|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Intermediate Accounting (ACG 3101) Homework 11 Intermediate Accounting Homework 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | Exams Chapters 1-3 4-7 8-9 10-11 | Final Exam
The allocation of the cost of a
tangible fixed asset is referred to as
(1), whereas the allocation of the cost of an intangible asset is referred to as (2). (Enter one word per blank.) 1. depreciation 2. amortization The amount of use that the company expects to obtain from an asset before disposing of it is referred to as the ______ life of the asset. service The gain or loss on disposal of an asset is calculated as consideration received less the book value of asset sold Which statement is true about the straight-line method of depreciation? It allocates an equal amount of depreciation to each year of the asset's service life Group and composite depreciation commonly is used to reduce cost of record-keeping Which of the following is an activity-based depreciation method? Units-of-Production Method For natural resources the depletion base is cost less any anticipated residual value On October 1, year 1, Johnson Corp. purchased equipment for $100,000. The equipment has a useful life of 5 years with no residual value. Johnson uses the double-declining-balance method of depreciation. The partial year depreciation for year 1 is $10,000 The depreciation rate is 1/5 x 2 = 40%. $100,000 x 40% x 1/4 = $10,000 depreciation expense in year 1 The allocation of the cost of a tangible fixed asset is referred to as ________, whereas the allocation of the cost of an intangible asset is referred to as ________. depreciation amortization The two categories for intangible assets are -intangibles with finite lives -intangibles with indefinite lives When selling a fixed asset, the seller recognizes a gain or loss for the difference between the consideration received and the ______ value of the asset sold. book If obsolescence were expected to limit the longevity of a protected product, the useful life of a patent might be _________ its legal life. less than What is the purpose of group or composite depreciation? To reduce the record-keeping costs of determining depreciation No amortization is recorded for intangible assets with indefinite lives The cost of a natural resource less its anticipated residual value is called the _____ _____. depletion base The service life or useful life of an asset is the amount of use the company expects to obtain before disposing of the asset. The depreciation method that allocates an equal amount of the depreciable base to each year of the asset's service life is the straight-line method If a company bases depreciation expense on the life of a machine in hours, and depreciates the machine for the number of hours used during the year, it is using the ______ method of depreciation. units-of-production On October 1, year 1, Kirby Corp. purchased equipment for $100,000. The equipment has a useful life of 5 years with no residual value. Kirby uses the straight-line method of depreciation. The partial year depreciation for year 1 is $5,000 $100,000/5 years = $20,000 per year x 1/4 year = $5,000 depreciation expense in year 1. Match Depreciation <--- > Allocation of the cost of a tangible fixed asset Depletion <--- > Allocation of the cost of natural resources Amortization <--- > Allocation of the cost of an intangible asset If there is a change in an intangible asset's estimated useful life, the change is treated on a prospective basis. Which of the following accounting changes must be justified in the notes to the financial statements? Changes in depreciation methods Allocation of the cost of an intangible asset is called Amortization What is the accounting treatment for the discovery of a material error in a previous year? Previous years' financial statements are restated The useful life of an intangible asset may be limited by what type of provisions? -Contractual -Regulatory -Legal Which of the following intangible assets are usually considered to have indefinite lives? Trademarks A change in accounting estimate requires a company to account for the change on a prospective basis in the current year and future years A change in depreciation method is treated as a change in estimate that is achieved by a change in accounting principle, and is accounted for Prospectively in the current and future periods Which of the following are required when a material error is discovered in a subsequent accounting period that impacts retained earnings? (Select all that apply.) A prior period adjustment is made to the beginning balance of retained earnings. A disclosure note describing the nature of the error and the impact of the correction on net income and earnings per share. Previous financial statements are retrospectively restated. Required information Exercise 11-1 (Algo) Depreciation methods [LO11-2] Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] On January 1, 2021, the Excel Delivery Company purchased a delivery van for $48,000. At the end of its five-year service life, it is estimated that the van will be worth $3,000. During the five-year period, the company expects to drive the van 175,000 miles. Required: Calculate annual depreciation for the five-year life of the van using each of the following methods. rev: 05_15_2019_QC_CS-168776, 11_22_2019_QC_CS-191707 Exercise 11-1 (Algo) Part 1 1. Straight line. Straight-line: $9000 Explanation 1. Straight-line:
Required information Exercise 11-1 (Algo) Depreciation methods [LO11-2] Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] On January 1, 2021, the Excel Delivery Company purchased a delivery van for $48,000. At the end of its five-year service life, it is estimated that the van will be worth $3,000. During the five-year period, the company expects to drive the van 175,000 miles. Required: Calculate annual depreciation for the five-year life of the van using each of the following methods. rev: 05_15_2019_QC_CS-168776, 11_22_2019_QC_CS-191707 Exercise 11-1 (Algo) Part 2 2. Double-declining balance. (Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) 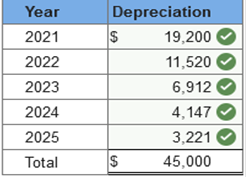 Explanation 2. Double-declining balance: Straight-line rate of 20% (1 ÷ 5 years) × 2 = 40% DDB rate.
Required information Exercise 11-1 (Algo) Depreciation methods [LO11-2] Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] On January 1, 2021, the Excel Delivery Company purchased a delivery van for $48,000. At the end of its five-year service life, it is estimated that the van will be worth $3,000. During the five-year period, the company expects to drive the van 175,000 miles. Required: Calculate annual depreciation for the five-year life of the van using each of the following methods. rev: 05_15_2019_QC_CS-168776, 11_22_2019_QC_CS-191707 Exercise 11-1 (Algo) Part 3 3. Units of production using miles driven as a measure of output, and the following actual mileage: (Do not round intermediate calculations.) 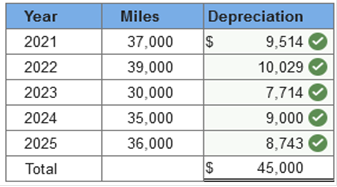 Explanation 3. Units-of-production:
Required information Exercise 11-8 (Algo) IFRS depreciation partial periods [LO11-2, 11-10] Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] On June 30, 2021, Rosetta Granite purchased equipment for $158,000. The estimated useful life of the equipment is eight years and no residual value is anticipated. An important component of the equipment is a specialized high-speed drill that will need to be replaced in four years. The $32,000 cost of the drill is included in the $158,000 cost of the equipment. Rosetta uses the straight-line depreciation method for all equipment. Exercise 11-8 (Algo) Part 1 Required: 1. Calculate depreciation for 2021 and 2022 applying the typical U.S. GAAP treatment. 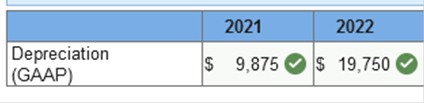 Explanation 1. U.S. GAAP: 2021: $158,000 ÷ 8 = $19,750 × 6/12 = $9,875 2022: $158,000 ÷ 8 = $19,750 Required information Exercise 11-8 (Algo) IFRS depreciation partial periods [LO11-2, 11-10] Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] On June 30, 2021, Rosetta Granite purchased equipment for $158,000. The estimated useful life of the equipment is eight years and no residual value is anticipated. An important component of the equipment is a specialized high-speed drill that will need to be replaced in four years. The $32,000 cost of the drill is included in the $158,000 cost of the equipment. Rosetta uses the straight-line depreciation method for all equipment. Exercise 11-8 (Algo) Part 2 2. Calculate depreciation for 2021 and 2022 applying IFRS.  Explanation 2. IFRS:
Exercise 11-17 (Algo) Depreciation and depletion [LO11-2, 11-3] At the beginning of 2021, Terra Lumber Company purchased a timber tract from Boise Cantor for $3,160,000. After the timber is cleared, the land will have a residual value of $610,000. Roads to enable logging operations were constructed and completed on March 30, 2021. The cost of the roads, which have no residual value and no alternative use after the tract is cleared, was $255,000. During 2021, Terra logged 510,000 of the estimated 5.1 million board feet of timber. Required: Calculate the 2021 depletion of the timber tract and depreciation of the logging roads assuming the units-of-production method is used for both assets. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter values in whole dollars.) 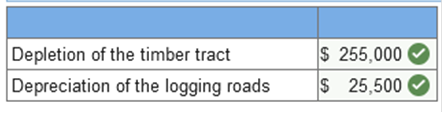 Explanation Timber tract:
510,000 × $0.50 = $255,000 depletion Logging roads: $255,000 ÷ 5,100,000 board feet = $0.050 per board foot 510,000 × $0.050 = $25,500 depreciation Required information Exercise 11-23 (Algo) Change in estimate; useful life and residual value of equipment [LO11-2, 11-5] Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Wardell Company purchased a mainframe on January 1, 2019, at a cost of $49,000. The computer was depreciated using the straight-line method over an estimated five-year life with an estimated residual value of $7,000. On January 1, 2021, the estimate of useful life was changed to a total of 10 years, and the estimate of residual value was changed to $400. Exercise 11-23 (Algo) Part 1 Required: 1. Prepare the year-end journal entry for depreciation in 2021. No depreciation was recorded during the year. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Round your final answer to nearest whole dollar.)  Explanation 1. Calculation of annual depreciation after the estimate change:
Required information Exercise 11-23 (Algo) Change in estimate; useful life and residual value of equipment [LO11-2, 11-5] Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Wardell Company purchased a mainframe on January 1, 2019, at a cost of $49,000. The computer was depreciated using the straight-line method over an estimated five-year life with an estimated residual value of $7,000. On January 1, 2021, the estimate of useful life was changed to a total of 10 years, and the estimate of residual value was changed to $400. Exercise 11-23 (Algo) Part 2 2. Prepare the year-end journal entry for depreciation in 2021. Assume that the company uses the sum-of-the-years' -digits method instead of the straight-line method. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answers to nearest whole dollar.)  Explanation 2. Calculation of annual depreciation after the estimate change:
Brief Exercise 10-6 (Algo) Goodwill [LO10-1] Pro-tech Software acquired all of the outstanding stock of Reliable Software for $20 million. The book value of Reliable’s net assets (assets minus liabilities) was $8.9 million. The fair values of Reliable’s assets and liabilities equaled their book values with the exception of certain intangible assets whose fair values exceeded book values by $3.1 million. Calculate the amount paid for goodwill. (Enter your answer in whole dollars.) Explanation Calculation of goodwill: Goodwill: 8,000,000
TB TF Qu. 10-10 (Static) A distinguishing characteristic of intangible... A distinguishing characteristic of intangible assets is that the extent and timing of their future benefits typically are highly uncertain. True TB TF Qu. 10-19 (Static) The relative fair values of individual assets... The relative fair values of individual assets acquired in a lump-sum purchase are used to determine the valuation of each of those assets. True TB MC Qu. 10-81 (Static) Lake Incorporated purchased all of the... Lake Incorporated purchased all of the outstanding stock of Huron Company paying $950,000 cash. Lake assumed all of the liabilities of Huron. Book values and fair values of acquired assets and liabilities were:
Lake would record goodwill of: $250,000 Explanation
Brief Exercise 11-14 (Algo) Change in estimate; useful life of equipment [LO11-5] At the beginning of 2019, Robotics Inc. acquired a manufacturing facility for $13.2 million. $10.2 million of the purchase price was allocated to the building. Depreciation for 2019 and 2020 was calculated using the straight-line method, a 25-year useful life, and a $2.2 million residual value. In 2021, the estimates of useful life and residual value were changed to 20 total years and $620,000, respectively. What is depreciation on the building for 2021? (Round answer to the nearest whole dollar.) $496,667 Explanation Calculation of annual depreciation after the estimate change:
TB MC Qu. 11-66 (Static) Assuming an asset is used evenly over a... Assuming an asset is used evenly over a four-year service life, which method of depreciation will always result in the largest amount of depreciation in the first year? Double-declining-balance Required information Exercise 11-1 (Algo) Depreciation methods [LO11-2] Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] On January 1, 2021, the Excel Delivery Company purchased a delivery van for $40,000. At the end of its five-year service life, it is estimated that the van will be worth $4,000. During the five-year period, the company expects to drive the van 121,000 miles. Required: Calculate annual depreciation for the five-year life of the van using each of the following methods. Straight-line: $7.200 per year , 11_22_2019_QC_CS-191707 Explanation 1. Straight-line:
Required information Exercise 11-1 (Algo) Depreciation methods [LO11-2] Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] On January 1, 2021, the Excel Delivery Company purchased a delivery van for $40,000. At the end of its five-year service life, it is estimated that the van will be worth $4,000. During the five-year period, the company expects to drive the van 121,000 miles. Required: Calculate annual depreciation for the five-year life of the van using each of the following methods. rev: 05_15_2019_QC_CS-168776, 11_22_2019_QC_CS-191707 Exercise 11-1 (Algo) Part 2 2. Double-declining balance. (Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) 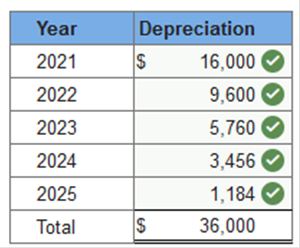 Explanation 2. Double-declining balance: Straight-line rate of 20% (1 ÷ 5 years) × 2 = 40% DDB rate.
Correct answers 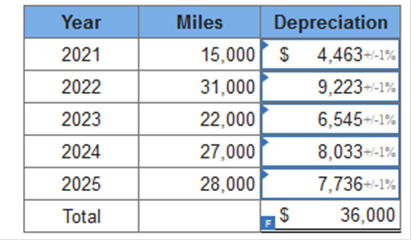 Explanation 3. Units-of-production:
Required information Exercise 11-1 (Static) Depreciation methods [LO11-2] Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] On January 1, 2021, the Excel Delivery Company purchased a delivery van for $33,000. At the end of its five-year service life, it is estimated that the van will be worth $3,000. During the five-year period, the company expects to drive the van 100,000 miles. Required: Calculate annual depreciation for the five-year life of the van using each of the following methods. Exercise 11-1 (Static) Part 1 1. Straight line. Straight-line: $6,000 per year Explanation 1. Straight-line:
Required information Exercise 11-1 (Static) Depreciation methods [LO11-2] Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] On January 1, 2021, the Excel Delivery Company purchased a delivery van for $33,000. At the end of its five-year service life, it is estimated that the van will be worth $3,000. During the five-year period, the company expects to drive the van 100,000 miles. Required: Calculate annual depreciation for the five-year life of the van using each of the following methods. Exercise 11-1 (Static) Part 2 Double-declining balance. (Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) 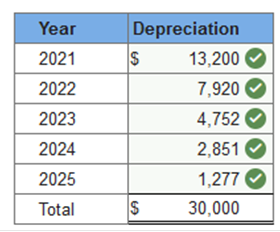 Explanation 2. Double-declining balance: Straight-line rate of 20% (1 ÷ 5 years) × 2 = 40% DDB rate.
Required information Exercise 11-1 (Static) Depreciation methods [LO11-2] Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] On January 1, 2021, the Excel Delivery Company purchased a delivery van for $33,000. At the end of its five-year service life, it is estimated that the van will be worth $3,000. During the five-year period, the company expects to drive the van 100,000 miles. Required: Calculate annual depreciation for the five-year life of the van using each of the following methods. Exercise 11-1 (Static) Part 3 Units of production using miles driven as a measure of output, and the following actual mileage: (Do not round intermediate calculations.) 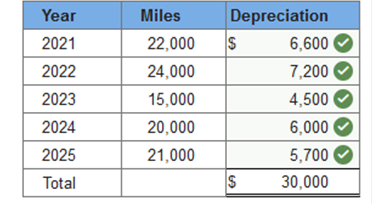 Explanation 3. Units-of-production:
Required information Exercise 11-3 (Algo) Depreciation methods partial periods [LO11-2] Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] On October 1, 2021, the Allegheny Corporation purchased equipment for $203,000. The estimated service life of the equipment is 10 years and the estimated residual value is $5,000. The equipment is expected to produce 300,000 units during its life. Required: Calculate depreciation for 2021 and 2022 using each of the following methods. Partial-year depreciation is calculated based on the number of months the asset is in service. Exercise 11-3 (Algo) Part 1 1. Straight-line. 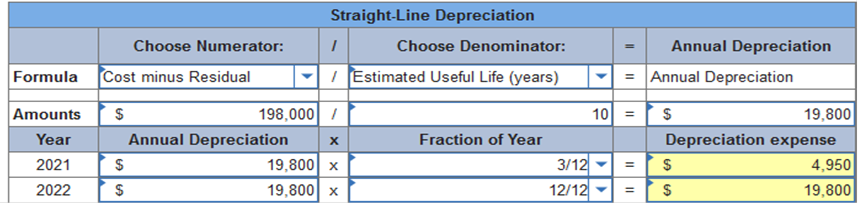 Explanation 1. Straight-line:
Required information Exercise 11-3 (Algo) Depreciation methods partial periods [LO11-2] Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] On October 1, 2021, the Allegheny Corporation purchased equipment for $203,000. The estimated service life of the equipment is 10 years and the estimated residual value is $5,000. The equipment is expected to produce 300,000 units during its life. Required: Calculate depreciation for 2021 and 2022 using each of the following methods. Partial-year depreciation is calculated based on the number of months the asset is in service. Exercise 11-3 (Algo) Part 2 2. Double-declining-balance. 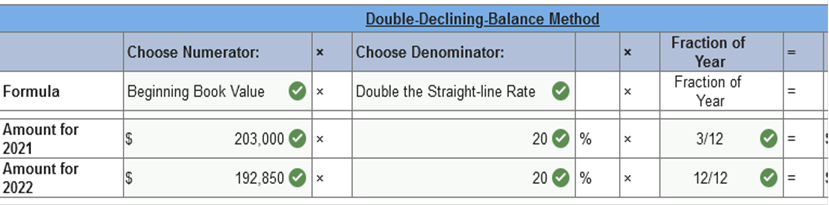 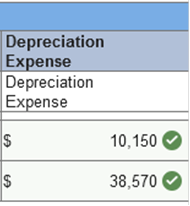 Explanation 2. Double-declining balance: Straight-line rate is 10% (1 ÷ 10 years) × 2 = 20% DDB rate
Exercise 11-3 (Algo) Depreciation methods partial periods [LO11-2] Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] On October 1, 2021, the Allegheny Corporation purchased equipment for $203,000. The estimated service life of the equipment is 10 years and the estimated residual value is $5,000. The equipment is expected to produce 300,000 units during its life. Required: Calculate depreciation for 2021 and 2022 using each of the following methods. Partial-year depreciation is calculated based on the number of months the asset is in service. Exercise 11-3 (Algo) Part 3 Units of production (units produced in 2021, 18,000; units produced in 2022, 33,000). (Round "Depreciation per unit rate" answers to 2 decimal places.) 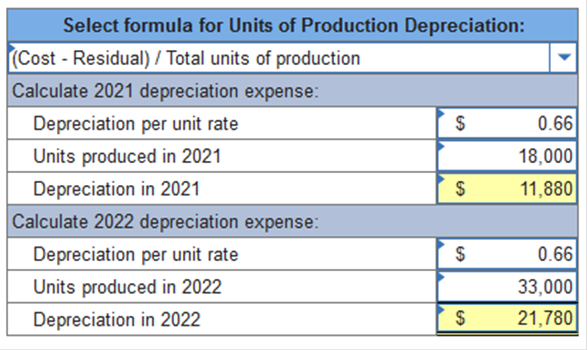 Explanation 3. Units-of-production:
TB MC Qu. 11-125 (Algo) In January of 2021, Vega Corporation purchased... In January 2021 Vega Corporation purchased a patent at a cost of $207,000. Legal and filing fees of $68,000 were paid to acquire the patent. The company estimated a 10-year useful life for the patent and uses the straight-line amortization method for all intangible assets. In January 2024, Vega spent $38,000 in legal fees for an unsuccessful defense of the patent and the patent is no longer usable. The amount charged to income (expense and loss) in 2024 related to the patent should be: $230,500 Explanation
Exercise 11-17 (Algo) Depreciation and depletion [LO11-2, 11-3] At the beginning of 2021, Terra Lumber Company purchased a timber tract from Boise Cantor for $3,510,000. After the timber is cleared, the land will have a residual value of $720,000. Roads to enable logging operations were constructed and completed on March 30, 2021. The cost of the roads, which have no residual value and no alternative use after the tract is cleared, was $279,000. During 2021, Terra logged 620,000 of the estimated 6.2 million board feet of timber. Required: Calculate the 2021 depletion of the timber tract and depreciation of the logging roads assuming the units-of-production method is used for both assets. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter values in whole dollars.)  Explanation Timber tract:
620,000 × $0.45 = $279,000 depletion Logging roads: $279,000 ÷ 6,200,000 board feet = $0.045 per board foot 620,000 × $0.045 = $27,900 depreciation Exercise 11-6 (Algo) Depreciation methods; solving for unknowns [LO11-2] For each of the following depreciable assets, determine the missing amount. Abbreviations for depreciation methods are SL for straight-line and DDB for double-declining-balance. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answers to nearest whole dollar.) 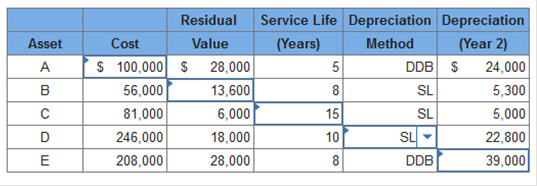 Explanation Asset A: Straight-line rate is 20% (1 ÷ 5 years) × 2 = 40% DDB rate
Cost − (Cost × 40%) = $60,000 0.60 × Cost = $60,000 Cost = $100,000 Asset B: ($56,000 − residual) × 1/8 = $5,300 ($56,000 − residual) = $42,400 Residual = $13,600 Asset C:
Life = 15 years Asset D: $246,000 − $18,000 = $228,000 depreciable base $228,000 ÷ 10 years = $22,800 per year Method used is straight-line. Asset E: Straight-line rate is 12.5% (1 ÷ 8 years) × 2 = 25% rate Year 1 $208,000 × 25.00% = $52,000 Year 2 ($208,000 − 52,000) × 25.00% = $39,000 Exercise 11-25 (Static) Change in principle; change in depreciation methods [LO11-2, 11-6] For financial reporting, Clinton Poultry Farms has used the declining-balance method of depreciation for conveyor equipment acquired at the beginning of 2018 for $2,560,000. Its useful life was estimated to be six years, with a $160,000 residual value. At the beginning of 2021, Clinton decides to change to the straight-line method. The effect of this change on depreciation for each year is as follows:
Required: 2. Prepare any 2021 journal entry related to the change. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Round final answers to the nearest whole dollars.)  Explanation 2.
Intermediate Accounting Homework 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | Exams Chapters 1-3 4-7 8-9 10-11
| Final Exam
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |