|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Intermediate Accounting (ACG 3101) Homework 7 Intermediate Accounting Homework 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | Exams Chapters 1-3 4-7 8-9 10-11 | Final Exam
Required information
Learning Objective 07-04 Describe the accounting treatment for merchandise returns. [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] When merchandise returns are anticipated, a refund liability should be recorded, and sales revenue should be reduced by anticipated sales returns. Knowledge Check 01 At the end of its first year of operations, Loring Industries estimates that sales returns in the amount of $20,000 will occur during Year 2. The cost of the inventory expected to be returned is $12,000. All of Loring’s sales are made for cash and the company uses a perpetual inventory system. Assume that no returns have occurred as of the end of Year 1. Prepare the appropriate adjusting journal entry to record the expected sales returns and the inventory expected to be returned in Year 2. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) 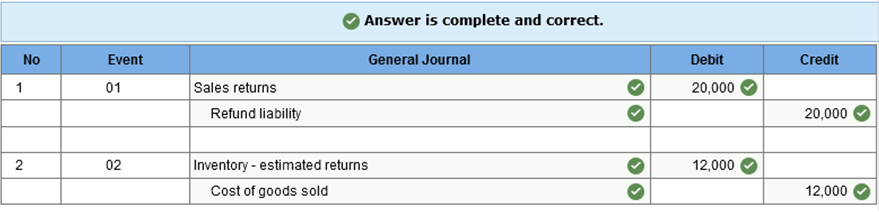
Knowledge Check 01 Manning Company uses the allowance method. At the end of its first year of operations, the company estimates that it will not collect $2,500 of its accounts receivable. Prepare the appropriate adjusting journal entry to establish the estimate for uncollectible accounts. (If no entry is required 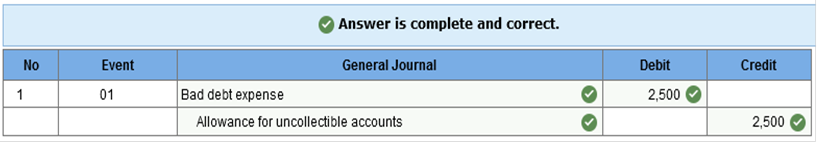
Required information Learning Objective 07-07 Describe the accounting treatment of notes receivable. Notes receivable are formal credit arrangements between a creditor (lender) and a debtor (borrower). The typical note receivable requires the payment of a specified face amount, also called principal, at a specified maturity date or dates. In addition, interest is paid at a stated percentage of the face amount. Interest on notes is calculated by multiplying the face amount by the annual rate by the fraction of the annual period. Knowledge Check 01 What is the amount of interest revenue that must be accrued on December 31st for a nine-month, 6%, $2,000 note receivable that was accepted on November 1st? 
Explanation Knowledge Check 01 Interest accrued = Face value × Interest rate × Fraction of the year Interest accrued = $2,000 × 6% × 2/12 = $20 Knowledge Check 01 Kleagle accepted a three-year, noninterest-bearing note in exchange for merchandise sold. Which of the following is true? Kleagle would credit a discount on note receivable when recording the sale. Explanation Knowledge Check 01 When a non-interest-bearing note is recorded at the sale, the face amount of the note is debited and a discount on notes receivable is credited along with the credit to sales revenue. The other three statements are false. Required information Learning Objective 07-08 Differentiate between the use of receivables in financing arrangements accounted for as a secured borrowing and those accounted for as a sale. A wide variety of methods exists for companies to use their receivables to obtain immediate cash. These methods can be described as either a secured borrowing or a sale of receivables. If three conditions indicating surrender of control are met, the transferor accounts for the transfer of receivables as a sale; otherwise as a secured borrowing. Knowledge Check 01 Accounting for the pledging of accounts receivable as collateral for a loan requires: Disclosure of the arrangement in notes to the financial statements. Explanation Knowledge Check 01 No special accounting treatment is needed for pledged receivables, but the arrangement should be described in a disclosure note. None of the other options are required for pledging a receivable. Knowledge Check 01 When accounts receivable are factored “with recourse”, it means: A special purpose entity is created. The risk of bad debts is transferred to the buyer. The buyer guarantees the seller will be paid. The seller retains all the risk of bad debts. Knowledge Check 02 Ferule, Inc. factors its accounts receivable without recourse. The factoring is recorded as: A secured borrowing. Only note disclosure of the arrangement is required. A sale. None of these answer choices are correct. Explanation Knowledge Check 01 When a company sells accounts receivable with recourse, the seller retains all of the risk of bad debts. In effect, the seller guarantees Knowledge Check 02 Accounts and notes receivable, like any other assets, can be sold at a gain or a loss. The basic accounting treatment for the sale of receivables is similar to accounting for the sale of other assets. The seller (transferor): (a) removes from the accounts the receivables (and any allowance for bad debts associated with them), (b) recognizes at fair value any assets acquired or liabilities assumed by the seller in the transaction, and (c) records the difference as a gain or loss. If a factoring arrangement is made without recourse, the buyer can’t ask the seller for more money if the receivables prove to be uncollectible. Therefore, the buyer assumes the risk of bad debts. Which of the following items are not included in cash? accounts receivable from customers Internal control consists of plans to -enhance the accuracy of accounting data. -enhance the reliability of accounting data. -promote operational efficiency. critical aspect of internal control system separation of duties Which of the following is an internal control procedure for cash disbursements? Disbursements should be made by check. Cash that is restricted and is not available for current use may be reported in the balance sheet as (Select all that apply.) other assets. investments and funds. a noncurrent asset. Which of the following items are included in cash? (Select all that apply.) currency and coins balance in checking accounts checks from customers When a company has a claim to receive assets in the future, how is this recorded on the balance sheet? A receivable Internal control consists of plans to (Select all that apply.) encourage adherence to company policies and procedures. minimize errors and theft. promote operational efficiency. Accounts receivable are almost always considered current assets because their normal collection, even if longer than a year, is part of the normal operating cycle. Which of the following is an example of separation of duties in a good system of internal control? The individual who receives the inventory does not have access to the accounting records. When initially recorded, the typical accounts receivable is valued at the amount expected to be received Internal control procedures for cash disbursements (other than small disbursements from petty cash) should include that -all disbursements (other than petty cash) are made by check. -all expenditures are authorized. -checks are signed by authorized individuals. A contra-asset account is used to reduce the carrying value of accounts receivable to the amount of cash expected to be received under the _____ method of accounting for bad debts. allowance Which of the following is usually reported on the balance sheet as a noncurrent asset? restricted asset Which of the following give rise to a note receivable? -A formal, written extension of the credit period to trade customers. -Loaning money to an affiliated company. -Loaning money to stockholders. Which of the following items are classified as receivables? -tax refund claims -amounts loaned and expected to be paid -amounts owed by customers (Face amount x annual rate x fraction of the annual period) is the formula for interest on a note An account receivable is normally classified as a current asset An interest-bearing note earns interest, whereas a noninterest-bearing note does not earn interest. False At what amount are accounts receivable recorded? The amount expected to be collected. An application where the interest rate stays the same over time, but interest revenue increases as the rate is multiplied by a receivable balance that increases is referred to as what? effective interest method When the amount of bad debts is material, GAAP requires the ___ method be used to reduce the carrying value of accounts receivable to the amount of cash expected to be received. (Enter only one word.) allowance Match the accounting standard with the appropriate treatment of receivables. 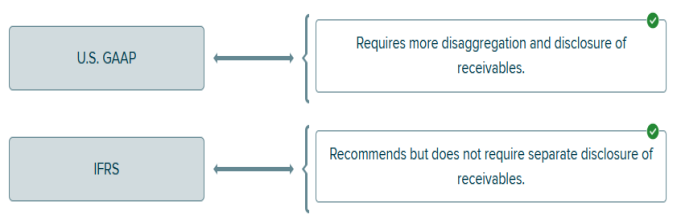
A formal, signed credit agreement between a lender and a borrower is called a(n) _____ by the lender. note receivable. Who houses the financed receivables on their balance sheet in a secured borrowing? Transferor The formula for calculating interest multiplies which of the following? -face amount of the note -annual interest rate -fraction of the annual period Assigning or pledging accounts receivable is used in a secured borrowing. Both interest bearing and noninterest bearing notes bear interest. True In a(n) (____) arrangement, the company sells its accounts receivable to a financial institution and the financial institution handles the billing and collections. (Enter only one word.) Factoring With the effective interest method, interest revenue differs between periods. True The transfer of a(n) ____ to a financial institution is called discounting. note receivable. Both IFRS and U.S. GAAP permit the fair value option for accounting for receivables. Which of the following is correct regarding the application of this option? IFRS restricts the circumstances for applying the fair value option Which of the following conditions must exist for a transfer of receivables to be treated as a sale? (Select all that apply.) The transferee has the right to pledge or exchange the assets. The transferor surrenders control of the asset. The assets are isolated and beyond the reach of the transferor. The (____) recognizes a note receivable in a secured borrowing agreement. (Enter only one word.) transferee Which of the following are costs of extending credit terms to customers? (Select all that apply.) Increase in uncollectible accounts. Increased investment in receivables. A(n) _____ borrowing occurs when accounts receivable are assigned or pledged as collateral for a loan. (Enter one word per blank) secured or secure Which of the following are services performed by a factor? (Select all that apply.) Handle billing and collection of accounts receivable. Buy accounts receivable. When adjusting the bank balance in a bank reconciliation, which item must be added to the bank balance? deposits in transit The transfer of a note receivable to a financial institution for an amount less than the face amount of the note is referred to as discounting a note receivable. A petty cash fund is an efficient way to handle what type of payments? Low cost office supply purchases. The most critical element in determining if a company can account for the transfer of receivables as a sale is the surrender of (____) control When a creditor changes the terms of a debt agreement in response to the debtor's financial difficulties, this is referred to as what? Troubled debt restructuring Which of the following is a cost of offering a cash discount? A reduction in the amount of cash collected from customers who take advantage of the discount. Assigning or pledging accounts receivable is used in a secured borrowing. When adjusting the book balance in a bank reconciliation, which items must be subtracted from the cash account book balance? charges for NSF checks service charges A petty cash account is used for small amounts of cash needed for low-cost items. A troubled debt restructuring occurs when the creditor changes the terms of the agreement to make it easier for the debtor to pay. Which of the following are adjustments to the book balance in a bank reconciliation? (Select all that apply.) Company errors Collections made by the bank on the company's behalf Bank service charges. Which of the following are adjustments to the bank balance in a bank reconciliation? Deduct checks outstanding Add deposits outstanding Adjustments for bank errors Brief Exercise 7-4 (Algo) Cash discounts; gross method [LO7-3] On December 28, 2021, Tristar Communications sold 14 units of its new satellite uplink system to various customers for $25,000 each. The terms of each sale were 2/10, n/30. Tristar uses the gross method to account for sales discounts. In what year will income before tax be affected by discounts, assuming that all customers paid the net-of-discount amount on January 6, 2022? By how much? 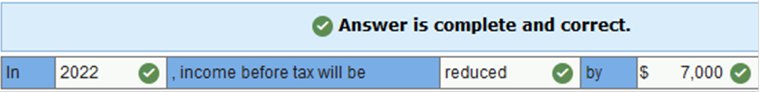
Explanation Income before tax in 2022 will be reduced by $7,000, the amount of the cash discounts. $25,000 × 14 = $350,000 × 2% = $7,000 Exercise 7-6 (Algo) Cash discounts; the gross method [LO7-3] Harwell Company manufactures automobile tires. On July 15, 2021, the company sold 1,300 tires to the Nixon Car Company for $50 each. The terms of the sale were 3/10, n/30. Harwell uses the gross method of accounting for cash discounts. Required: 1. Prepare the journal entries to record the sale on July 15 (ignore cost of goods) and collection on July 23, 2021. 2. Prepare the journal entries to record the sale on July 15 (ignore cost of goods) and collection on August 15, 2021. Required 1 Prepare the journal entries to record the sale on July 15 (ignore cost of goods) and collection on July 23, 2021. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) 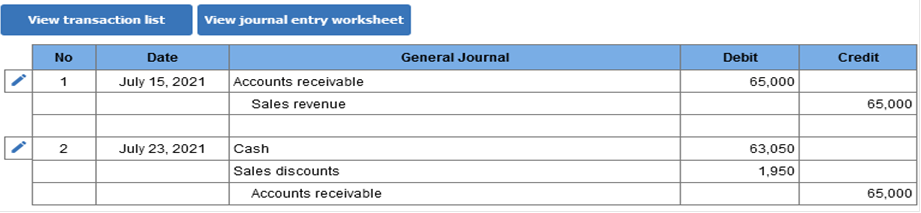
Required 2 Prepare the journal entries to record the sale on July 15 (ignore cost of goods) and collection on August 15, 2021. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) 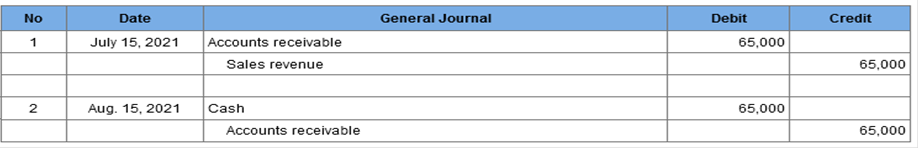 Explanation 1. Sales price = 1,300 units × $50 = $65,000 July 23, 2021: Cash (97% × $65,000) = $63,050 Sales discounts (3% × $65,000) = $1,950 Exercise 7-15 (Algo) Uncollectible accounts; allowance method; balance sheet approach [LO7-5, 7-6] Colorado Rocky Cookie Company offers credit terms to its customers. At the end of 2021, accounts receivable totaled $630,000. The allowance method is used to account for uncollectible accounts. The allowance for uncollectible accounts had a credit balance of $33,000 at the beginning of 2021 and $21,500 in receivables were written off during the year as uncollectible. Also, $1,300 in cash was received in December from a customer whose account previously had been written off. The company estimates bad debts by applying a percentage of 10% to accounts receivable at the end of the year. Required: 1. Prepare journal entries to record the write-off of receivables, the collection of $1,300 for previously written off receivables, and the year-end adjusting entry for bad debt expense. 2. How would accounts receivable be shown in the 2021 year-end balance sheet? 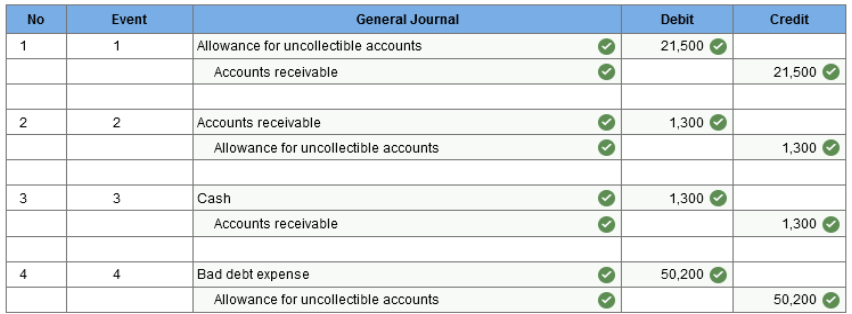
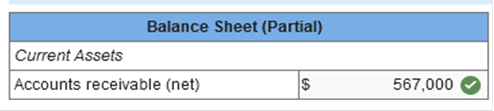
Explanation 1.
2. Accounts receivable, net of $63,000 allowance for uncollectible accounts = $567,000 Exercise 7-18 (Algo) Notes receivable [LO7-7] On June 30, 2021, the Esquire Company sold some merchandise to a customer for $54,000. In payment, Esquire agreed to accept a 7% note requiring the payment of interest and principal on March 31, 2022. The 7% rate is appropriate in this situation. Required: 1. Prepare journal entries to record the sale of merchandise (omit any entry that might be required for the cost of the goods sold), the December 31, 2021 interest accrual, and the March 31, 2022 collection. (Do not round intermediate calculations.) 2. If the December 31 adjusting entry for the interest accrual is not prepared, by how much will income before income taxes be over-or understated in 2021 and 2022? 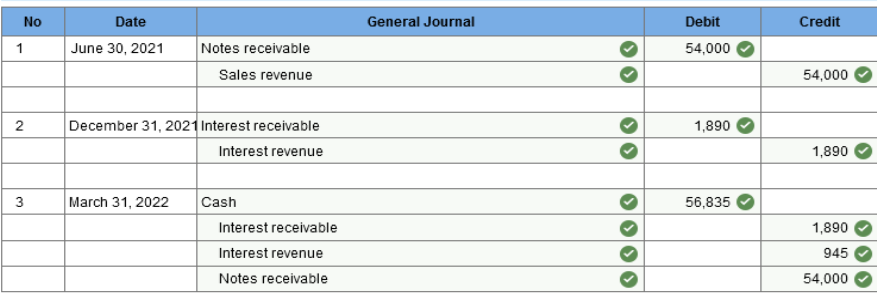
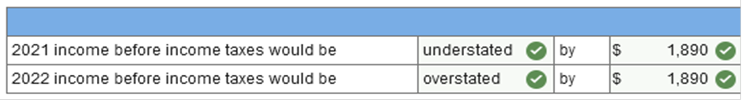
Explanation 1. December 31, 2021: Interest revenue ($54,000 × 7% × 6/12) = $1,890 March 31, 2022: Cash [$54,000 + ($54,000 × 7% × 9/12)] = $56,835 Interest revenue ($54,000 × 7% × 3/12) = $945 Exercise 7-30 (Algo) Ratio analysis [LO7-9] The current asset section of the Moorcroft Outboard Motor Company’s balance sheet reported the following amounts:
The average collection period for 2021 is 50 days. Required: Determine net sales for 2021. (Use 365 days in a year. Do not round intermediate calculations.) 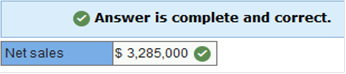
Explanation
Exercise 7-31 (Algo) Petty cash [Appendix 7A] Loucks Company established a $270 petty cash fund on October 2, 2021. The fund is replenished at the end of each month. At the end of October 2021, the fund contained $65 in cash and the following receipts:
Prepare the necessary general journal entries to establish the petty cash fund on October 2 and to replenish the fund on October 31. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) 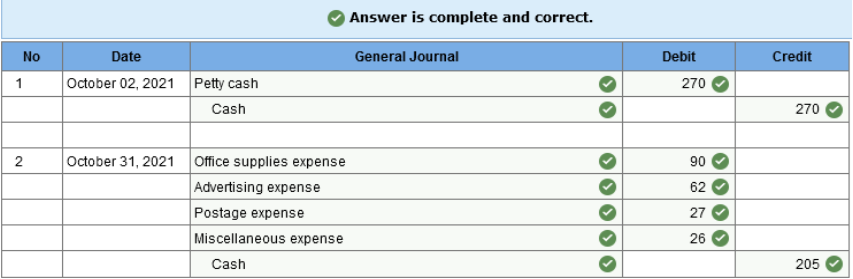
Exercise 7-34 (Algo) Bank reconciliation and adjusting entries [Appendix 7A] Harrison Company maintains a checking account at the First National City Bank. The bank provides a bank statement along with canceled checks on the last day of each month. The July 2021 bank statement included the following information:
The company’s general ledger account had a balance of $39,598 at the end of July. Deposits outstanding totaled $6,700 and all checks written by the company were processed by the bank except for those totaling $8,460. In addition, a $2,400 July deposit from a credit customer was recorded as a $240 debit to cash and credit to accounts receivable, and a check correctly recorded by the company as a $50 disbursement was incorrectly processed by the bank as a $500 disbursement. Required: 1. Prepare a bank reconciliation for the month of July. 2. Prepare the necessary journal entries at the end of July to adjust the general ledger cash account. ` 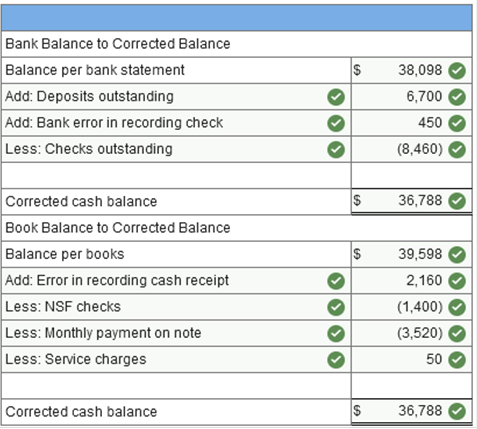
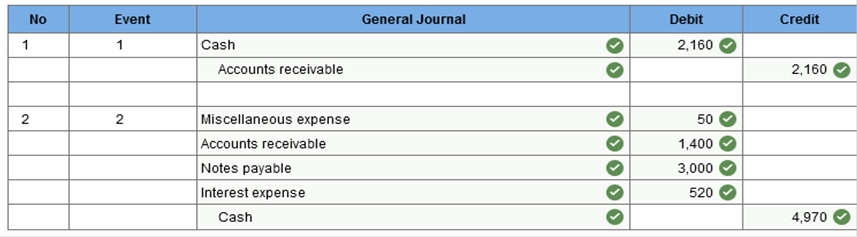
Explanation 1. Error in recording cash receipt: ($2,400 − $240) = $2,160 Note: Each of the adjustments to the book balance required journal entries. None of the adjustments to the bank balance require entries. Oswego Clay Pipe Company sold $46,000 of pipe to Southeast Water District #45 on April 12 of the current year with terms 1/15, n/60. Oswego uses the gross method of accounting for sales discounts. What entry would Oswego make on April 12?
As of January 1, 2021, Farley Co. had a credit balance of $524,000 in its allowance for uncollectible accounts. Based on experience, 4% of Farley's credit sales have been uncollectible. During 2021, Farley wrote off $631,000 of accounts receivable. Credit sales for 2021 were $19,500,000. In its December 31, 2021, balance sheet, what amount should Farley report as allowance for uncollectible accounts? $673,000 Explanation Current year expense = $19,500,000 × 4% = $780,000; $780,000 + $524,000 – $631,000 = $673,000. Cash that is restricted and not available for current operations is reported in the balance sheet as: Investments uncollectible accounts of $471,000 and $1,540 respectively, at December 31, 2020. During 2021, Calistoga's credit sales and collections were $324,000 and $309,000, respectively, and $1,740 in accounts receivable were written off. Calistoga's 2021 bad debt expense is: $972.00
Explanation
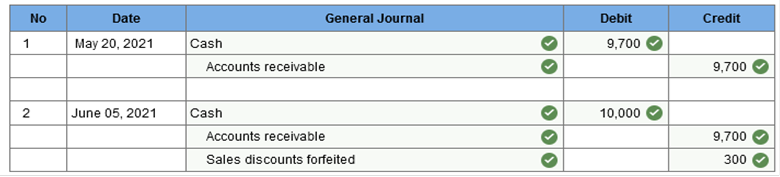
Cash equivalents do not include: High grade marketable equity securities On May 12, 2021, Falwell Computing sold five computers to Computing Plus for $10,000, subject to terms 3/10, n/30. Falwell uses the net method of accounting for sales discounts. Required: 1. Prepare the journal entry to record the sale. 2 & 3. Prepare the journal entries to record receipt of the payment, assuming the correct amount was received on May 20, 2021 and June 5, 2021. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
As of January 1, 2021, Barley Co. had a credit balance of $520,000 in its allowance for uncollectible accounts. Based on experience, 2% of Barley’s gross accounts receivable have been uncollectible. During 2021, Barley wrote off $650,000 of accounts receivable. Barley’s gross accounts receivable as December 31, 2021 is $18,000,000. How much bad debt expense should Barley record for 2021? $490,000 Explanation $520,000 – $650,000 + x = $360,000. x = $490,000. The following information relates to a company’s accounts receivable: gross accounts receivable balance at the beginning of the year, $380,000; allowance for uncollectible accounts at the beginning of the year, $27,000 (credit balance); credit sales during the year, $1,350,000; accounts receivable written off during the year, $18,000; cash collections from customers, $1,250,000. Assuming the company estimates bad debts at an amount equal to 2% of credit sales. 1. Calculate bad debt expense for the year. 2. Calculate the year-end balance in the allowance for uncollectible accounts. 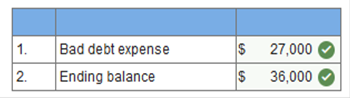
Explanation 1. Bad debt expense = $1,350,000 × 2% = $27,000 2.
On December 28, 2021, Tristar Communications sold 19 units of its new satellite uplink system to various customers for $15,000 each. The terms of each sale were 3/15, n/30. Tristar uses the net method to account for sales discounts. In what year will income before tax be affected by discounts, assuming that all customers paid the net-of-discount amount on January 6, 2022? By how much? 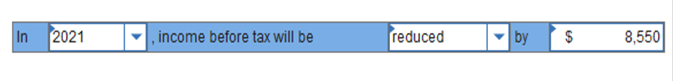
Explanation Income before tax in 2021 will be reduced by $8,550, the anticipated amount of cash discounts. $15,000 × 19 = $285,000 × 3% = $8,550 Calistoga Produce estimates bad debt expense at 0.50% of credit sales. The company reported accounts receivable and allowance for uncollectible accounts of $481,000 and $1,450 respectively, at December 31, 2020. During 2021, Calistoga's credit sales and collections were $316,000 and $303,000, respectively, and $1,770 in accounts receivable were written off. Calistoga's 2021 bad debt expense is: $1,580 Explanation
Intermediate Accounting Homework 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | Exams Chapters 1-3 4-7 8-9 10-11
| Final Exam
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |