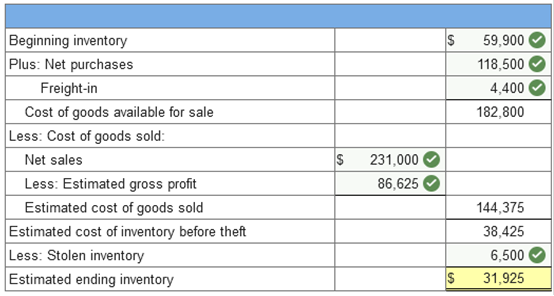 Explanation 1. Net purchases ($124,000 – $5,500) = 118,500 Net sales ($250,000 – $19,000) = $231,000 Estimated gross profit of 40% = 92,400 2. Mark-up as a % of cost ÷ (1 + Mark-up as a % of cost) = Gross profit as a % of sales. 60% ÷ 160% = 37.5% Net purchases ($124,000 – $5,500) = 118,500 Net sales ($250,000 – $19,000) = $231,000 Estimated gross profit of 37.5% = 86,625 Items held for sale in the normal course of business are referred to as __________. Intentory A _____ company resells goods while a _____ company produces goods. merchandising; manufacturing Inventory for a ____ company consists of raw materials, work in process, and finished goods. (Enter only one word.) Manufacturing In a perpetual inventory system the inventory account is continually adjusted. A periodic inventory system allows management to determine the amount of goods on hand without having to take a physical count. False Inventory is _____. an asset A periodic inventory system allocates cost of goods available for sale _____ a perpetual inventory system allocates cost of goods available for sale _____. at the end of the period each time goods are sold The goods a wholesale company purchases in finished form are referred to as what? Merchandise inventory Ownership of inventory at the end of the accounting period is determined for (Select all that apply.) goods shipped to customers. goods shipped by suppliers. Which of the following accounts are typically reported on the balance sheet of a manufacturing company? B. Work in process C. Raw materials D. Finished goods What type of expenditures should be included in the cost of inventory of a manufacturing company? (Select all that apply.) Expenditures necessary to bring inventory to sales location. Expenditures necessary to acquire inventory. A ___ inventory system adjusts for each change caused by a purchase, a sale, or a return of merchandise. Perpetual Dollar amounts are assigned to goods sold and goods remaining in ending inventory by making an assumption regarding what? How units of goods and their associated costs flow through the system. A periodic inventory system (Select all that apply.) does not continuously track the cost of merchandise sold. does not continuously track the quantity of merchandise. Select all that apply The specific identification method (select all that apply): matches each unit of inventory with its actual cost would be beneficial to a company that makes fine jewelry. Which inventory system allocates cost of goods available for sale only at the end of each reporting period? periodic inventory system Determining ownership of goods that are in transit at the end of the accounting period is important to assure proper inventory cutoff. Which inventory costing method assumes that cost of goods sold and ending inventory consist of a mixture of all the goods available for sale? Average Cost The cost of inventory includes (Select all that apply.) expenditures to acquire the inventory. the cost to bring inventory to its desired location Inventory cost flow assumptions can be used to assign dollar amounts to (Select all that apply.) ending inventory. goods sold. The FIFO method assumes that units sold are the _________ units acquired and that units remaining in ending inventory are the ________ units purchased. first; last What method of inventory valuation matches each unit on hand at the end of the period with its actual cost? specific identification The LIFO inventory method assumes that the units that remain in ending inventory are the oldest units in inventory A periodic inventory system allocates cost of goods available for sale _____; a perpetual inventory system allocates cost of goods available for sale _____. at the end of the period; each time goods are sold Assuming that prices rise over time, which inventory cost flow assumption will result in the highest cost of goods sold? LIFO The average cost method assumes that cost of goods sold consists of a mixture of all the goods available for sale Turn Company utilizes the LIFO inventory method to calculate taxable income. Which method is available to turn for financial reporting purposes? LIFO only What type of expenditures should be included in the cost of inventory of a manufacturing company? (Select all that apply.) Expenditures necessary to bring inventory to sales location. Expenditures necessary to acquire inventory. Pernell Company reported LIFO reserves of $150,000 and $100,000 in 2016 and 2015, respectively. The company utilized the FIFO assumption for internal purposes. Based on this information, we can conclude that Pernell's cost of goods sold for the 2016 fiscal year would have been $50,000 lower if it had used FIFO. Which inventory costing method assumes that items sold are those that were acquired first? FIFO High recordkeeping costs and possible LIFO liquidation are disadvantages of unit LIFO. The _____ inventory method assumes that the units in ending inventory were the items acquired first. last-in, first-out Assuming that prices rise over time, which inventory cost flow assumption will result in the highest cost of goods sold? LIFO Advantages of using LIFO inventory pools include which of the following? (Select all that apply.) Simplify recordkeeping Reduce the risk of LIFO layer liquidations If a company uses _____ to measure taxable income, they must use the same method for external financial reporting. LIFO Which of the following are disadvantages of unit LIFO? (Select all that apply.) Significant recordkeeping costs Possibility of LIFO liquidation A DVL pool is made up of items that are likely to have similar cost change pressures. The LIFO inventory method assumes that the units that remain in ending inventory are the oldest units in inventory Use of LIFO inventory pools reduces the chance of unintentional LIFO layer _____. (Enter only one word.) liquidations or liquidation Doris recently started her position at Monro Company. The company uses the dollar-value LIFO inventory method. On her first day at work, Doris was asked to calculate the cost index for a new inventory layer. The company's records reveal that the cost in terms of the base year was $50,000 and the cost in terms of the layer year was $100,000. What is the cost index for the new layer? 2 If a company uses LIFO to measure its taxable income, the IRS requires that LIFO also be used to measure income reported to investors and creditors. This is known as the. LIFO conformity rule. Smith Company adopted dollar-value LIFO (DVL) as of January 1, 2016, when it had an inventory of $690,000. Its inventory as of December 31, 2016, was $758,100 at year-end costs and the cost index was 1.05. What was DVL inventory on December 31, 2016? $723,600 Reason: $758,100/1.05 = $722,000 giving 2 layers of $690,000 and $32,000. $690,000 x 1.0 = $690,000 $32,000 x 1.05 = $33,600 $690,000 + $33,600 = $723,600 True or false: Dollar-value LIFO allows a company to combine a large variety of goods into one pool. True The dollar-value LIFO (DVL) inventory method allows a broader range of goods to be included in pools. The _____ inventory method assumes that the units in ending inventory were the items acquired first. last-in, first-out The layer year cost index is calculated by dividing the cost in ______ year by the cost in ______ year. layer; base Western Company adopted dollar-value LIFO (DVL) as of January 1, 2016, when it had an inventory of $715,000. Its inventory as of December 31, 2016, was $815,400 at year-end costs and the cost index was 1.08. What was DVL inventory on December 31, 2016? $758,200 Pernell Company reported LIFO reserves of $150,000 and $100,000 in 2016 and 2015, respectively. The company utilized the FIFO assumption for internal purposes. Based on this information, we can conclude that Pernell's pretax income for the 2016 fiscal year would have been $50,000 higher if it had used FIFO. The dollar-value LIFO (DVL) method (Select all that apply.) reduces the risk of liquidation of layers. simplifies recordkeeping. Which inventory costing method assumes that the units sold are the most recent units purchased? LIFO GAAP requires companies to report inventory (Select all that apply.)at the lower of cost or market value for companies using LIFO. at the lower of cost and net realizable value for companies using FIFO. Feather Company's inventory is recorded at its historical cost of $100,000. The replacement cost currently is $95,000; estimated selling price is $102,000; estimated selling cost is $5,000; normal profit is $10,000. The estimated net realizable value of the inventory is $97,000. $102,000 - $5,000 Smith Company's inventory cost is $100. The expected sales price is $110, estimated selling costs are $6. The normal gross profit ratio is 20% of selling price. The replacement cost of the inventory is $95. Smith Company uses the LIFO inventory method so must use the lower of cost or market approach and this inventory item should be valued at $95 Berta Company recently lost its entire inventory in a fire. The following information is available from its accounting records: Beginning inventory: $1,000; purchases: $13,000; net sales: $20,000. The company's average gross profit percentage is 40%. Using the gross profit method, a reasonable estimate of cost of goods sold for this past period would be $12,000. $20,000 x (1 - 40%) = $12,000 Applying the retail inventory method to approximate the lower of average cost or market value is often referred to as the conventional retail method. The lower of cost or market approach is _____ for companies that use _____. required under GAAP; LIFO or the retail inventory Tore Company's records reveal the following information regarding its inventory. Beginning inventory was $100,000 at cost and 160,000 at retail. Purchases during the year were $300,000 at cost and $500,000 at retail. Markups were $10,000 and markdowns, $20,000. Assuming the conventional retail method and net sales of $500,000, ending inventory at cost would be $89,550 Reason: Markdowns are excluded from the calculation of the cost-to-retail percentage Cost $400,000 ($100,000+$300,000) divided by Retail of $670,000 ($160,000+$500,000+$10,000) =59.7% x estimated ending inventory at retail = ($160,000 + $500,000 + $10,000 - $20,000 - $500,000) = 59.7% x $150,000 = $89,550 Net realizable value of inventory is determined by subtracting selling cost from the expected sales price. The _____ method assumes that units sold are those most recently acquired. LIFO Smith Company's inventory cost is $100. The expected sales price is $110, estimated selling costs are $6. The normal gross profit ratio is 20% of selling price. The replacement cost of the inventory is $95. Smith Company uses the LIFO inventory method so must use the lower of cost or market approach and this inventory item should be valued at $100 Ceiling is NRV = $110 - 6 = $104. Floor is NRV less normal profit of 20% so $104 - 22 = $82. Replacement cost is $95. Market is the middle of these three values so = $95 compared to cost of $100. Market is lower so record at market. Berta Company recently lost its entire inventory in a fire. The following information is available from its accounting records: Beginning inventory: $1,000; purchases: $13,000; net sales: $20,000. The company's average gross profit percentage is 40%. Using the gross profit method, a reasonable estimate of the lost inventory would be $2,000. Reason: $1,000 + 13,000 = $14,000 goods available for sale Net sales $20,000 less gross profit 40% = $12,000 $14,000 - 12,000 = 2,000 The retail inventory method is also referred to as the _____ retail method. (Enter only one word.) conventional Tore Company's records reveal the following information regarding its inventory. Beginning inventory was $100,000 at cost and 160,000 at retail. Purchases during the year were $300,000 at cost and $500,000 at retail. Markups were $10,000 and markdowns, $20,000. Assuming the conventional retail method is used and net sales were $500,000, ending inventory at retail would be (round the cost-to-retail percentage to two digits after the decimal point) $150,000 $160,000 + $500,000 + $10,000 - $20,000 - $500,000 = $150,000 A LIFO liquidation occurs when there is _____ in inventory quantity. a net decrease Western Company recently lost its entire inventory in an earthquake. The following information is available from its accounting records: Beginning inventory: $5,000; purchases: $18,000; net sales: $40,000. The company's average gross profit percentage is 40%. Using the gross profit method, a reasonable estimate of cost of goods sold for this past period would be: $24,000 $40,000 x (1 - 40%) = $24,000 In a period when costs are rising and inventory quantities are stable, the inventory method that would result in the highest ending inventory is: FIFO TB MC Qu. 8-73 (Algo) Fulbright Corp. uses the periodic inventory... Fulbright Corp. uses the periodic inventory system. During its first year of operations, Fulbright made the following purchases (listed in chronological order of acquisition): 44 units at $107 per unit 75 units at $73 per unit 175 units at $60 per unit Sales for the year totaled 269 units, leaving 25 units on hand at the end of the year. Ending inventory using the LIFO method is: $2675 Explanation 25 units × $107 = $2,675. TB MC Qu. 8-68 (Static) Company C is identical to Company D in... Company C is identical to Company D in every respect except that Company C uses LIFO and Company D uses average costs. In an extended period of rising inventory costs, Company C's gross profit and inventory turnover ratio, compared to Company D's, would be:
TB MC Qu. 8-105 (Algo) Anthony Thomas Candies... Anthony Thomas Candies (ATC) reported the following financial data for 2021 and 2020:
ATC's gross profit ratio (rounded) in 2021 is: (Round your answer to one decimal place e.g., 0.123 as 12.3%.) 54.1% Explanation $161,200 ÷ $298,200 = 54.1% TB MC Qu. 8-30 (Static) In a perpetual inventory system, the cost... In a perpetual inventory system, the cost of purchases is debited to: inventory Brief Exercise 8-7 (Algo) Inventory cost flow methods; periodic system [LO8-4] Samuelson and Messenger (SAM) began 2021 with 360 units of its one product. These units were purchased near the end of 2020 for $25 each. During the month of January, 180 units were purchased on January 8 for $28 each and another 360 units were purchased on January 19 for $30 each. Sales of 140 units and 260 units were made on January 10 and January 25, respectively. There were 500 units on hand at the end of the month. SAM uses a periodic inventory system. Required: 1. Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold for January using FIFO. 2. Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold for January using average cost. 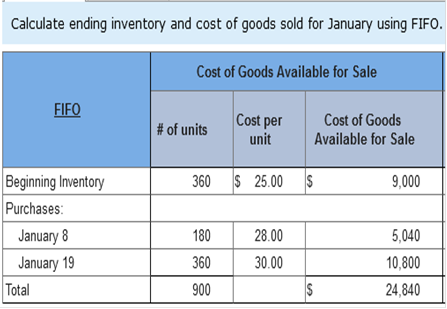  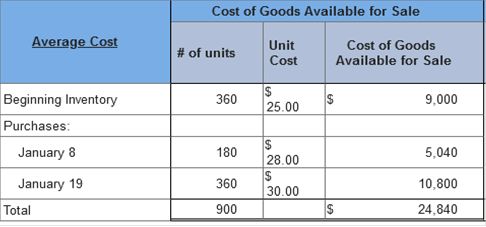 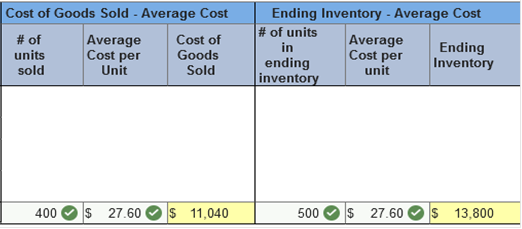 Explanation 1. Cost of goods available for sale:
First-in, first-out (FIFO)
Cost of ending inventory:
2. Average cost
Cost of ending inventory:
500 units × $27.60 = $13,800
*Alternatively, could be determined by multiplying the units sold by the average cost: 400 units × $27.60 = $11,040 Brief Exercise 8-12 (Algo) Supplemental LIFO reserve disclosures; Walgreens [LO8-6] Walgreens Boots Alliance, Inc., reported inventories of $2,325 million and $2,452 million in its August 31, 2017, and August 31, 2016, balance sheets, respectively. Cost of goods sold for the year ended August 31, 2017, was $30,444 million. The company uses primarily the LIFO inventory method. A disclosure note reported that if FIFO had been used instead of LIFO, inventory would have been higher by $304 million and $275 million at the end of the August 31, 2017, and August 31, 2016, periods, respectively. Calculate cost of goods sold for the year ended August 31, 2017, assuming Walgreens used FIFO instead of LIFO. (Enter your answer in millions.) Cost of goods sold: 30,415 Million. Explanation Cost of goods sold for the year ended August 31, 2017, would have been $29 million lower had Walgreens used FIFO for its LIFO inventory. The LIFO reserve increased in 2017 by $29 million, from $275 million to $304 million. An increase in the LIFO reserve has the effect of increasing
TB TF Qu. 9-5 (Static) Losses on reduction to NRV may be charged to... Losses on reduction to NRV may be charged to either cost of goods sold or to a line item among operating expenses. True Exercise 9-8 (Algo) Gross profit method [LO9-2] On September 22, 2021, a flood destroyed the entire merchandise inventory on hand in a warehouse owned by the Rocklin Sporting Goods Company. The following information is available from the records of the company’s periodic inventory system:
Required: Complete the below table to estimate the cost of inventory destroyed in the flood using the gross profit method. 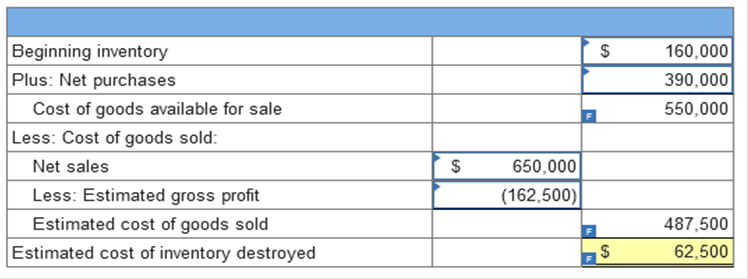 Explanation Estimated gross profit of 25% = $162,500 TB MC Qu. 9-132 (Algo) Haskell Corporation has determined its... Haskell Corporation has determined its year-end inventory on a FIFO basis to be $813,000. Information pertaining to that inventory is as follows:
What should be the reported value of Haskell’s inventory, if the company prepares its financial statements according to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)? $798,000 Explanation Under IFRS, inventory is valued at the lower of cost or net realizable value. NRV = $847,000 − $49,000 = $798,000 which is less than $813,000 cost. Intermediate Accounting Homework 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | Exams Chapters 1-3 4-7 8-9 10-11
| Final Exam
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |