|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Intermediate Accounting (ACG 3101) Homework 3 Intermediate Accounting Homework 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | Exams Chapters 1-3 4-7 8-9 10-11 | Final Exam
Learning Objective 03-02 Identify and describe the
various asset classifications.
Current assets include cash and other assets that are reasonably expected to be converted to cash or consumed within one year Knowledge Check 01 Which of the following would be reported as a current asset?
A nine-month insurance policy paid in
advance. Which of the following would be
considered a long-term asset?
Machinery the company intends to use over the next seven years. Which of the following is likely
never a current liability?
Prepaid insurance. Which of the following is a
long-term liability? Bonds payable that are due in 5 years. The amount that the shareholders
have invested into the company is called: Paid-in capital. Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Financial statement disclosures are used to convey additional information about the account balances in the basic financial statements as well as to provide supplemental information. This information is disclosed, often parenthetically in the basic financial statements, or in disclosure notes that often include supporting schedules. Which of the following subjects is most likely to be discussed in the summary of significant accounting policies? Depreciation methods used. Bribery committed by a sales person in another country. An important event that happened after the financial statements were issued. A loan made by the company to the CEO. Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] The balance sheet provides information that can be useful in assessing risk. A key element of risk analysis is investigating a company’s ability to pay its obligations when they come due. Liquidity ratios and solvency ratios provide information about a company’s ability to pay its obligations. The current ratio is calculated by dividing: Explanation Current assets include cash and other assets that are reasonably expected to be converted to cash or consumed within the coming year, or within the normal operating cycle of the business, if longer. The insurance policy will be consumed within the next year. The other assets are expected to be converted to cash or consumed over more than one year. The financial statement that
displays a firm's financial position on a particular date is the ___ ___ .
(Enter one word per blank) Balance sheet
Solvency and liquidity. Assets minus liabilities, measured
according to GAAP, is not likely to be representative of the ____ value of
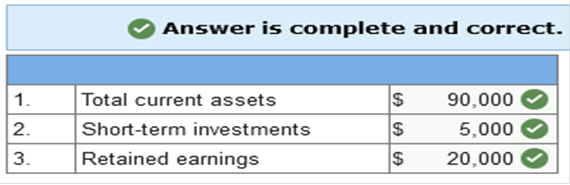
the entity. (Enter only one word.) market monetary; nonmonetary fixed; variable equity; nonequity current; noncurrent Current ____ include cash and other items that will be converted to cash or consumed within the coming year. (Enter only one word.) assets Which of the following financial statements shows a firm's financial position on a particular date? Multiple choice question. balance sheet statement of cash flows income statement statement of stockholders' equity The time period necessary to convert cash to raw materials, convert raw materials into finished products, sell the products, and collect on the account receivable is referred to as the ______ cycle. liquidity production collection operating The financial statement that provides information about liquidity and long-term solvency is the balance sheet statement of owners' equity statement of cash flows income statement Investments in stock and debt securities of other corporations are included as _____ if the company has the ability and intent to sell them within the next 12 months. long-term liabilities short-term liabilities long-term investments short-term investments True or false: The balance sheet will directly measure the company's market value. True False True or false: Accounts receivable result from the sale of goods or services for cash. True False In a balance sheet, how are assets classified? Mature and nonmature. Redeemable and nonredeemable. Current and noncurrent. High risk and low risk. Schwinn is a company that makes bicycles. Which of the following items would be included in Schwinn's inventory? (Select all that apply.) bicycle chains finished bicycles bicycle tires salary for salesperson Cash and other assets that are reasonably expected to be converted to cash or consumed within 1 year or the current operating cycle are classified as noncurrent assets. nonmonetary assets. current assets. fixed assets. Obligations to other entities are classified as ___ on the balance sheet. (Enter only one word.) liabilities True or false: The operating cycle for most firms is 1 year or less. True False Which of the following is true regarding disclosure notes? They outline the business plan of the company. They explain or elaborate on data presented in the financial statements. They are required for each line item on the financial statements. They are presented as part of Management Discussion and Analysis in the annual report. How should liquid investments expected to be converted to cash within the current operating cycle be reported in the balance sheet? As a short-term investment in the current asset section. As a current liability in the liability section of the balance sheet. As a restricted stockholders' equity account on the balance sheet. As a long-term investment in the noncurrent asset section. What is the principle that requires that financial statements provide all material relevant information concerning the entity? full-disclosure realization conservatism going concern ___ ___ result from the sale of goods or services on credit. (Enter one word per blank.) Accounts receivable The Management Discussion and Analysis section of the financial statements includes a perspective on which of the following? (Select all that apply.) Job costing Auditors' report Capital resources Operations Liquidity Which of the following are included in inventory? (Select all that apply.) Trade receivables Finished goods Work in process Raw materials Intangibles What does a liability represent? Obligations due from other entities. Receivables due from customers. Expenses paid in advance of use. Obligations owed to other entities. Responsibility for the financial statements and other information found in the annual report lies with ___. (Enter only one word.) Management Additional ___ are critical to understanding financial statements and to evaluating a firm's performance. (Enter only one word.) disclosures Which of the following are required SEC disclosures? (Select all that apply.) Director compensation Executive stock option information Executive compensation Director and executive hourly wage information Director and executive daily activity report The full-disclosure principle requires financial statements to provide all____ ____ information regarding the company. (Enter one word per blank.) material relevant What is the role of the auditor? To attest to the solvency of the company. To attest to the accuracy of the financial statements. To attest to the accuracy of information in the annual report. To attest to the fairness of the financial statements. An analysis provided by the company's management is included in the Multiple choice question. notes to the financial statements. summary of significant accounting policies. Management Discussion and Analysis. earn positive net income year over year. withstand various events that may impair its ability to earn profits. pay its obligations when they come due. Schwinn is a company that makes bicycles. Which of the following items would be included in Schwinn's inventory? (Select all that apply.) bicycle tires bicycle chains salary for salesperson finished bicycles Who is responsible for the information in the annual report? Board of directors of the company. Internal auditors of the company. CPA firm that audits the company. Management of the company. A ratio used to measure liquidity is the earnings per share ratio. return on assets. debt to equity ratio. current ratio. SEC requirements provide for disclosures on executive and director compensation, particularly concerning ____ options. (Enter only one word.) stock The ability to pay its long-term debts as they become due is referred to as ______ of the company. liquidity working capital solvency The role of a(n) ____ is to attest to the fairness of the financial statements they have examined. (Enter only one word.) auditors Companies that operate in more than one significant business must provide which of the following? notes to financial statements segment information subsidiary financial statements multiple financial statements Default risk refers to how adept a company is at withstanding various events that might impair its ability to earn profits. True False ____ consist of assets that a retail or wholesale company acquires for resale or goods that manufacturers produce for sale. (Enter only one word.) Inventory Which of the following are liquidity ratios? (Select all that apply.) current ratio return on equity ratio debt to asset ratio acid-test or quick ratio What refers to the riskiness of a company with regard to the amount of liabilities in its capital structure? Liquidity Long-term solvency Cash flow risk The FASB requires that companies that engage in more than one significant business must provide supplemental information concerning individual operating ____ segment If a company has a large amount of long-term debt in its capital structure, this will affect the firm's ______. liquidity working capital solvency Exercise 3-1 (Static) Balance sheet; missing elements [LO3-2, 3-3, 3-8] The following December 31, 2021,
fiscal year-end account balance information is available for the Stonebridge
Corporation:
The only liabilities not listed are $30,000 notes payable due in two years and related accrued interest of $1,000 due in four months. The current ratio at year-end is 1.5:1. Required: Determine the following at December 31, 2021:
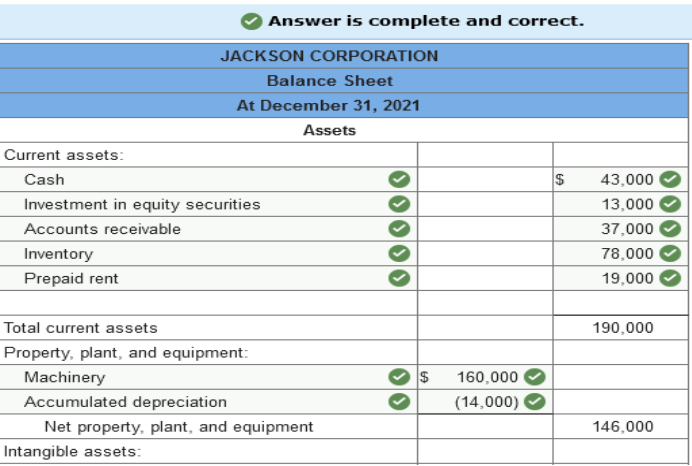
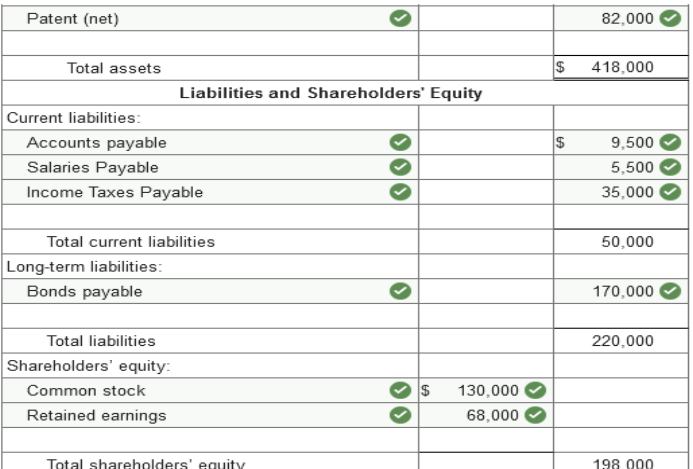
Exercise 3-4 (Algo) Balance sheet
preparation [LO3-2, 3-3] The following is a December 31,
2021, post-closing trial balance for the Jackson Corporation.
(Amounts to be
deducted should be indicated by a minus sign.)
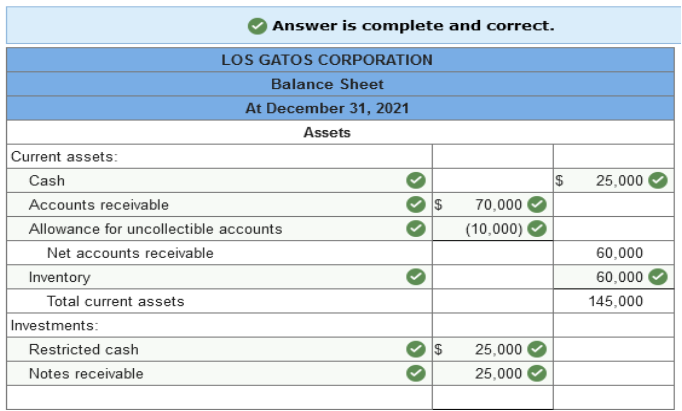
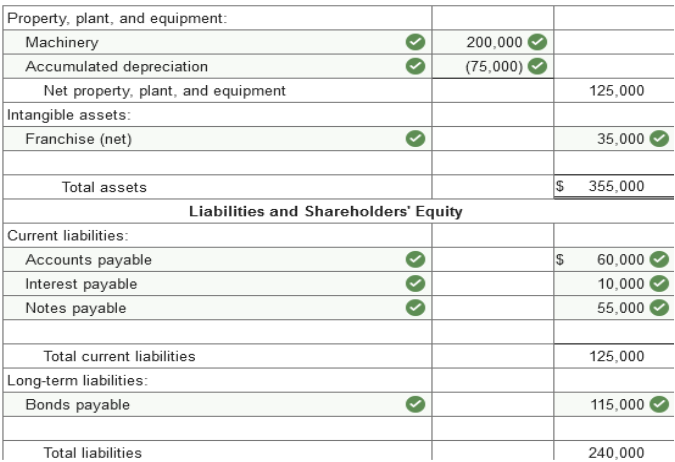
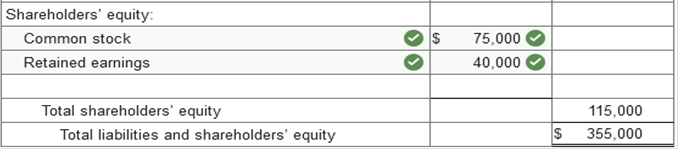
The following balance sheet for the Los Gatos Corporation was prepared by a recently hired accountant. In reviewing the statement you
notice several errors.
1.
Cash includes a $25,000 restricted
amount to be used for repayment of the bonds payable in 2025. 2.
The cost of the machinery is
$200,000. 3.
Accounts receivable includes a
$25,000 notes receivable from a customer due in 2024. 4.
The notes payable balance includes
accrued interest of $10,000. Principal and interest are both due on February
1, 2022. 5.
The company began operations in
2016. Net income less dividends since inception of the company totals
$40,000. 6.
55,000 shares of no par common stock
were issued in 2016. 200,000 shares are authorized. Prepare a corrected, classified balance sheet. Use the additional information to help determine appropriate classifications and account balances. The cost of machinery and its accumulated depreciation are shown separately. (Amounts to be deducted should be indicated by a minus sign.)
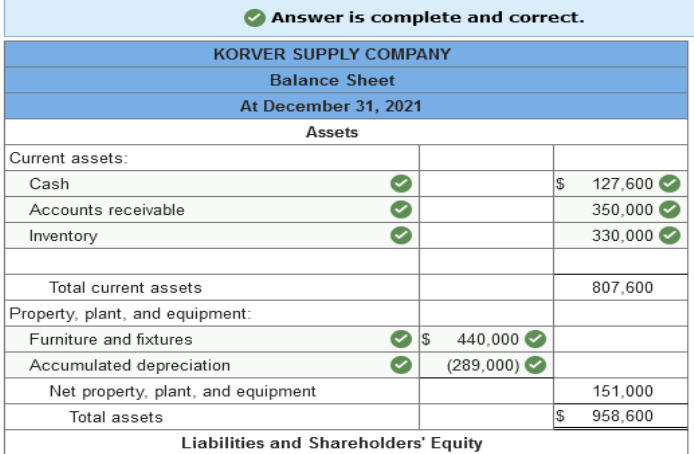
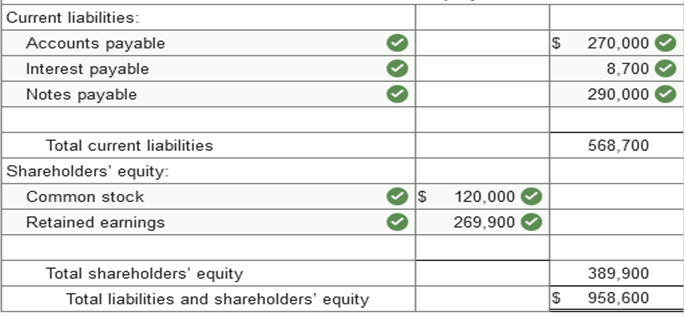
The following is the balance sheet of Korver Supply Company at December 31, 2020 (prior year).
Transactions during 2021 (current year) were as follows:
Additional Information: The notes payable are dated June 30, 2020, and are due on June 30, 2022. Interest at 6% is payable annually on June 30. Depreciation on the furniture and fixtures for 2021 is $34,000. The furniture and fixtures originally cost $440,000. Required: Prepare a classified balance sheet at December 31, 2021, by updating ending balances from 2020 for transactions during 2021 and the additional information. The cost of furniture and fixtures and their accumulated depreciation are shown separately. (Amounts to be deducted should be indicated by a minus sign.)
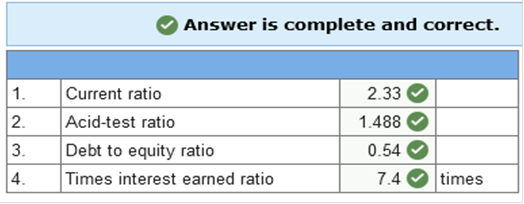
Exercise 3-16 (Algo) Calculating
ratios [LO3-8] The
2021 balance sheet for Hallbrook Industries, Inc., is shown below.
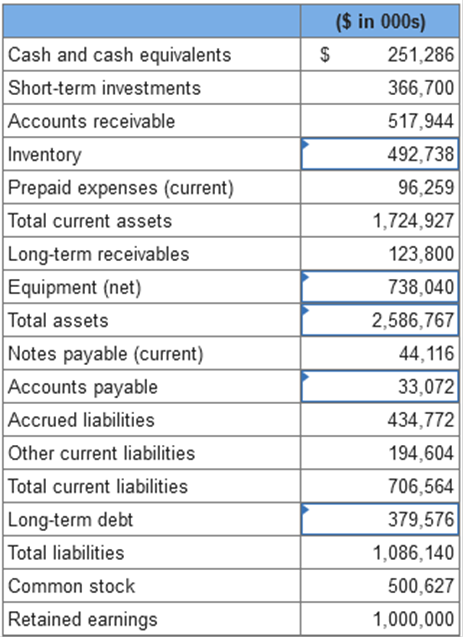
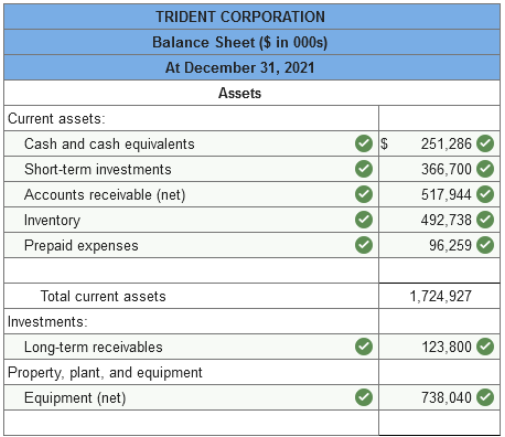
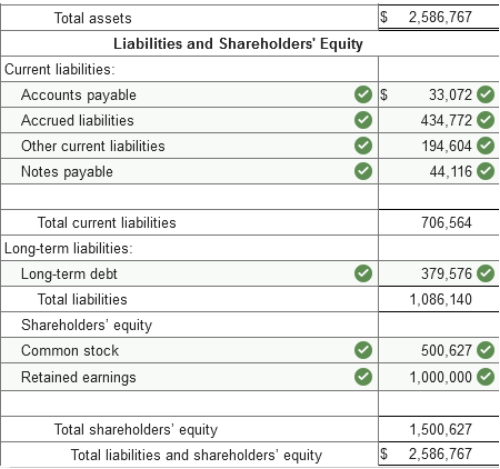
Problem 3-2 (Algo) Balance sheet
preparation; missing elements [LO3-2, 3-3] The data listed below are taken from
a balance sheet of Trident Corporation at December 31, 2021.
Problem 3-3 (Algo) Balance sheet
preparation [LO3-2, 3-3] The following is a December 31,
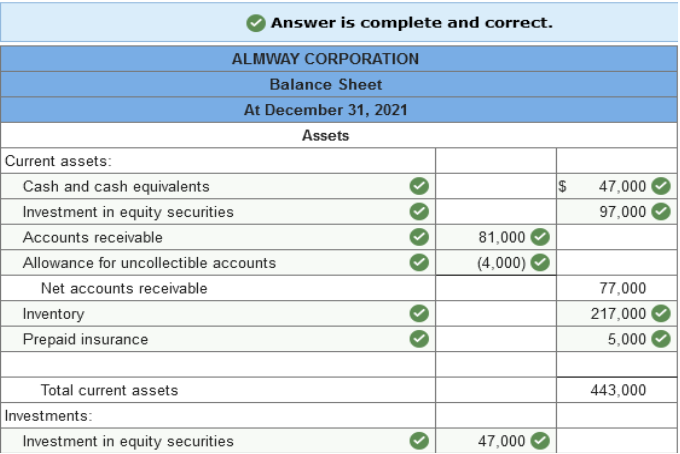
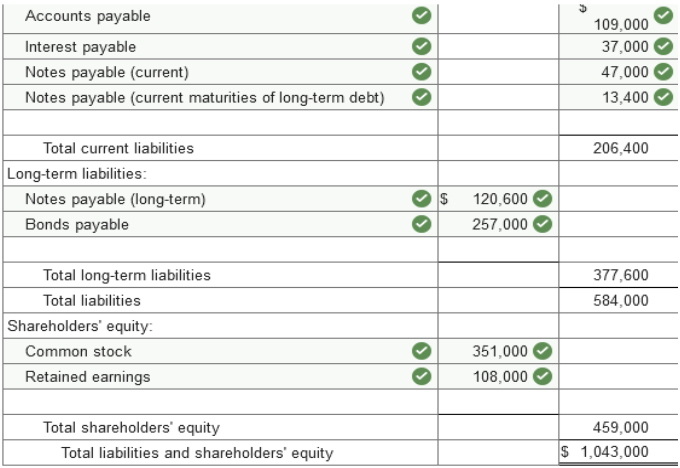
2021, post-closing trial balance for Almway Corporation.
The investment in equity securities account includes an investment in common stock of another corporation of $47,000 which management intends to hold for at least three years. The balance of these investments is intended to be sold in the coming year. The land account includes land which cost $42,000 that the company has not used and is currently listed for sale. The cash account includes $32,000 restricted in a fund to pay bonds payable that mature in 2024 and $40,000 restricted in a three-month Treasury bill. The notes payable account consists of the following: a $47,000 note due in six months. a $67,000 note due in six years. a $67,000 note due in five annual installments of $13,400 each, with the next installment due February 15, 2022. The $77,000 balance in accounts receivable is net of an allowance for uncollectible accounts of $4,000. The common stock account represents 117,000 shares of no par value common stock issued and outstanding. The corporation has 500,000 shares authorized. Required: Prepare a classified balance sheet for the Almway Corporation at December 31, 2021. (Amounts to be deducted should be indicated by a minus sign.)
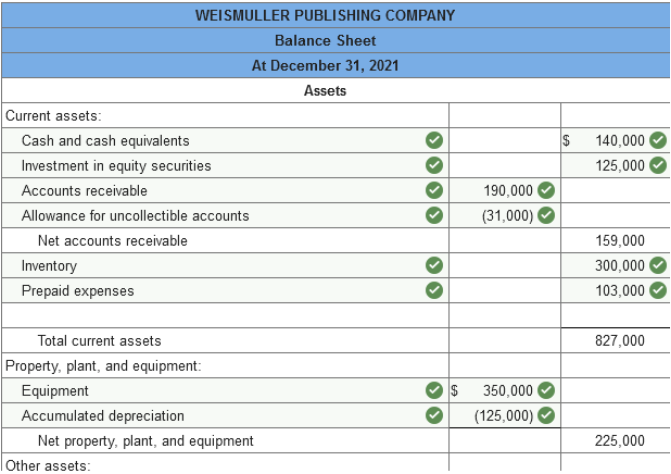
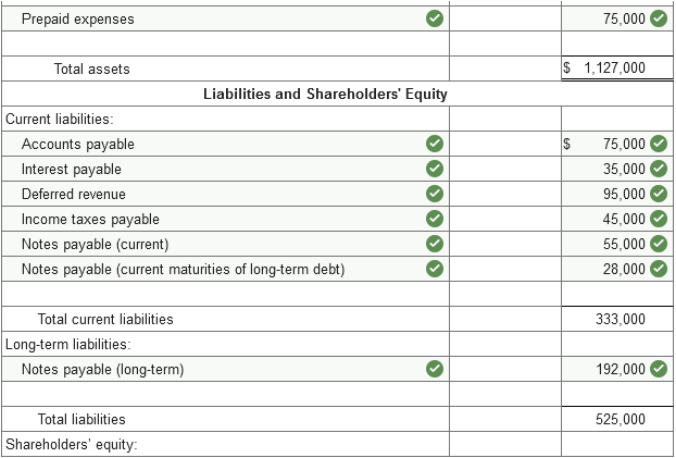
Problem 3-4 (Algo) Balance sheet
preparation [LO3-2, 3-3] The following is the ending balances
of accounts at December 31, 2021, for the Weismuller Publishing Company.
Prepaid expenses include $150,000 paid on December 31, 2021, for a two-year lease on the building that houses both the administrative offices and the manufacturing facility. Investments include $45,000 in Treasury bills purchased on November 30, 2021. The bills mature on January 30, 2022. The remaining $125,000 is an investment, in equity securities that the company intends to sell in the next year. Deferred revenue represents customer prepayments for magazine subscriptions. Subscriptions are for periods of one year or less. The notes payable account consists of the following: a $55,000 note due in six months. a $136,000 note due in six years. a $84,000 note due in three annual installments of $28,000 each, with the next installment due August 31, 2022. The common stock account represents 415,000 shares of no par value common stock issued and outstanding. The corporation has 830,000 shares authorized. Required: Prepare a classified balanced sheet for the Weismuller Publishing Company at December 31, 2021. (Amounts to be
deducted should be indicated by a minus sign.)
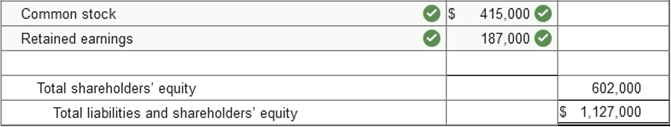
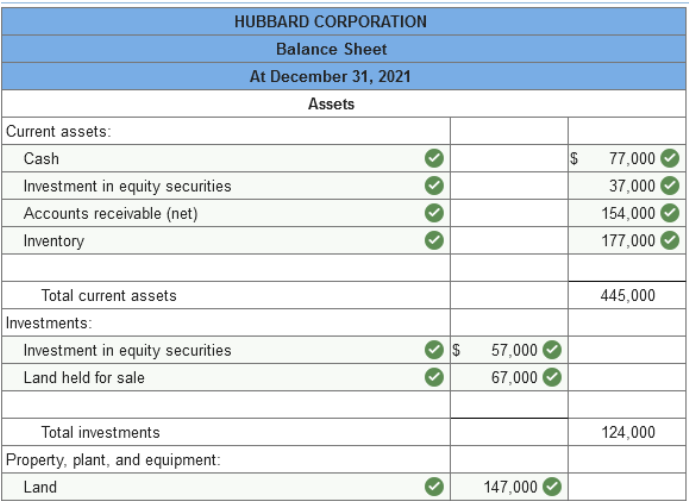
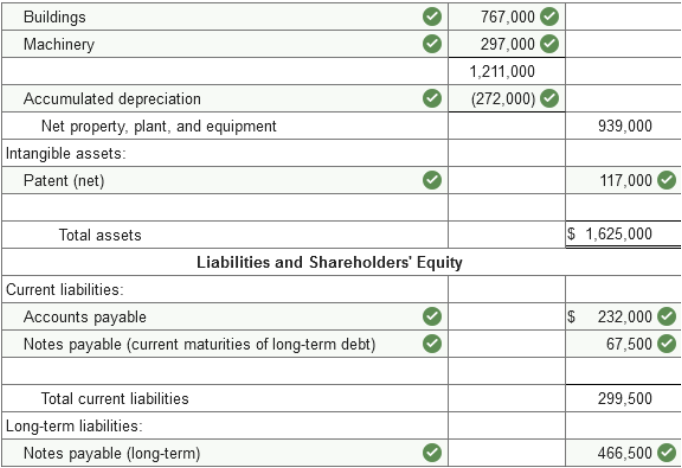
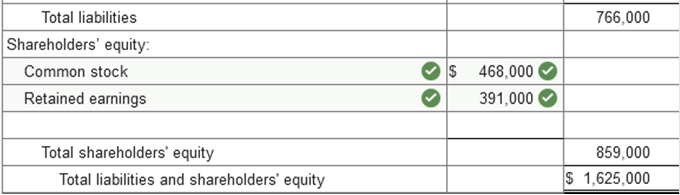
Problem 3-7 (Algo) Balance sheet
preparation; errors [LO3-2, 3-3] The following balance sheet for the
Hubbard Corporation was prepared by the company:
The buildings, land, and machinery are all stated at cost except for a parcel of land that the company is holding for future sale. The land originally cost $67,000 but, due to a significant increase in market value, is listed at $154,000. The increase in the land account was credited to retained earnings. The investment in equity securities account consists of stocks of other corporations and are recorded at cost, The remainder will be held indefinitely. Notes payable are all long term. However, a $270,000 note requires an installment payment of $67,500 due in the coming year. Inventory is recorded at current resale value. The original cost of the inventory is $177,000. Required: Prepare a corrected classified balance sheet for the Hubbard Corporation at December 31, 2021. (Amounts to be deducted should be indicated by a minus sign.)
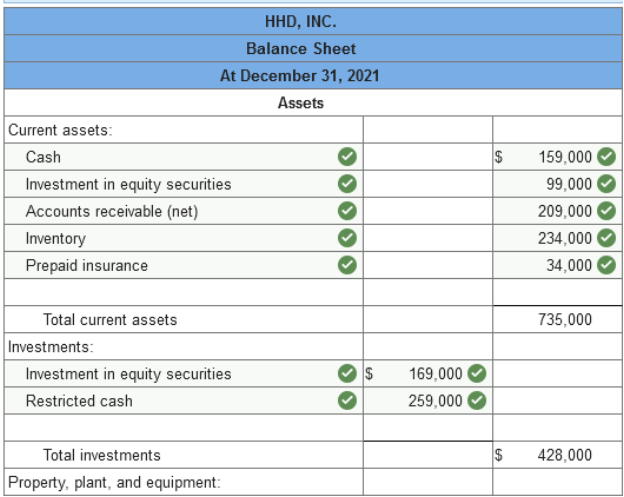
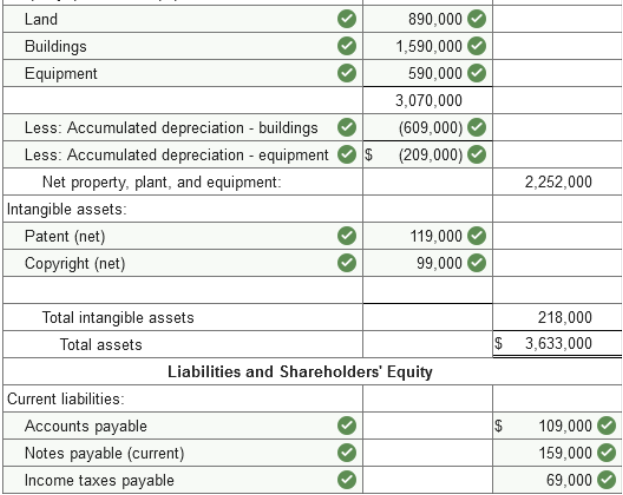
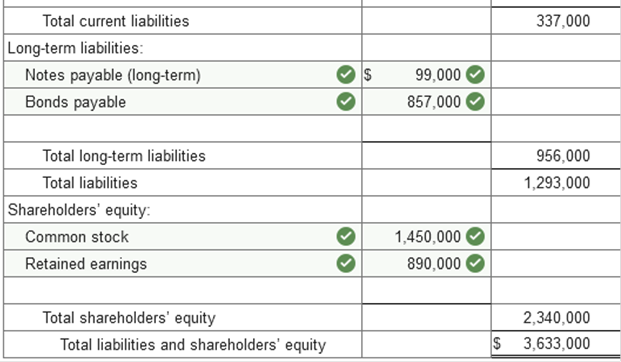
Problem 3-9 (Algo) Balance sheet
preparation [LO3-2, 3-3] Presented below is the balance sheet
for HHD, Inc., at December 31, 2021.
Current assets: cash, $159,000; accounts receivable (net), $209,000; inventory, $234,000; and prepaid insurance, $34,000. Investments: investment in equity securities, short term, $99,000, and long term, $169,000; and restricted cash, long term, $259,000. Property, plant, and equipment: buildings, $1,590,000 less accumulated depreciation, $609,000; equipment, $590,000 less accumulated depreciation, $209,000; and land, $890,000. Intangible assets net of amortization: patent, $119,000; and copyright, $99,000. Current liabilities: accounts payable, $109,000; notes payable, short term, $159,000, and long term, $99,000; and income taxes payable, $69,000. Long-term liabilities: bonds payable due 2023. Shareholders’ equity: common stock, $1,450,000; retained earnings, $890,000 Five hundred thousand shares of no par common stock are authorized, of which 290,000 shares were issued and are outstanding. Required: Prepare a corrected classified balance sheet for HHD, Inc., at December 31, 2021. (Amounts to be
deducted should be indicated by a minus sign.)
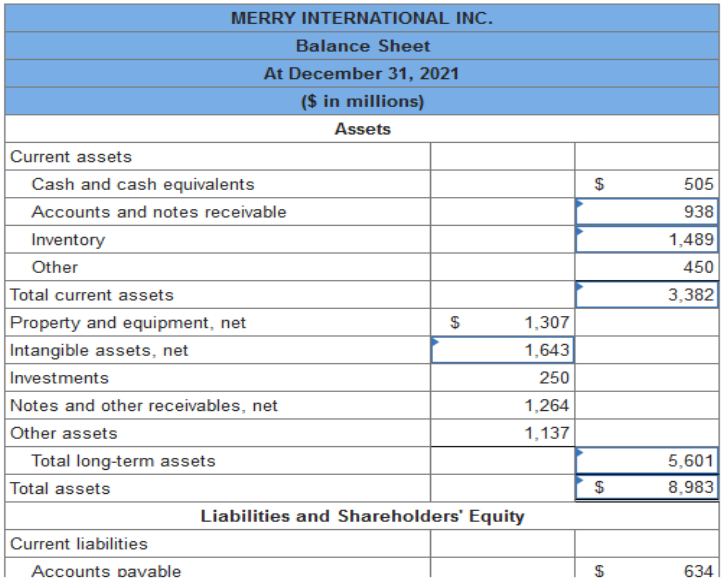
The following balance sheet information (in $ millions) comes from the Annual Report to Shareholders of Merry International Inc. for the 2021 fiscal year. The following additional information from an analysis of Merry's financial position is available: Current ratio = 1.352259; Acid-test ratio = 0.5769692; Debt to equity ratio = 1.505718 Required: Compute the missing amounts in the balance sheet. (Enter your answers in millions of dollars. Round your intermediate and final answers to the nearest whole dollar.)
To solve the problem, students can start by using the debt to equity ratio to solve for total liabilities ($3,585 × 1.505718 = $5,398 in total liabilities). Then they can determine the other missing data in the bottom half of the balance sheet by subtraction. With total liabilities and shareholders' equity known, so are the total assets. The current assets can be computed by the current ratio ($2,501 × 1.352259 = $3,382 in current assets). The quick assets can be found from the acid-test ratio: ($2,501 × 0.5769692 = $1,443 in quick assets less $505 in cash and cash equivalents = $938 in accounts and notes receivable). With that known, students can compute the inventory balance ($3,382 – $505 – $938 – $450 = $1,489). Finally, with current and total assets determined, the long-term assets can be found, leading to the missing balance in intangible assets. Depreciation methods used and estimated useful life. Definition of cash equivalents. Details of pension plans. Data to adjust the financial statements so that they are not misleading. Property, plant, and equipment. Investment. Current asset. Goodwill. Bronco Electronics' current assets
consist of cash, short-term investments, accounts receivable, and inventory.
The following data were abstracted from a recent financial statement:
Compute the long-term liabilities for Bronco: $640,000 Explanation
(1) Total debt + Total
equity = Total assets (given) = $1,400,000 TB MC Qu. 3-50 (Static) Listed below
are year-end account balances... Listed below are year-end account
balances ($ in millions) taken from the records of Symphony Stores.
$148 millions. $158 millions. $128 millions. $113 millions. Explanation
Current assets. Current liabilities. Current assets plus current liabilities. Current assets minus current liabilities. TB MC Qu. 3-86 (Algo) The following
partial balance sheet... The following partial balance sheet
($ in thousands) for Paisano Seafood Inc. is shown below.
$248 thousand. $310 thousand. $68 thousand. $351 thousand. Explanation Quick assets: $569 – $218 – $41 = $310 TB MC Qu. 3-47 (Static) Listed below are year-end account balances... Listed
below are year-end account balances ($ in millions) taken from the records of
Symphony Stores.
$823 millions. $838 millions. $863 millions. $1,696 millions. Explanation Total current assets: $710 + $39 + $30 + $16 + $20 + $8 = $823 TB Problem 3-132 (Static) Indicate whether each of the actions listed below will immediately increase (I), decrease (D), or have no effect (N) on the ratios shown. Assume each ratio is greater than 1.0 before the action is taken. 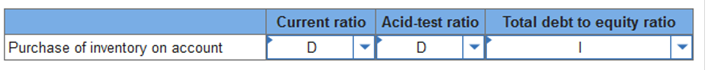 TB MC Qu. 3-47 (Algo) Listed below are year-end account balances... Listed below are year-end account balances ($ in millions) taken from the records of Symphony Stores.
What would Symphony report as total current assets? $871 millions. $846 millions. $1,704 millions. $831 millions. Explanation Total current assets: $668 + $54 + $42 + $25 + $29 + $13 = $831 The following information is provided for Sacks Company.
What is the amount of total assets? $81,500. $82,500. $68,500. $83,500. Explanation Total assets: $12,000 + $4,500 + $2,000 + $65,000 = $83,500 TB Problem 3-115 (Algo) The condensed balance sheet and income statement for Marjoram Company are presented below.
Compute the return on shareholders' equity ratio for Marjoram Company. (Round your percentage answer to nearest whole percent.) Return on Shareholder’s Equity: 54% Explanation $131,880 / ($80,000 + $165,600) = 54% Return on shareholders' equity A payment on account has no effect on working capital but will increase the current ratio if it is already greater than 1.0. True TB TF Qu. 3-12 (Static) The details of transactions between the company... The details of transactions between the company and its owners’ family members do not need to be disclosed separately in the notes to the financial statements. False TB MC Qu. 3-74 (Static) Lack of long-term solvency refers to: Lack of long-term solvency refers to: Risk of nonpayment of both current and long-term liabilities. The length of time before long-term debt becomes due. The ability to refinance long-term debt when it becomes due. Long-term assets. TB MC Qu. 3-86 (Static) The following partial balance sheet... The following partial balance sheet ($ in thousands) for Paisano Seafood Inc. is shown below.
$60 thousand. $230 thousand. $280 thousand. $305 thousand. Explanation Quick assets: $505 − $200 − $25 = $280 TB Problem 3-110 (Algo) The December 31, 2021, post-closing trial balance ($ in thousands) for Libby Corporation is presented below:
Required: Prepare a classified balance sheet for Libby Corporation at December 31, 2021. (Enter your answers in the order of their liquidity. Negative amounts should be entered by a minus sign. Enter your answers in thousands of dollars.) 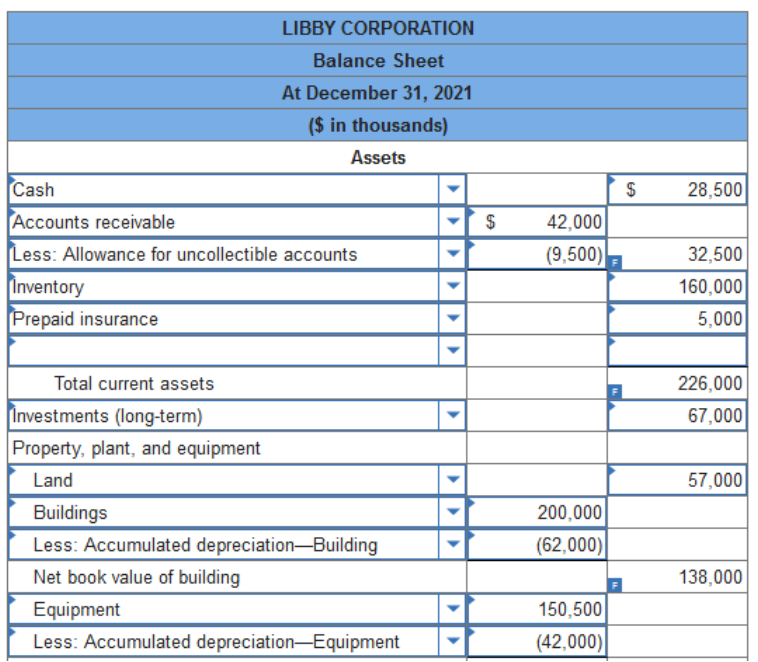 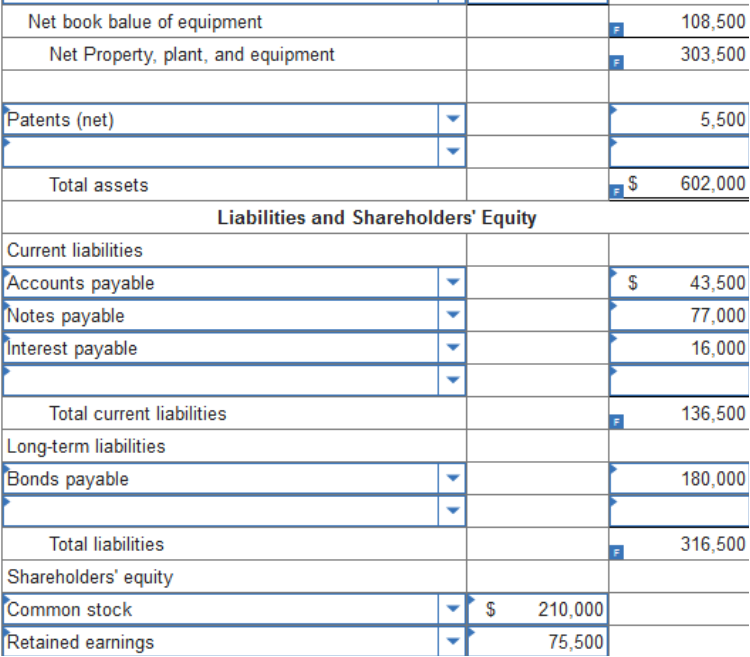  The following partial balance sheet
($ in thousands) for Paisano Seafood Inc. is shown below.
The acid-test ratio is (Round your answer to 2
decimal places.): 1.06. 1.46. 0.29. Explanation Acid test ratio: ($575 – $218 – $37) / $303 = 1.06 TB MC Qu. 3-92 (Static) A company that borrows funds at... A company that borrows funds at 6% and then generates a return on those funds of 9% typically has: Greater default risk. Favorable financial leverage. Higher return on equity. All of the other answers are true. The following partial balance sheet ($ in thousands) for Paisano Seafood Inc. is shown below.
0.25. 0.88. 1.17. 1.58. Explanation Acid-test ratio: ($505 − $200 − $25)/$320 = 0.88 Intermediate Accounting Homework 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | Exams Chapters 1-3 4-7 8-9 10-11
| Final Exam
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |