|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Intermediate Accounting (ACG 3101) Homework 9 Intermediate Accounting Homework 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | Exams Chapters 1-3 4-7 8-9 10-11 | Final Exam
Required information
Learning Objective 10-01 Identify the various costs included in the initial cost of property, plant, and equipment, natural resources, and intangible assets. Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] The initial cost of property, plant, and equipment and intangible assets acquired in an exchange transaction includes the purchase price and all expenditures necessary to bring the asset to its desired condition and location for use. The cost of a natural resource includes the acquisition costs for the use of land, the exploration and development costs incurred before production begins, and restoration costs incurred during or at the end of extraction. Purchased intangible assets are valued at their original cost to include the purchase price and legal and filing fees. Mendelson Laboratories purchased engineering equipment at a cost of $420,000. Shipping costs totaled $15,000. Installation cost was $8,000. An additional electrical line had to be run to the equipment at a cost of $3,000. Labor and testing costs totaled $6,000. Materials used up in testing cost $3,000. The capitalized cost is: $455,000 Explanation Knowledge Check 01
Match the term and the definition  Required information Learning Objective 10-02 Determine the initial cost of individual property, plant, and equipment and intangible assets acquired as a group for a lump-sum purchase price. Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] If a lump-sum purchase involves different assets, it is necessary to allocate the lump-sum acquisition price among the separate items according to some Spice World Corporation purchased for $180,000 cash the following assets: land with a fair value of $60,000, a building with a fair value of $90,000, Prepare the appropriate journal entry for Spice World’s purchase. 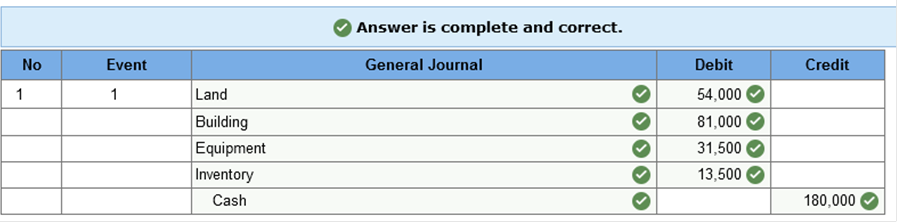 Explanation Knowledge Check 01 Step 1: Sum the fair values; $60,000 + $90,000 + $35,000 + $15,000 = $200,000 Step 2: Find the proportionate percentage of fair values for each asset;
Step 3: Multiply the purchase price by the proportional share for each asset
Required information Learning Objective 10-06 Determine the initial cost of property, plant, and equipment and intangible assets acquired in exchange for other nonmonetary assets. [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] The basic principle used for nonmonetary exchanges is to value the asset(s) received based on the fair value of the asset(s) given up. In certain situations, the valuation of the asset(s) received is based on the book value of the asset(s) given up. If a company exchanges an asset with a book value of $260,000, an original cost of $500,000, and a fair value of $300,000 plus cash of $100,000 for a new asset, what is the gain or loss recognized on the transaction? $40,000 | Gain Explanation Knowledge Check 01
The new asset is recorded at $400,000, the fair value of the old equipment, $300,000, plus the cash given, $100,000. The old asset’s account and accumulated depreciation are written off for their balances at the date of the exchange, and cash paid is recorded. Accumulated depreciation is the asset’s original cost, $500,000, minus book value, $260,000. The gain of $40,000 is the difference between the old asset’s fair value, $300,000, and its book value, $260,000. The gain of $40,000 also is the amount needed to allow the debits to equal credits in the journal entry. Interest may be capitalized whether or not there is specific borrowing for the construction Explanation Knowledge Check 01 Interest may not be capitalized on routinely manufactured goods, interest is only capitalized starting on the date of the first expenditure for the product. Even if the company did not borrow specifically for the construction, the weighted average rate from all other borrowings is used to capitalize interest. Required information Learning Objective 10-08 Explain the difference in the accounting treatment of costs incurred to purchase intangible assets versus the costs incurred to internally develop intangible assets. Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Research and development costs incurred to internally develop an intangible asset are expensed in the period incurred. Filing and legal costs for developed intangibles are capitalized. Research and development costs Generally pertain to activities that occur prior to the start of production. Explanation Knowledge Check 01 Research and development costs generally pertain to activities that occur prior to the start of production. Under US GAAP they are expensed as incurred. Required information Learning Objective 11-02 Determine periodic depreciation using both time-based and activity-based methods and account for dispositions. Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] The allocation process for plant and equipment is called depreciation. Time-based depreciation methods estimate service life in years and then allocate depreciable base, cost less estimated residual value, using either a straight-line or accelerated pattern. Activity-based depreciation methods allocate the depreciable base by estimating service life according to some measure of productivity. When an item of property, plant, and equipment or an intangible asset is sold, a gain or loss is recognized for the difference between the consideration received and the asset’s book value. On January 1, Year 1, Canseco Plumbing Fixtures purchased equipment for $52,000. Residual value at the end of an estimated four-year service life is expected to be $4,000. The company uses the straight-line method. For how much would each item below be reported at the end of Year 3? 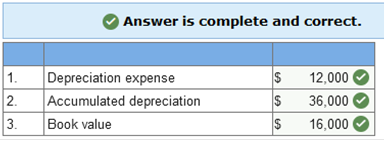 Explanation Knowledge Check 01 1. Annual depreciation = Depreciable base ÷ Number of years in asset’s life Annual depreciation = ($52,000 − $4,000) ÷ 4 = $12,000 2. Accumulated depreciation in Year 3 = $12,000 × 3 years = $36,000 3. Book value in Year 3 = Cost – Accumulated depreciation in Year 3 Book value in Year 3 = $52,000 – $36,000 (see 2. above) = $16,000 On January 1, Year 1, Miller Company purchased equipment for $36,000. Residual value at the end of an estimated six-year service life is expected to be $8,000. The company uses the double-declining balance method. For how much would each item below be reported at the end of Year 2? 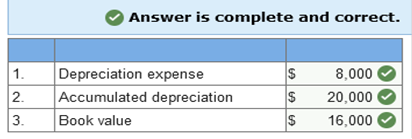 Explanation Knowledge Check 01 1. Depreciation expense each year = Book value at beginning of year × Depreciation rate* * Depreciation rate = (1 ÷ Service Life) × 2 = (1 ÷ 6) × 2 = 1/3 or 33.33% (rounded) Depreciation expense in Year 1 = $36,000 × 33.33% = $12,000 Depreciation expense in Year 2 = ($36,000 − $12,000) × 33.33% = $8,000 2. Accumulated depreciation in Year 2 = Depreciation in Year 1 + Year 2 (see 1. above) = $20,000 3. Book value in Year 2 = Cost – Accumulated depreciation in Year 2 Book value in Year 2 = $36,000 – $20,000 (see 2. above) = $16,000 On January 1, Year 1, Corcoran Company purchased equipment for $36,000. Residual value at the end of an estimated four-year service life is expected to be $6,000. The company uses the sum-of-the-years’ digits method. For how much would each item below be reported at the end of Year 2? 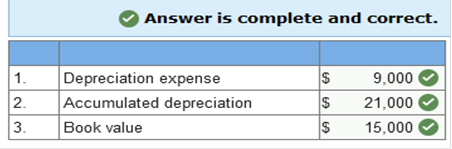 Explanation Knowledge Check 01 1. Depreciation expense in Year 2 = Depreciable base × (Remaining service life ÷ Sum-of-the-years’-digits) Year 1 = ($36,000 − $6,000) × (4 ÷ (1 + 2 + 3 + 4)) = $12,000 Year 2 = ($36,000 − $6,000) × (3 ÷ (1 + 2 + 3 + 4)) = $9,000 2. Accumulated depreciation in Year 2 = Depreciation in Year 1 + Year 2 (see 1. above) = $21,000 3. Book value in Year 2 = Cost – Accumulated depreciation in Year 2 Book value in Year 2 = $36,000 – $21,000 (see 2. above) = $15,000 On January 1, Year 1, Andrei’s Design Inc., purchased equipment for $60,000. Residual value at the end of an estimated four-year service life is expected to be $10,000. The company expects the machine to operate for 20,000 hours. The machine operated for 3,600 and 4,000 hours in Year 1 and Year 2, respectively. The company uses the units-of-production method. For how much would each item below be reported at the end of Year 2? 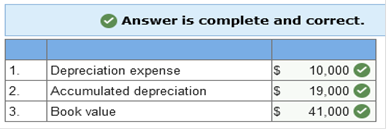 Explanation Knowledge Check 01 1. Depreciation expense each year = Units of activity × Depreciation rate* * Depreciation rate = ($60,000 − $10,000) ÷ 20,000 hours = $2.50/hour Depreciation expense in Year 1 = 3,600 × $2.50 = $9,000 Depreciation expense in Year 2 = 4,000 × $2.50 = $10,000 2. Accumulated depreciation in Year 2 = Depreciation in Year 1 + Year 2 (see 1. above) = $19,000 3. Book value in Year 2 = Cost – Accumulated depreciation in Year 2 Book value in Year 2 = $60,000 – $19,000 (see 2. above) = $41,000 If a company sells one of its trucks for consideration (cash and receivables) that is less than the book value of the truck (updated through the date of the sale), which of the following is true? A loss will be recognized by the seller Required information Learning Objective 11-03 Calculate the periodic depletion of a natural resource. Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] The allocation process for natural resources is called depletion. The activity-based method called units-of-production usually is employed to determine periodic depletion. Manson Company incurred costs of $5,720,000 for the acquisition and development of a mineral deposit. The company expects to extract 2,200,000 tons during a four-year period, after which the mineral deposit is expected to have no residual value. The company extracted 880,000 tons during the current year. What was the depletion expense for the current year? Current year depletion: $2,288,000 Explanation Knowledge Check 01 Depletion per ton = $5,720,000 ÷ 2,200,000 tons = $2.60 per ton Current year depletion = 880,000 tons × $2.60 per ton = $2,288,000 Required information Learning Objective 11-04 Calculate the periodic amortization of an intangible asset. Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] The allocation process for intangible assets is called amortization. For an intangible asset with a finite useful life, the capitalized cost less any estimated residual value must be allocated to periods in which the asset is expected to contribute to the company’s revenue-generating activities. An intangible asset that is determined to have an indefinite useful life is not subject to periodic amortization. Goodwill is perhaps the most typical intangible asset with an indefinite useful life. On August 1, Year 1, SuperCool Software (SCS) began developing a software program to allow individuals to customize their investment portfolios. Technological feasibility was established on January 31st of year 2, and the program was available for release on March 31, year 2. Development costs were incurred as follows:
SCS expects a useful life of five years for the software and total revenues of $10,000,000 during that time. During Year 2, SCS recognized $2,000,000 in revenue, included in the $10,000,000 total revenue estimate. Calculate the required amortization for Year 2 (Hint: calculate using both methods, choose the greater number) Amortization for year 2: $180,000 Explanation Knowledge Check 01 (1) Percentage-of-revenue method:
(2) Straight-line method $900,000 × 1/5 × 9/12 = $135,000. The percentage-of-revenue method is used since it produces the greater amortization of $180,000. On January 1, Year 1, Lowing Company acquired a patent from Generics Research Corporation for $3 million. The legal life of the patent is 20 years, but Lowing expects to use it for 5 years. Pawson Company has committed to purchase the patent from Lowing for $500,000 at the end of that 5-year period. Lowing uses the straight-line method to amortize intangible assets with finite useful lives. What is the amount of amortization expense each year? Amortization Expense: $500,000 Explanation Knowledge Check 01 Amortization expense = ($3,000,000 − $500,000) ÷ 5 years = $500,000 From a financial reporting perspective, property, plant, and equipment and intangible assets exhibit the following characteristics (Select all that apply.) revenue-producing long-lived The purchase price and all costs to bring an asset to its desired condition and location for use should be ______. Capitalized Which of the following items should be capitalized in the cost of equipment? insurance on equipment during shipping Purchase price freight to deliver the equipment to its location installation and testing of equipment Larry purchases land to be used for a new corporate headquarters. Which of the following items are capitalized in the cost of land? costs to remove an old building legal fees to secure title Accounting for land improvements requires that the costs of land improvements are depreciated or amortized over the periods benefited. capitalized. Long-term assets are typically classified in one of these two categories: intangible assets Property, plant, and equipment True or false: The initial cost of property, plant, and equipment includes the purchase price and all expenditures necessary to bring the asset to its desired condition and location for use. True Which of the following costs should be capitalized in the costs of acquiring a building? remodeling building legal fees to obtain title realtor commissions Indicate which costs would be capitalized as part of the cost of manufacturing equipment. Freight-in set-up cost insurance during transit _____ ______ are physically diminished as minerals and other materials are extracted from the ground and are sold or used in the production process, whereas equipment, land, and buildings have physical characteristics that remain unchanged. natural resources Sarah purchases land to be used for a new storage facility. Which of the following items are capitalized in the cost of land? costs to remove an old building real estate agent commissions legal fees to secure title When assets are purchased in a group for a single sum, it is referred to as a lump-sum purchase Accounting for land improvements requires that the land improvements are capitalized and then ____ over periods benefited by their use. expensed When a company acquires assets by issuing debt or equity securities, the first indicator of fair value is the fair value of the debt or equity securities given. From a financial reporting perspective, property, plant, and equipment and intangible assets exhibit the following characteristics revenue-producing long-lived A company acquires equipment by signing an interest-bearing note payable for $20,000. The interest rate is realistic so the company will record debit machine $20,000 credit note payable $20,000 Which of the following costs should be capitalized in the costs of acquiring a building? (Select all that apply.) legal fees to obtain title purchase price Which of the following are classified as natural resources? timber tracts mineral deposits A company issues its equity securities to purchase land. The common stock is publicly traded, and both the value of the stock and the land is known. The best indicator of fair value is the value of the Stock In a lump-sum purchase of assets, the cost must be allocated to the individual assets because the assets have different useful lives. When a company receives an asset from an unrelated party by a donation, the assets are valued at fair value and revenue is recorded When assets are acquired in a noncash transaction, if the fair value of the noncash items given is not clearly evident, then the ____ value of the assets received is used to record the assets. Fair The basic principle for valuing assets in a nonmonetary exchange is to value the asset received at fair value A company acquires equipment by signing an interest-bearing note payable. If the interest rate is realistic, the company will record the equipment at the Present value of the note payable, which is the face amount of the note An asset is exchanged for another asset and cash is received in the transaction. The fair value of the assets are not determinable. At what amount should the new asset be recorded? Book value of the asset given up less the cash received. Which of the following should be included in the cost of buildings? real estate commissions relating to purchase of building When assets are exchanged and the transaction lacks commercial substance, which of the following occurs? The asset received is valued at the book value of the asset given. A company issues its equity securities to purchase land. The common stock is not publicly traded. The best indicator of fair value is the appraised value of the land When a company receives an asset from an unrelated party by a donation, the assets are valued at ______ value. Market The two important accounting issues related to self-constructed assets are treatment of interest charges. allocation of overhead. Which of the following is true regarding a nonmonetary exchange of assets a gain or loss is recognized for the difference between the fair value and the book value of the asset given up Because it is difficult to estimate the future value of research and development, FASB requires that research and development costs be treated a an expense on the income statement An asset is exchanged for another asset and no cash is exchanged in the transaction. The fair value of the assets are not determinable. At what amount should the new asset be recorded? Book value of the asset given. When assets are exchanged and the transaction lacks commercial substance, the asset received is valued at the book value of the asset given up. The two important accounting issues related to self-constructed assets are interest charges and allocation of overhead. The FASB requires research and development costs to be expensed because it is difficult to objectively determine the future benefits Exercise 10-1 (Algo) Acquisition costs; land and building [LO10-1] On March 1, 2021, Beldon Corporation purchased land as a factory site for $76,000. An old building on the property was demolished, and construction began on a new building that was completed on December 15, 2021. Costs incurred during this period are listed below:
Required: Determine the amounts that Beldon should capitalize as the cost of the land and the new building. 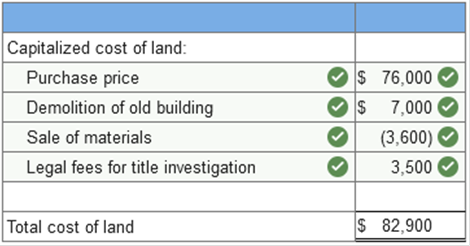 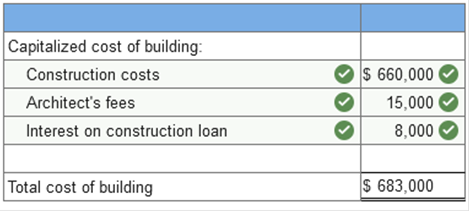 Exercise 10-3 (Algo) Acquisition costs; lump-sum acquisition [LO10-1, 10-2] Samtech Manufacturing purchased land and building for $3 million. In addition to the purchase price, Samtech made the following expenditures in connection with the purchase of the land and building:
An independent appraisal estimated the fair values of the land and building, if purchased separately, at $3 and $1 million, respectively. Shortly after acquisition, Samtech spent $83,000 to construct a parking lot and $41,000 for landscaping. Required: 1. Determine the initial valuation of each asset Samtech acquired in these transactions. 2. Determine the initial valuation of each asset, assuming that immediately after acquisition, Samtech demolished the building. Demolition costs were $260,000 and the salvaged materials were sold for $6,500. In addition, Samtech spent $80,000 clearing and grading the land in preparation for the construction of a new building. 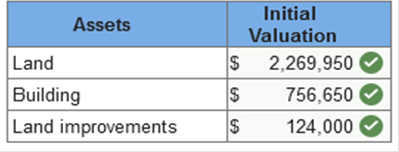 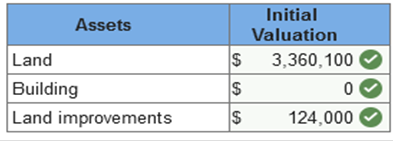 Explanation 1.
Note: The pro-rated property taxes for the period after acquisition are not included in the initial valuation of the land and building. They are recorded instead as prepaid taxes and expensed over the related period. The total is allocated to the land and building based on their relative fair values:
2.
Exercise 10-6 (Algo) Goodwill [LO10-1] On March 31, 2021, Wolfson Corporation acquired all of the outstanding common stock of Barney Corporation for $18,300,000 in cash. The book values and fair values of Barney’s assets and liabilities were as follows:
Required: Calculate the amount paid for goodwill. 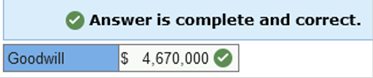 Explanation
Exercise 10-8 (Algo) Lump-sum acquisition [LO10-2] Pinewood Company purchased two buildings on four acres of land. The lump-sum purchase price was $2,600,000. According to independent appraisals, the fair values were $1,080,000. (building A) and $675,000 (building B) for the buildings and $945,000 for the land. Required: Determine the initial valuation of the buildings and the land. 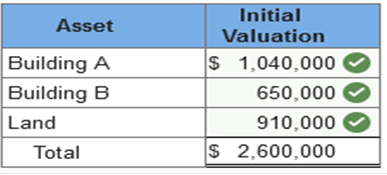 Explanation
Intermediate Accounting Homework 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | Exams Chapters 1-3 4-7 8-9 10-11
| Final Exam
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |