|
Accounting | Business | Computer
Science | General
Studies | Math | Sciences | Civics Exam | Help/Support | Join/Cancel | Contact Us | Login/Log Out
Intermediate Accounting (ACG 3101) Homework 1 Intermediate Accounting Homework 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | Exams Chapters 1-3 4-7 8-9 10-11 | Final Exam
Required information
Learning Objective 01-02 Explain the difference between cash and accrual accounting. Cash basis accounting provides a measure of periodic performance called net operating cash flow, which is the difference between cash receipts and cash disbursements from transactions related to providing goods and services to customers. Accrual accounting provides a measure of performance called net income, which is the difference between revenues and expenses. Periodic net income is considered a better indicator of future operating cash flows than is current net operating cash flows. Knowledge Check 01 On July 1, Year 1, a company paid $48,000 for 24 months of advance rent on its warehouse. Assuming the company has a December year end, what would be the amount of rent expense in Year 1 under cash basis versus accrual accounting? Cash basis = $48,000; Accrual = $12,000. The objective of financial reporting is to provide useful financial information to capital providers. The primary decision-specific qualities that make financial information useful are relevance and faithful representation. To be relevant, information must possess predictive value and/or confirmatory value, and all material information should be included. Completeness, neutrality, and freedom from error enhance faithful representation. The 10 elements of financial statements are assets, liabilities, equity, investments by owners, distributions to owners, revenues, expenses, gains, losses, and comprehensive income. The primary focus of financial accounting information is to provide useful information for users to make:
Relevance Which of the following qualities is not a requirement of representational faithfulness? neutrality timeliness free from error complete The four basic assumptions underlying GAAP are (1) the economic entity assumption, (2) the going concern assumption, (3) the periodicity assumption, and (4) the monetary unit assumption. Match the term and the definition. Revenues: Inflows or other enhancements of assets of an entity or settlements of its liabilities during a period from delivering or producing goods, rendering services, or other activities that constitute the entity's ongoing central operations Expenses: Outflows or other using up of assets or incurrences of liabilities during a period from delivering or producing goods, rendering services, or other activities that constitute the entity's ongoing central operations Assets: Probable future economic benefits obtained or controlled by a particular entity as a result of past transactions or events Liabilities: Probably future sacrifices of economic benefits arising from present obligations of a particular entity to transfer assets or provide services to other entities in the future as a result of past transactions of events Equity: Residual interest in the assets of an entity that remains after deducting its liabilities Choose the word pair that fills in the blanks correctly: A parent company and its subsidiaries are separate ________entities but one _______ entity. legal; accounting Which of the following assumes that in the absence of contrary information a business entity will continue indefinitely? Going concern assumption Periodicity assumption Which of the following is a presumption of the monetary unit assumption? The value of the currency used in measuring transactions is stable over time. Describe the recognition, measurement, and disclosure concepts that guide accounting practice. Recognition determines whether an item is reflected in the financial statements, and measurement determines the amount of the item. Measurement involves choice of a monetary unit and choice of a measurement attribute. In the United States, the monetary unit is the dollar. Various measurement attributes are used in GAAP, including historical cost, net realizable value, current cost, present value, and fair value. (1) Definitions—The item meets the definition of an element of financial statements. (2) Measurability—It has a relevant attribute measurable with sufficient reliability. (3) Relevance—The information is capable of making a difference in user decisions. (4) Reliability—The information is representationally faithful, verifiable, and neutral. Which of the following methods of measurement is allowed under U.S. GAAP? a. Current cost b. Fair value c. Historical cost d. All of these methods are allowed. Notes to the company’s financial statements are: An integral part of the company's financial statements. Exercise 1-2 (Algo) Accrual accounting [LO1-2] Listed below are several transactions that took place during the second and third years of operations for the RPG Company Year 2 year 3
In addition, you learn that the company incurred advertising costs of $16,000 in year 2, owed the advertising agency $4,100 at the end of year 1, and there were no liabilities at the end of year 3. Also, there were no anticipated bad debts on receivables, and the rent payment was for a two-year period, year 2 and year 3. Required: 1. Calculate accrual net income for both years. 2. Determine the amount due the advertising agency that would be shown as a liability on RPG’s balance sheet at the end of year 2. 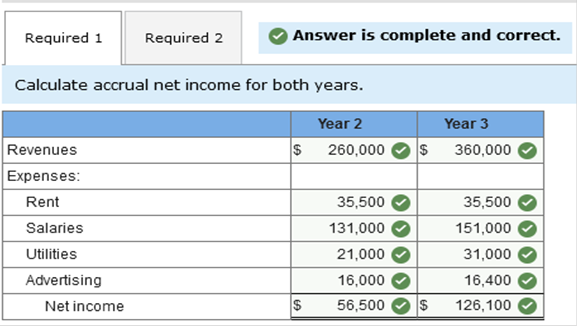 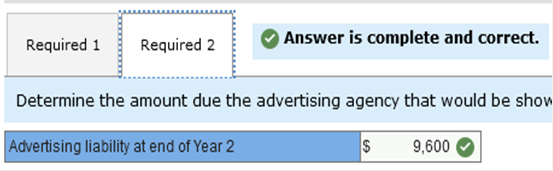 Exercise 1-6 (Static) Financial statement elements [LO1-7] For each of the items listed below, identify the appropriate financial statement element. 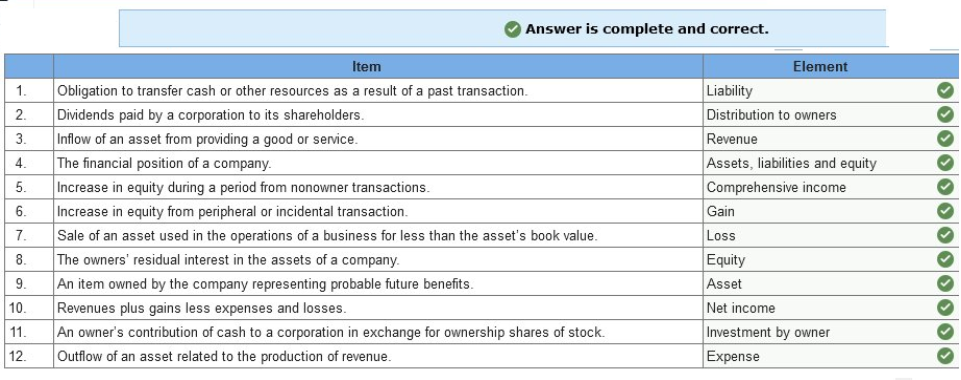 Exercise 1-7 (Static) Concepts; terminology; conceptual framework [LO1-7] Listed below are several terms and phrases associated with the FASB’s conceptual framework. Pair each item from List A with the item from List B that is most appropriately associated with it. 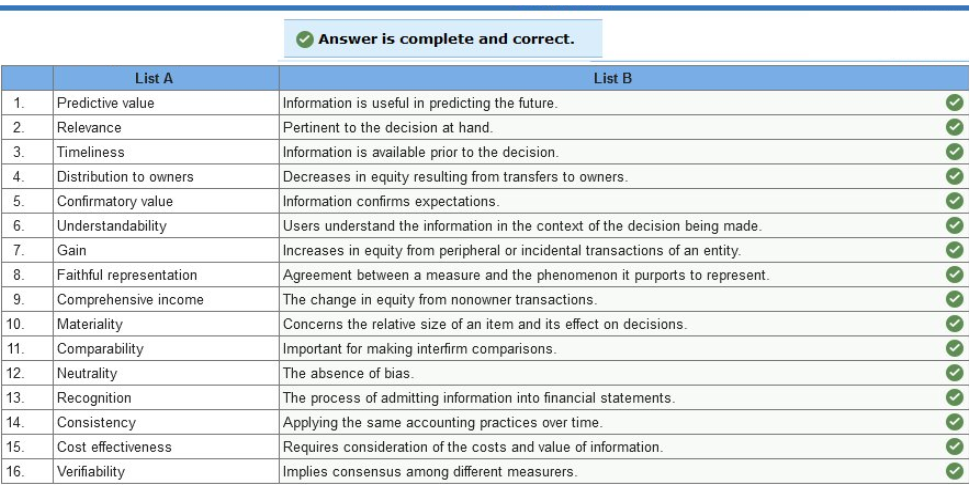 Exercise 1-9 (Static) Basic assumptions, principles, and constraints [LO1-7, 1-8, 1-9] Listed below are several terms and phrases associated with the accounting concepts. Pair each item from List A with the item from List B that is most appropriately associated with it. 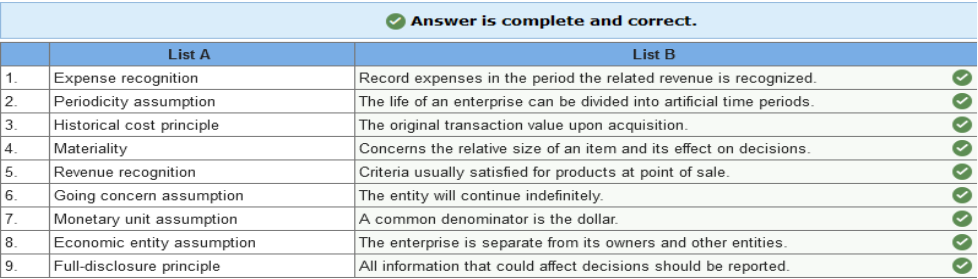 Exercise 1-10 (Static) Basic assumptions and principles [LO1-7, 1-8, 1-9] Listed below are several statements that relate to financial accounting and reporting. Identify the accounting concept that applies to each statement. 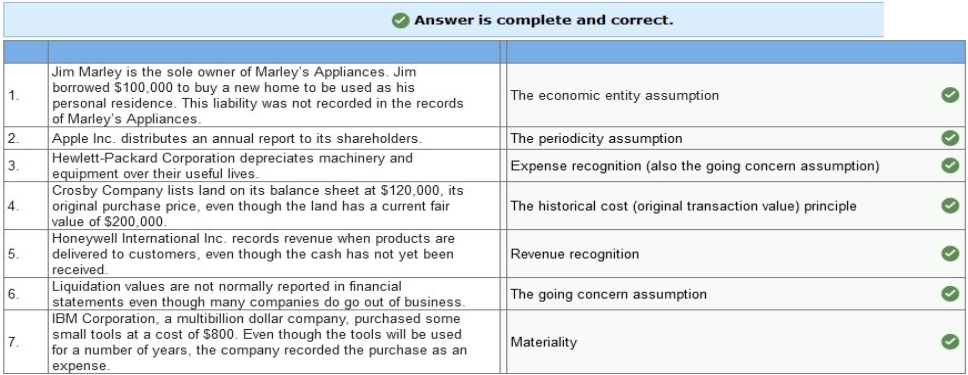 Exercise 1-11 (Static) Basic assumptions and principles [LO1-8, 1-9] Identify the accounting concept that was violated in each of the following situations. 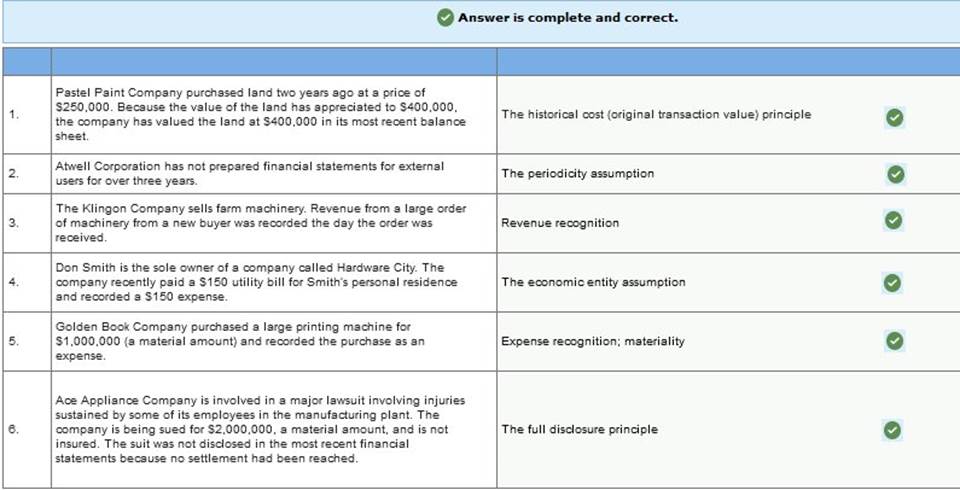 TB MC Qu. 1-129 (Algo) The following information ($ in millions) comes from a recent annual... The following information ($ in millions) comes from a recent annual report of Amazon.com, Inc.:
Compute the income before income tax for Amazon.
Multiple Choice $486
Explanation Net income = Gross profit
− Operating expenses + Other income (expense), net TB MC Qu. 1-124 (Algo) Tri Fecta, a partnership, had revenues of... Tri
Fecta, a partnership, had revenues of $373,000 in
its first year of operations. The
partnership has not collected on $45,200 of its sales and still owes $38,600
on $190,000 of merchandise it purchased. There
was no inventory on hand at the end of the year. The partnership paid $33,500
in salaries. The
partners invested $43,000 in the business and $26,000 was borrowed on a
five-year note. The
partnership paid $2,080 in interest that was the amount owed for the year and
paid $9,700 for a two-year insurance policy on the first day of business.
Multiple
Choice $142,570 Explanation
TB MC Qu. 1-127 (Algo) The following
information ($ in millions) comes from a recent annual... The following information ($ in
millions) comes from a recent annual report of Amazon.com, Inc.:
Compute Amazon's total liabilities
at the end of the year.
Multiple Choice $3,955
Explanation Total assets = Total
liabilities + Total Stockholders' equity TB MC Qu. 1-61 (Static) The FASB's
conceptual framework's qualitative... The FASB's conceptual framework's
qualitative characteristics of accounting information include:
Multiple Choice Relevance. TB MC Qu. 1-101 (Static) The full
disclosure principle requires a... The full disclosure principle
requires a balance between:
Multiple Choice Relevance and cost-effectiveness. TB TF Qu. 1-19 (Static) The FASB's
conceptual framework lists... The FASB's conceptual framework
lists relevance and timeliness as the two fundamental qualitative
characteristics of decision, useful information. False TB MC Qu. 1-89 (Static) Which of the
following Statements of... Which of the following Statements of
Financial Accounting Concepts defines the 10 elements of financial
statements?
Multiple Choice SFAC 6 TB TF Qu. 1-20 (Static) The monetary
unit assumption requires that... The monetary unit assumption
requires that items in financial statements be measured in a particular
monetary unit. True TB MC Qu. 1-42 (Static) Which of the
following is... Which of the following is not
a provision of the Public Company Accounting Reform and Investor Protection
Act of 2002 (Sarbanes-Oxley)? The Act: Changed the entity responsible for
setting accounting standards. TB TF Qu. 1-26 (Static) In IFRS, the
conceptual framework indicates appropriate... In IFRS, the conceptual framework
indicates appropriate accounting when a more specific accounting standard
does not apply. True Brief Exercise 1-5 (Static) Basic
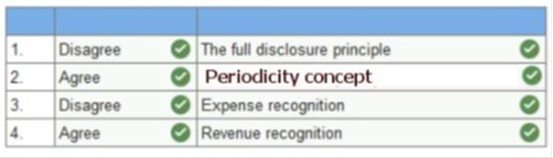
assumptions and principles [LO1-7, 1-8, 1-9] For each of the following
situations, (1) indicate whether you agree or
disagree with the financial reporting practice employed and (2) state the accounting concept
that is applied (if you agree), or violated (if you
disagree). 1.
Winderl Corporation did not disclose
that it was the defendant in a material lawsuit because the trial was still
in progress. 2.
Alliant Semiconductor Corporation
files quarterly and annual financial statements with the SEC. 3.
Reliant Pharmaceutical paid rent on
its office building for the next two years and charged the entire expenditure
to rent expense. 4.
Rockville Engineering records
revenue only after products have been shipped, even though customers pay
Rockville 50% of the sales price in advance.
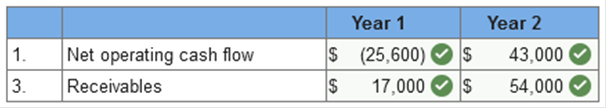
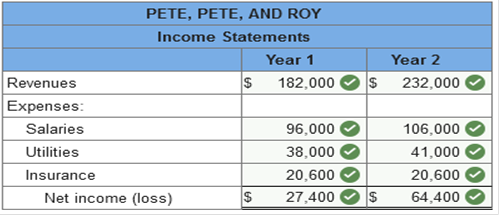
Exercise 1-1 (Algo) Accrual
accounting [LO1-2] Listed below are several
transactions that took place during the first two years of operations for the
law firm of Pete, Pete, and Roy.
no anticipated bad debts on receivables,
and that the insurance policy covers a three-year period. 1. & 3. Calculate the net operating cash flow for years 1 and 2 and
determine the amount of receivables from clients that the firm would show in its year 1 and
year 2 balance sheets prepared according to the accrual accounting model. Calculate the net operating cash
flow for years 1 and 2 and determine the amount of receivables
from clients that the firm would show in its year 1 and year 2 balance sheets
prepared according to the accrual accounting model. (Net cash outflows
should be indicated by a minus sign.)
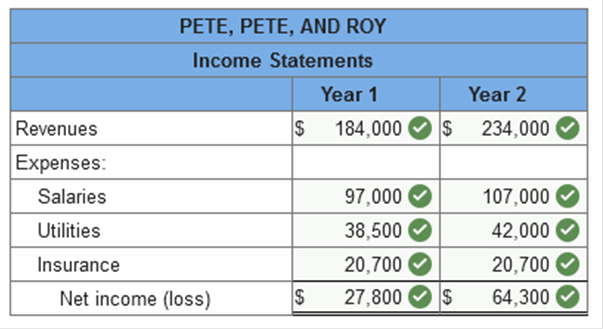
Prepare an income statement for each
year according to the accrual accounting model.
Explanation 1. & 3.
TB MC Qu. 1-124 (Algo) Tri Fecta, a partnership, had revenues of... Tri Fecta,
a partnership, had revenues of $375,000 in its first year of operations. The partnership has not collected on
$45,800 of its sales and still owes $38,000 on $150,000 of merchandise it
purchased. There was no inventory on hand at
the end of the year. The partnership paid $28,300 in salaries. The partners invested $47,000 in the
business and $24,000 was borrowed on a five-year note. The partnership paid $2,160 in
interest that was the amount owed for the year and paid $9,800 for a two-year
insurance policy on the first day of business.
$189,640
Explanation
TB MC Qu. 1-128 (Algo) The following
information ($ in millions) comes from a recent annual... The following information ($ in
millions) comes from a recent annual report of Amazon.com, Inc.:
Compute Amazon's cost of goods sold
for the year.
Multiple Choice $8,189
Explanation Gross profit = Net
sales − Cost of goods sold TB
MC Qu. 1-123 Alpaca
Corporation had revenues of $310,000 in its first year of operations. The
company has not collected on $20,100 of its sales and still owes $28,200 on
$97,000 of merchandise it purchased. The
company had no inventory on hand at the end of the year. The company paid
$13,900 in salaries. Owners
invested $20,000 in the business and $20,000 was borrowed on a five-year
note. The
company paid $4,800 in interest that was the amount owed for the year, and paid $8,800 for a two-year insurance policy on
the first day of business. Alpaca
has an effective income tax rate of 40%. (Assume taxes are paid in the
same year).
$157,640 Explanation
Cost of goods sold of $97,000 less $13,900 in salaries less $4,800 interest less $4,400 for insurance ($8,800/2) equals $189,900. Taxes at 40% are $75,960. TB MC Qu. 1-58 (Static) One of the
elements that many... One
of the elements that many believe distinguishes a profession from other occupations
is the acceptance of responsibility by
its members for the interests of those it serves, which is often articulated
in:
Its
code of ethics. TB TF Qu. 1-3 (Static) The FASB is
currently the public-sector organization... The FASB is currently the
public-sector organization responsible for setting accounting standards in
the United States. False TB MC Qu. 1-99 (Static) Disclosure
notes to a company's financial... Disclosure
notes to a company's financial statements:
Multiple
Choice Are
an integral part of a company's financial statements. TB MC Qu. 1-33 (Static) Which of the
following was the first... Which of the following was the first
private-sector entity that set accounting standards in the United States?
Multiple Choice Committee on Accounting Procedure. TB MC Qu. 1-85 (Static) According to
the conceptual framework, verif... According to the conceptual
framework, verifiability implies: Top of Form Multiple Choice Consensus.
Regarding convergence of accounting
standards, the FASB and IASB: Are not likely to achieve full
convergence of accounting standards in the near future. The asset/liability approach
emphasizes: Whether amounts on the balance sheet
meet the definitions of assets and liabilities. Brief Exercise 1-1 (Algo) Accrual
accounting [LO1-2] Cash flows during the first year of
operations for the Harman-Kardon Consulting Company were as follows: Cash collected from customers, $360,000; Cash paid for rent, $44,000; Cash paid to employees for services
rendered during the year, $124,000; Cash paid for utilities, $54,000. Also, the company owed the gas and
electric company $2,400 at year-end, and the rent payment was for a two-year
period.
Explanation
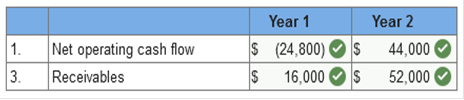
Exercise 1-1 (Algo) Accrual
accounting [LO1-2] Listed below are several
transactions that took place during the first two years of operations for the
law firm of Pete, Pete, and Roy.
no anticipated bad debts on
receivables, and that the insurance policy covers a three-year period. Calculate the net operating cash
flow for years 1 and 2 and determine the amount of receivables
from clients that the firm would
Prepare an income statement for each
year according to the accrual accounting model.
Explanation 1. & 3.
Intermediate Accounting Homework 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | Exams Chapters 1-3 4-7 8-9 10-11
| Final Exam
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Home |
Accounting & Finance | Business |
Computer Science | General Studies | Math | Sciences |
Civics Exam |
Everything
Else |
Help & Support |
Join/Cancel |
Contact Us |
Login / Log Out |